Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 12 Chemistry Pre Board Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. Haryana Board Class 12th Pre Board Question Paper PDF Download 2024. Haryana Board Class 12th Pre Board Question Paper Chemistry 2024. HBSE Class 12th Chemistry Pre Board Question Paper Solution 2024. HBSE Chemistry Pre Board Question Paper 2024 Class 12.
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Pre-Board Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (1 Mark)
1. The values of van’t hoff factor for KCI, NaCl and K2SO4 respectively are :
(a) 2, 2, 2
(b) 2, 2, 3
(c) 1, 1, 1
(d) 1, 1, 2
Answer – (b) 2, 2, 3
2. Standard Electrode Potential for Standard Hydrogen Electrode is?
(a) –0.5 V
(b) +2.0 V
(c) +1.0 V
(d) 0.0 V
Answer – (d) 0.0 V
3. The role of catalyst is to change :
(a) Enthalpy of reaction
(b) Activation energy of reaction
(c) Gibbs free energy of reaction
(d) All the of above
Answer – (b) Activation energy of reaction
4. The stability of ferric ion is due to :
(a) Half-filled d-orbitals
(b) completely filled f-orbitals
(c) Half-filled f-orbitals
(d) completely filled d-orbitals
Answer – (a) Half-filled d-orbitals
5. Dehydration of secondary alcohol with copper at 573K gives :
(a) alkenes
(b) ketone
(c) phenol
(d) ether
Answer – (b) ketone
6. Molecules whose mirror is non-superimposable over them are known as chiral. Which of the following mirror images is chiral?
(a) 2-bromobutane
(b) 2-bromopropane
(c) 1-bromobutane
(d) 2-bromopropan-2-ol
Answer – (a) 2-bromobutane
7. Glycogen is an example of :
(a) monosaccharide’s
(b) Disaccharide’s
(c) polysaccharide’s
(d) vitamins
Answer – (c) polysaccharide’s
8. When attraction between A-B is less than that of AA and BB, the solution will show which type of deviation from Raoult’s law :
(a) negative
(b) positive
(c) both
(d) no deviation
Answer – (b) positive
9. Aldehyde and ketone can be distinguished by :
(a) NaHSO3
(b) Fehling solution
(c) Silver nitrate
(d) concentrated sulphuric acid
Answer – (b) Fehling solution
10. The SI unit of molar conductivity is :
(a) S m2 mol–1
(b) S m2 mol–1
(c) S Cm2 mol–1
(d) S m3 mol–1
Answer – (a) S m2 mol–1 (Siemen metre square mol inverse)
11. The IUPAC name of (CH3)2–C=CH–COCH3 is :
(a) 2-Methylpent-3-ene-4-one
(b) 4-Methylpent-3-ene-2-one
(c) 1,1-Dimethyl-2-ene-1-one
(d) 2,4-Dimethyl-2-ene-4-one
Answer – (b) 4-Methylpent-3-ene-2-one
12. The value of Henry’s constant is :
(a) increases with increase in temperature
(b) decreases with increase in temperature
(c) remains constant
(d) first increases then decreases
Answer – (a) increases with increase in temperature
13. The atomic number of cerium is 58. The correct electronic configuration of Ce3+ is :
(a) [Xe]4f1
(b) [Kr]4f1
(c) [Xe]4f13
(d) [Kr]4d1
Answer – (a) [Xe]4f1
14. Identify the order of reaction when units of rate constant is mol L–1 Sec–1 ?
(a) Second
(b) Zero
(c) Third
(d) First
Answer – (b) Zero
15. Assertion (A) : Molality of the solution does not change with change in temperature.
Reason (R) : The molarity is expressed as number of moles per 1000 g of the solvent.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Ascertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer – (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
16. Assertion (A) : Oxidation state of Ni in [Ni(CN)4]2– is +2.
Reason (R) : The charge on cyanide ion is –1 and the total charge on the complex anion is –2.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Ascertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer – (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
17. Assertion (A) : All aldehydes do not take part in aldol condensation.
Reason (R) : Carbanion is generated by the removal of alpha hydrogen by the base in the Aldol condensation.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Ascertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer – (b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
18. Assertion (A) : All amino acids exist as Zwitter ion.
Reason (R) : Alpha – amino acids have both –NH2 and –COOH group.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Ascertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Both assertion and reason are false.
