Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Question Paper 2024 PDF Download. HBSE Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Question Paper 2024. Haryana Board Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Exam 2024. HBSE Class 12th Physics Half Yearly Paper 2024 Answer. Haryana Board Class 12 Half Yearly Paper PDF Download. Haryana Board Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Paper 2024 Solution. हरियाणा बोर्ड कक्षा 12 भौतिक विज्ञान अर्धवार्षिक पेपर 2024.
HBSE Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
Instructions :
• All questions are compulsory.
• Questions (1-9) carry 1 mark each.
• Questions (10-12) carry 2 marks each.
• Questions (13-14) carry 3 marks each.
• Question (15) case study, carry 4 marks.
• Questions (16-17) carry 5 marks each.
1. With the increase of area of cross section of a conductor, its resistivity :
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) may increase or decrease
(d) does not change
Answer – (d) does not change
2. Magnetic susceptibility of diamagnetic substance is :
(a) small and negative
(b) small and positive
(c) large and positive
(d) none of these
Answer – (a) small and negative
3. What is the relative magnetic permeability of a substance whose magnetic susceptibility is –1 ?
(a) 1
(b) –1
(c) 0
(d) 2
Answer – (c) 0
4. Torque acting on a dipole in electric field is given by :
(a) pE
(b) pEsinθ
(c) pEcosθ
(d) 0
Answer – (b) pEsinθ
5. Kirchhoff’s second law, also known as Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL), is based on the law of conservation of …………..
Answer – energy
6. The SI unit of magnetic dipole moment of a bar magnet is …………..
Answer : Am2
7. Direction of induced e.m.f. is given by Lenz’s law. (True / False)
Answer – True
8. Are Kirchhoff’s rules applicable to both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) circuits?
Answer : Yes
9. Assertion (A) : Total flux through a closed surface is zero if net charge enclosed by the surface is zero.
Reason (R) : Gauss Law is true for any closed Surface, no matter what its shape or size.
Answer – Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true and reason (R) is the correct explanation of assertion (A).
10. What is the number of electrons in 1 µC?
Answer : Total charge = number of electrons × charge on one electron
Q = n × e
n = Q/e = 10–6/(1.6×10–19) = 6.25 × 1012 e–
Hence, number of electrons = 6.25 × 1012 e–
11. On which factors does the capacitance of a capacitor depend?
Answer – The capacitance of a capacitor depends on area of each plate, dielectric medium between the plates and distance between the plates.
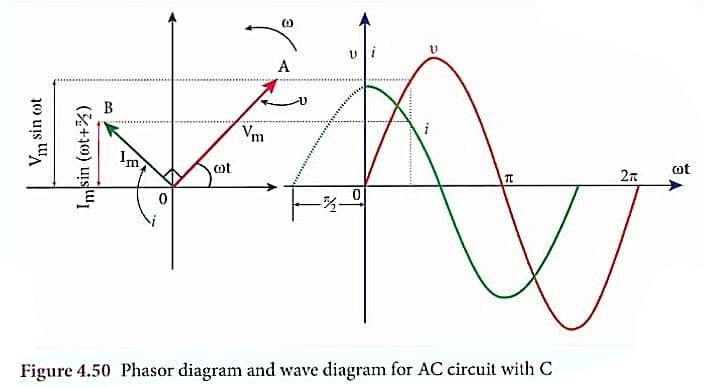
12. Draw the phasor diagram for a.c. circuit containing capacitor only.
Answer –
13. State ampere’s circuital law.
Answer – Ampere’s circuital law states that, the line integral of the magnetic field surrounding closed loop equals to the number of times the algebraic sum of currents passing through the loop.
14. When the distance between two charged particles is made half, the force between them becomes.
Answer – Initial Force (F) = kq1q2/r2
New force (F’) = kq1q2/(r/2)2 = 4 k(q1q2)/r2 = 4 F
F’ = 4 F
when the distance between the two charges is half, the force is increased 4 times.
15. CASE STUDY : According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the end of the conductors i.e. I ∝ V ⇒V/I = R, where R is resistance of the conductor.
Electrical resistance of a conductor is the obstruction posed by the conductors to the flow of electric current through it. It depends upon length, area of cross-section, nature of material and temperature of conductor. We can write, R ∝ L/A or R = ρ (L/A), where ρ is the electrical resistivity of material of the conductor.
Questions :
(i) Dimensions electric resistance is :
(a) [M L2 T–2 A–2]
(b) [M L2 T–3 A–2]
(c) [M–1 L–2 T–1 A]
(d) [M–1 L2 T2 A–1]
Answer – (b) [M L2 T–3 A–2]
(ii) If 1 µA current flows through a conductor when potential difference of 2 volt is applied across its ends, then the resistance of the conductors is :
(a) 2 × 106 Ω
(b) 3 × 105 Ω
(c) 1.5 × 105 Ω
(d) 5 × 107 Ω
Answer – (a) 2 × 106 Ω
R = V/I = 2/(1×10–6) = 2 × 106 Ω
(iii) Resistance of a wire depends upon :
(a) length
(b) cross-sectional area
(c) mass
(d) All of these
Answer – (d) All of these
(iv) The slope of graph between potential difference and current through a conductor is :
(a) a straight line
(b) curve
(c) first curve then straight line
(d) first straight line then curve
Answer – (a) a straight line
16. What do you mean by electromagnetic waves? Give two uses of gamma rays.
Answer – Electromagnetic waves are a form of energy that is propagated through space as a combination of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other and the direction of wave propagation. These waves travel at the speed of light (approximately 3,00,000 kilometres per second in a vacuum) and do not require a medium to propagate, meaning they can travel through the vacuum of space.
Two uses of gamma (γ) rays :
(i) γ-rays are used in the treatment of cancer and tumours.
(ii) γ-rays are used to produce nuclear reactions.
17. Write the characteristics of electric field lines.
Answer – Characteristics of electric field lines are following :
(i) Electric field lines always start from a positive charge and end at a negative charge.
(ii) Electric field lines never cross each other.
(iii) Electric field lines are always perpendicular to the surface of a conductor.
(iv) Electric field lines can be curved or straight, depending on the configuration of the charges producing the field.
(v) The closer the electric field lines are to each other, the stronger the electric field at that point.
