Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 12 Chemistry Important Question Answer 2025. HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions 2025. BSEH Class 12 Chemistry vv important Questions 2025. Class 12 Chemistry Most important questions for Board Exam 2025. हरियाण बोर्ड कक्षा 12 रसायन विज्ञान के अति महत्वपूर्ण प्रश्न 2025.
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Question Answer 2025
Objective Questions
1. Which of the following is involved in blood clotting?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin C
(c) Vitamin E
(d) Vitamin K
Answer – (d) Vitamin K
2. Which of the following is not affected by catalyst?
(a) Enthalpy
(b) Gibbs energy
(c) Speed of reaction
(d) None of the above
Answer – (b) Gibbs energy
3. Which of the following is an example of solid solution?
(a) Copper dissolved in Gold
(b) Glucose in water
(c) Camphor in nitrogen gas
(d) None of these
Answer – (a) Copper dissolved in Gold
4. Value of KH for a gas is :
(a) Constant at all temperatures
(b) Increases with increase in temperature
(c) Decreases with increase in temperature
(d) Increases with decrease in temperature
Answer – (b) Increases with increase in temperature
5. What is SI unit of conductivity?
(a) S cm
(b) S cm-¹
(c) S m
(d) S m-¹
Answer – (d) S m-¹ (siemens per metre)
6. Which of the following is an example of corrosion?
(a) Tarnishing of silver
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Green coating on copper
(d) All of these
Answer – (d) All of these
7. Which of the following cannot be molecularity of a chemical reaction?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer – (a) 0
8. What is represented by A in Arrhenius equation?
(a) Temperature
(b) Frequency factor
(c) Activation energy
(d) Collision frequency
Answer – (b) Frequency factor
9. Which of the following does not exhibit variable oxidation state?
(a) Sc
(b) Cu
(c) Ti
(d) Fe
Answer – (a) Sc (scandium, Z=21)
10. Which of the following is a coordination compound of cobalt?
(a) Vitamin B12
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Haemoglobin
(d) All of the above
Answer – (a) Vitamin B12
11. Which reagent is used in Finkelstein reaction?
(a) NaCl
(b) NaBr
(c) NaI
(d) All of the above
Answer – (c) NaI (sodium iodide)
12. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point?
(a) Pentan-1-ol
(b) n-Butane
(c) Pentanal
(d) Ethoxyethane
Answer – (b) n-Butane
13. What is IUPAC name of cinnamaldehyde?
(a) 2-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
(b) 3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-al
(c) 3-Hydroxybenzaldehyde
(d) 3-Phenylbut-2-en-1-al
Answer – (b) 3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-al
14. What is the type of isomerism between Propan-1-amine and Propan-2-amine?
(a) Chain isomerism
(b) Functional group isomerism
(c) Position isomerism
(d) Optical isomerism
Answer – (c) Position isomerism
15. Which of the following is not a disaccharide?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Ribose
(c) Maltose
(d) Lactose
Answer – (b) Ribose
16. Which of the following is often used to express the concentration of pollutants in water or air?
(a) mg/mL
(b) ppb
(c) μg/mL
(d) mol L-¹
Answer – (c) μg/mL (microgram per milliliter)
17. The osmotic pressure of fluid inside human blood cell is equivalent to that of :
(a) 9.0% (mass/volume) NaCl
(b) 0.9% (mass/volume) NaCl
(c) 1.9% (mass/volume) NaCl
(d) None of these
Answer – (b) 0.9% (mass/volume) NaCl
18. In a Galvanic cell, the half-cell in which oxidation takes place is called :
(a) Cathode
(b) Anode
(c) Electrolyte
(d) Salt bridge
Answer – (b) Anode
19. Which of the following is a unit of rate of reaction?
(a) mol L-¹
(b) mol L s-¹
(c) mol L-¹ s-¹
(d) s-¹
Answer – (c) mol L-¹ s-¹
20. Which of the following is not a transition element?
(a) Au
(b) Ag
(c) Zn
(d) Cu
Answer – (c) Zn (zinc)
21. What is obtained from pyrolusite ore?
(a) KMnO4
(b) K2Cr2O7
(c) KNO3
(d) Na2Cr2O7
Answer – (a) KMnO4
22. What is secondary valency of CoCl3.4NH3 if its one mole reacts with excess AgNO3 to give one mole of AgCl?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer – (d) 6