Answer – (a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
SECTION – B (2 Marks)
19 Define Kohlrausch law.
Answer – The law states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
20. Give two differences between DNA and RNA?
Answer –
| DNA | RNA |
| 1. DNA Stands for Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid. | 1. RNA stands for Ribo Nucleic Acid. |
| 2. It is double stranded nucleic acid. | 2. It is single stranded nucleic acid. |
| 3. It contains deoxyribose sugar. | 3. It contains ribose sugar. |
21. Time required to decompose thionyl chloride to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Answer – Here, Time (t½) = 60 min
t½ = 0.693/k
k = 0.693/t½ = 0.693/60 = 1.155 × 10–2 m–1 or 1.925 × 10–4 s–1
22. Write equation for the preparation of 1-bromobutane from the following :
(a) Butan-1-ol
Answer : CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–OH + HBr → CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–Br + H2O
(b) 1-chlorobutane
Answer : CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–Cl + NaBr → CH3–CH2–CH2–CH2–Br + NaCl
23. (a) What is the name of the linkage joining two amino acids?
Answer – Peptide bond
(b) Arrange the following in increasing order of acidic strength and Give reason.
p-nitrophanol, phenol, p-methyl phenol
Answer : phenol < p-nitrophanol < p-methyl phenol
24. Write a note on Wurtz reaction.
Answer – Alkyl halides react with sodium in dry ether to give hydrocarbons containing double the number of carbon atoms present in the halide. This reaction is known as Wurtz reaction.
2CH3Br + 2Na + dry ether → CH3CH3 + 2NaBr
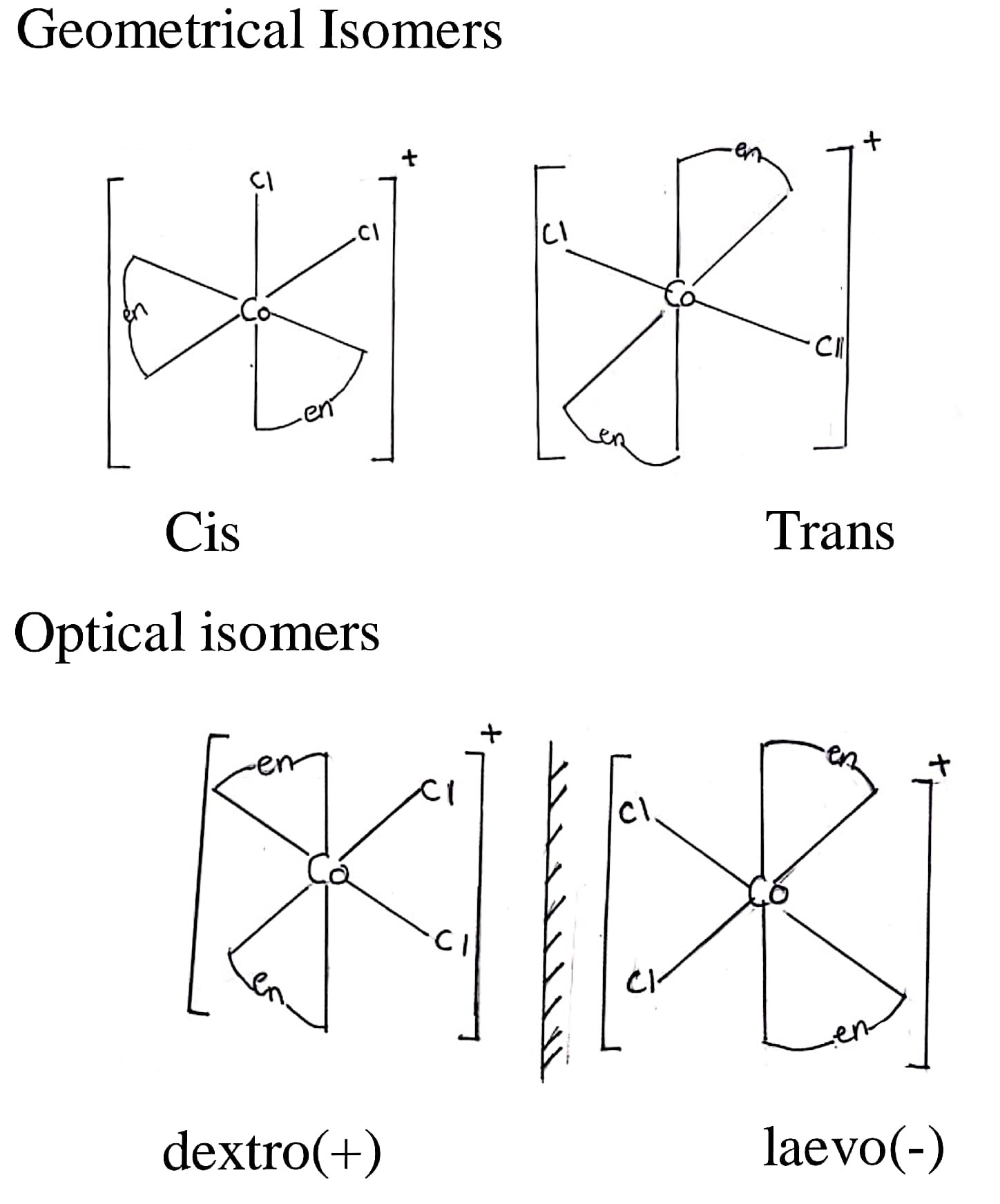
25. Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [COCl2(en)2]+.
Answer –
SECTION – C (3 Marks)
26. Define isotonic solution. A 4% solution of sucrose C12H22O11 is isotonic with 3% solution of an unknown organic compound. Calculate molecular mass of the unknown compound?
Answer – Two solutions having the same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions. When such solutions are seprated by a semipermeable membrane, sovlent flow between one to the other on either direction is same, the net solvent flow between two isotonic solutions is zero.
As the solutions are isotonic, the molarities of the two solutions are equal.
Msucrose = Munknown
4/342 × 1000/100 = 3/x × 1000/100
x = 256.5 g mol–1
Molecular mass of the unknown compound is 256.5 g mol–1.
27. Explain [Co(NH3)6]3+ is an inner orbital complex, whereas [Ni(NH3)6]2+ is an outer orbital complex?
Answer – In [Co(NH3)6]3+, Co is in +3 state and has configuration 3d⁶. In the presence of NH3, 3d electrons pair up leaving two d-orbitals empty. Hence, the hybridization is d²sp³ forming and inner orbital complex. In [Ni(NH3)6]2+, Ni is in +2 state and has configuration 3d⁸. In presence of NH3, the 3d electrons do not pair up. The hybridization is sp³d² forming an outer orbital complex.
28. Explain the following reactions :
(a) Stephen Reduction
Answer – An alkyl or aryl cyanide dissolved in ether is reduced with stannous chloride and HCl to give aliphatic or aromatic aldehydes. The reaction proceeds by the formation of aldimine hydrochloride (present as stannichloride), which are not stable and hydrolyse to give aldehydes.
(b) Kolbe’s reaction
Answer – When phenol is treated with sodium hydroxide, sodium phenoxide is produced. This sodium phenoxide when treated with carbon dioxide, followed by acidification, undergoes electrophilic substitution to give ortho-hydroxybenzoic acid as the main product. This reaction is known as Kolbe’s reaction.
(c) Reimer Tiemann reaction
Answer – On treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide, a –CHO group is introduced at ortho position of benzene ring. The intermediate substituted benzal chloride is hydrolysed in the presence of alkali to produce salicylaldehyde.
29. Account for the following :
(a) pKb of aniline is more than methylamine.
Answer – In aniline, the electron pair on nitrogen atom is involved in conjugation with ring and is less available for protonation than in methyl amine. Therefore, pKb value of aniline is more than that of methylamine and aniline is less basic, (As higher the pKb value, less is the basicity).
(b) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not.
Answer – Ethylamine is soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding. In aniline due to bulky hydrocarbon part, the extent of hydrogen bonding is less and it is not soluble in water.
(c) Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis is preferred for synthesizing primary amines.
Answer – Gabriel phthalimide synthesis produces primary amines only without the traces of secondary or tertiary amines. So, this method is preferred for the synthesis of primary amines.
30. How are vitamins classified. Name the vitamin responsible for coagulation of blood?
Answer – On the basis of their solubility in water or fat, vitamins are classified into two groups :
(i) Fat-soluble vitamins – Vitamins that are soluble in fat and oils, but not in water, belong to this group. Eg. Vitamins A, D, E, and K.
(ii) Water-soluble vitamins – Vitamins that are soluble in water belong to this group. Eg. vitamin B groups (B1, B2, B6, B12, etc.) and vitamin C.
However, vitamin H (biotin) is neither soluble in water nor in fat.
Vitamin K is responsible for the coagulation of blood.
SECTION – D (4 Marks)
31. CASE STUDY : Transition elements have partly filled d-orbitals in their normal oxidation states or in their commion oxidation states. There are four series in transition elements and these are 3d-series (first transition series), 4d-series (second transition series), 5d-series (third transition series) and 6d-series (fourth transition series). Each series contains ten elements. Elements of group 12 are not considered as transition elements as these have fully-filled d-subshells. Transition elements show all the characteristics of metals. These elements show variable oxidation states, form coloured ions, form complexes from alloys and interstitial compounds. They show high enthalpies of atomisation, show catalytic properties and magnetic moment.
Questions :
(a) Why Zn, Cd and Hg are not considered as transition elements?
Answer – Transition metals are defined as the elements having incompletely filled d-orbitals. Since Zn, Cd and Hg have completely filled d-orbital, they are not regarded as transition elements.
(b) Which element of d-block shows maximum oxidation state?
Answer – Manganese
(c) Why transition elements show variable oxidation states?
Answer – Transition elements show variable state oxidation in their compounds because there is a very small energy difference in between (n–1)d and ns orbitals. As a result, electrons of (n–1)d orbitals as well as ns-orbitals take part in bond formation. Thus, transition elements have variable oxidation states.
(d) Calculate the magnetic moment of a divalent ion in its aqueous solution if its atomic number is 25.
Answer : Magnetic moment (µ) = √n(n+2) = √5(5+2) = √35 = 5.92 BM
32. CASE STUDY : In case of optically active alkyl halides, product formed as a result of SN2 mechanism has the inverted configuration as compared to the reactant. This is because the nucleophile attaches itself on the side opposite to the one where halogen atom is present thus, SN2 reactions of optically active halides are accompanied by inversion of configuration. In case of optically active alkyl halides SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization. Actually the carbocation formed in the slow step being sp2 hybridized is achiral. The attack of nucleophile is accomplished from either side resulting in mixture of products having same configuration.
Questions :
(a) Define racemization.
Answer – When equal amounts of dextrorotatory and laevorotatory isomers are mixed then the resulting mixture becomes optically inactive because optical activities of each isomer cancel each other. Such a mixture is called a racemic mixture and this phenomenon is called racemization.
(b) Write two differences between SN1 and SN2 reactions.
Answer – (i) SN1 is a unimolecular reaction while SN2 is a bimolecular reaction.
(ii) SN1 involves two steps while SN2 involves one step.
(c) Which alkyl halide from the following pair would react more rapidly by SN2 mechanism, explain :
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3
Answer : CH3CH2CH2CH2Br is a 1° alkyl halide while CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 is 2° alkyl halide. There will be more steric hindrance in 2° alkyl halides than in 1° alkyl halides.
Therefore, CH3CH2CH2CH2Br will react faster than CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 in SN2 reaction.
(d) Which alkyl halide from the following pair would react more rapidly by SN1 mechanism, explain :
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br or CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3
Answer : CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 will react faster than CH3CH2CH2CH2Br in SN1 reaction.
SECTION – E (5 Marks)
33. (a) The rate constants of reaction at 500K and 700K are 0.02 s–1 and 0.07 s–1 respectively.
Calculate the value of Ea.
Answer – Here, k1 = 0.02 s–1, T1 = 500K
k2 = 0.07 s–1, T2 = 700K
log[k2/k1] = Ea/2.303R [T2–T1/T1T2]
log[0.07/0.02] = Ea/2.303×8.314 [700–500/700×500]
Ea = 18230.8 J mol–1 = 18.2 kJ mol–1
(b) What are the factors affecting rate of reaction.
Answer – Concentration of reactants & pressure in case of gases, temperature, and catalyst.
OR
(a) Define pseudo first order reaction with example?
Answer – The reaction which is not of first order but behaves like first order is called pseudo first order reaction. Eg. acid hydrolysis of ethyl acetate or inversion of cane sugar.
(b) Define energy of activation. The rate of a particular reaction doubles when temperature changes from 27°C to 37°C . Calculate the energy of activation?
Answer – Here, k1 = k, T1 = 27°C = 27 + 273 = 300K
k2 = 2k, T2 = 37°C = 37 + 273 = 310K
log[k2/k1] = Ea/2.303R [T2–T1/T1T2]
log[2k/k] = Ea/2.303×8.314 [310–300/310×300]
Ea = 53598.6 J mol–1 = 53.6 kJ mol–1
34. (a) Explain Sandmeyer reaction.
Answer – The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction which is used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts. This reaction is a method for substitution of an aromatic amino group by preparing diazonium salt, that is followed by its displacement and copper salts often catalyze it.
(b) Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes why?
Answer – In haloarenes there is double bond character between carbon and halogen due to resonance effect which makes him less reactive. In benzene carbon being sp² hybridised which is smaller in size than sp³ present in haloalkanes. So, C–Cl bond in aryl halides is shorter and stronger.
(c) Write one use of DDT?
Answer – DDT is used as an insecticide. It can also be used as a mosquito repellent.
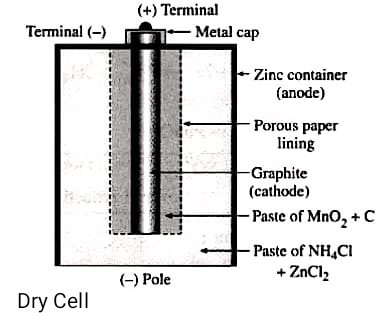
35. (a) Draw diagram of dry cell.
Answer – The dry cells convert the stored chemical energy into electrical energy. They undergo reduction-oxidation (Redox) reactions at the cathode and anode. Some dry cells can be recharged while others can be used only once.
(b) Represent the cell in which the following reaction takes place
Mg(s) + 2Ag+ (0.0001M) → Mg2+ (0.130M) + 2Ag(s)
Calculate its Ecell if E°cell = 3.17 V.
Answer : Ecell = E°cell – 0.0591/n log[Mg2+/(Ag+)2]
Ecell = 3.17 – 0.0591/2 log[0.130/(0.0001)2]
Ecell = 3.17 – 0.21 = 2.96 V