23. Which of the following is effective in inhibiting growth of tumours?
(a) Dimethylglyoxime
(b) cis-platin
(c) α-nitroso-β-naphthol
(d) cupron
Answer – (b) cis-platin
24. Which of the following is allylic halide?
(a) Bromomethane
(b) Bromoethene
(c) 3-Chloropropene
(d) None of the above
Answer – (c) 3-Chloropropene
25. What is carbolic acid?
(a) Acetic acid
(b) Acetone
(c) Phenol
(d) Acetaldehyde
Answer – (c) Phenol
26. Which of the following is major product for nitration anisole?
(a) 2-Nitroanisole
(b) 3-Nitroanisole
(c) 4-Nitroanisole
(d) None of the above
Answer – (c) 4-Nitroanisole
27. What is the monomer of cellulose?
(a) α-D-Glucose
(b) β-D-Glucose
(c) α-D-Fructose
(d) β-D-Fructose
Answer – (b) β-D-Glucose
28. How many amino acids are present in insulin?
(a) 51
(b) 52
(c) 53
(d) 54
Answer – (a) 51
29. Which of the following is not fat soluble?
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin C
(c) Vitamin E
(d) Vitamin K
Answer – (b) Vitamin C
30. What is unit of cryoscopic constant?
(a) kg K-¹ mol-¹
(b) K kg mol-¹
(c) K kg-¹ mol-¹
(d) K kg mol
Answer – (b) K kg mol-¹
31. What happens to conductivity upon dilution of solution of a strong electrolyte?
(a) decreases
(b) increases
(c) remains same
(d) may increase or decrease
Answer – (b) increases
32. Which of the following is a secondary cell?
(a) Leclanche cell
(b) Mercury cell
(c) Fuel cell
(d) Nickel-Cadmium cell
Answer – (d) Nickel-Cadmium cell
33. Which of the following is not a lanthanoid?
(a) Thorium
(b) Lutetium
(c) Terbium
(d) Europium
Answer – (a) Thorium
34. How many nitrogen atoms can make a coordination bond in EDTA ion?
(a) 0
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer – (b) 2
35. Which of the following is dihydroxy derivative of benzene?
(a) Catechol
(b) Resorcinol
(c) Quinol
(d) All of the above
Answer – (d) All of the above
36. What is the name of the reaction in which toluene is treated with chromyl chloride to produce benzaldehyde?
(a) Etard reaction
(b) Stephen reaction
(c) Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Gatterman reaction
Answer – (a) Etard reaction
37. What is Fehling solution B?
(a) Ammonical silver nitrate
(b) Alkaline sodium potassium tartarate
(c) Aqueous copper sulphate
(d) Acidified potassium permanganate
Answer – (b) Alkaline sodium potassium tartarate
38. Which of the following is most soluble in water?
(a) Dimethylamine
(b) Trimethylamine
(c) Methylamine
(d) Aniline
Answer – (c) Methylamine
39. What is Hinsberg’s reagent?
(a) C6H5SO2Cl
(b) CH3SO2Cl
(c) C6H5CH2SO2Cl
(d) None of the above
Answer – (a) C6H5SO2Cl
40. Which of the following is an essential amino acid?
(a) Glycine
(b) Lysine
(c) Alanine
(d) Proline
Answer – (b) Lysine
41. Deficiency of which vitamin causes cheilosis?
(a) Vitamin B1
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin B6
(d) Vitamin B12
Answer – (b) Vitamin B2
42. Thyroxine is an iodinated derivative of which amino acid?
(a) Tryptophan
(b) Tyrosine
(c) Histidine
(d) Lysine
Answer – (b) Tyrosine
43. Double strand helix structure of DNA is its ……………. structure.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) Quaternary
Answer – (b) Secondary
44. Which of the following is an example of ideal solution?
(a) Bromobenzene and Bromoethane
(b) Chloroethane and Chlorobenzene
(c) Benzene and Ethanol
(d) Benzene and Toluene
Answer – (d) Benzene and Toluene
45. What is order of thermal decomposition of HI on gold surface?
(a) 1
(b) 1.5
(c) 0
(d) 0.5
Answer – (c) 0
46. Which of the following ion has highest oxidation state of Mn.
(a) Mn²+
(b) MnO4²-
(c) MnO4–
(d) All of the above
Answer – (c) MnO4– (oxidation number is +7)
47. Which of the following has the highest magnetic moment?
(a) V²+
(b) Ti²+
(c) Cr²+
(d) Co²+
Answer – (c) Cr²+
48. What is oxidation number of Ni in [Ni(CO)4]?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer – (a) 0
49. Which of the following has the highest boiling point?
(a) Bromomethane
(b) Bromoform
(c) Chloromethane
(d) Dibromomethane
Answer – (b) Bromoform
50. Which of the following is fastest to react by SN1 mechanism?
(a) tert-Butyl bromide
(b) sec-Butyl bromide
(c) Isobutyl bromide
(d) n-Butyl bromide
Answer – (a) tert-Butyl bromide
51. Which of the following is obtained from isopropyl benzene?
(a) Phenol
(b) Acetone
(c) Both of the above
(d) None of the above
Answer – (c) Both of the above
52. Which reagent is used to yield picric acid from phenol?
(a) Conc. H3PO4
(b) Conc. HNO3
(c) Dilute H2SO4
(d) Dilute HNO3
Answer – (b) Conc. HNO3
53. Which of the following does not give iodoform test?
(a) Ethanal
(b) Acetone
(c) Benzaldehyde
(d) Acetophenone
Answer – (c) Benzaldehyde
54. What is the major product formed by Friedel-Crafts methylation of benzoic acid?
(a) o-methylbenzoic acid
(b) m-methylbenzoic acid
(c) p-methylbenzoic acid
(d) None of the above
Answer – (d) None of the above
55. Which of the following regulate glucose level in blood?
(a) Insulin and Thyroxine
(b) Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
(c) Insulin and Glucagon
(d) Glucagon and Estradiol
Answer – (c) Insulin and Glucagon
56. How many hydrogen bonds are formed between adenine and guanine in a DNA?
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer – (a) 0
57. The deficiency of which of the following Vitamins causes pernicious anemia.
(a) Vitamin B1
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin B6
(d) Vitamin B12
Answer – (d) Vitamin B12
58. In comparison to 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in freezing point of 0.01 M MgCl2 solution is :
(a) the same
(b) about twice
(c) about three times
(d) about six times
Answer – (c) about three times
59. Electrode potential for Cu electrode varies according to the equation is :
ECu²+/Cu = E°Cu²+/Cu – 0.0591/2 log1/[Cu²+]
The graph of ECu²+/Cu vs log [Cu²+] is
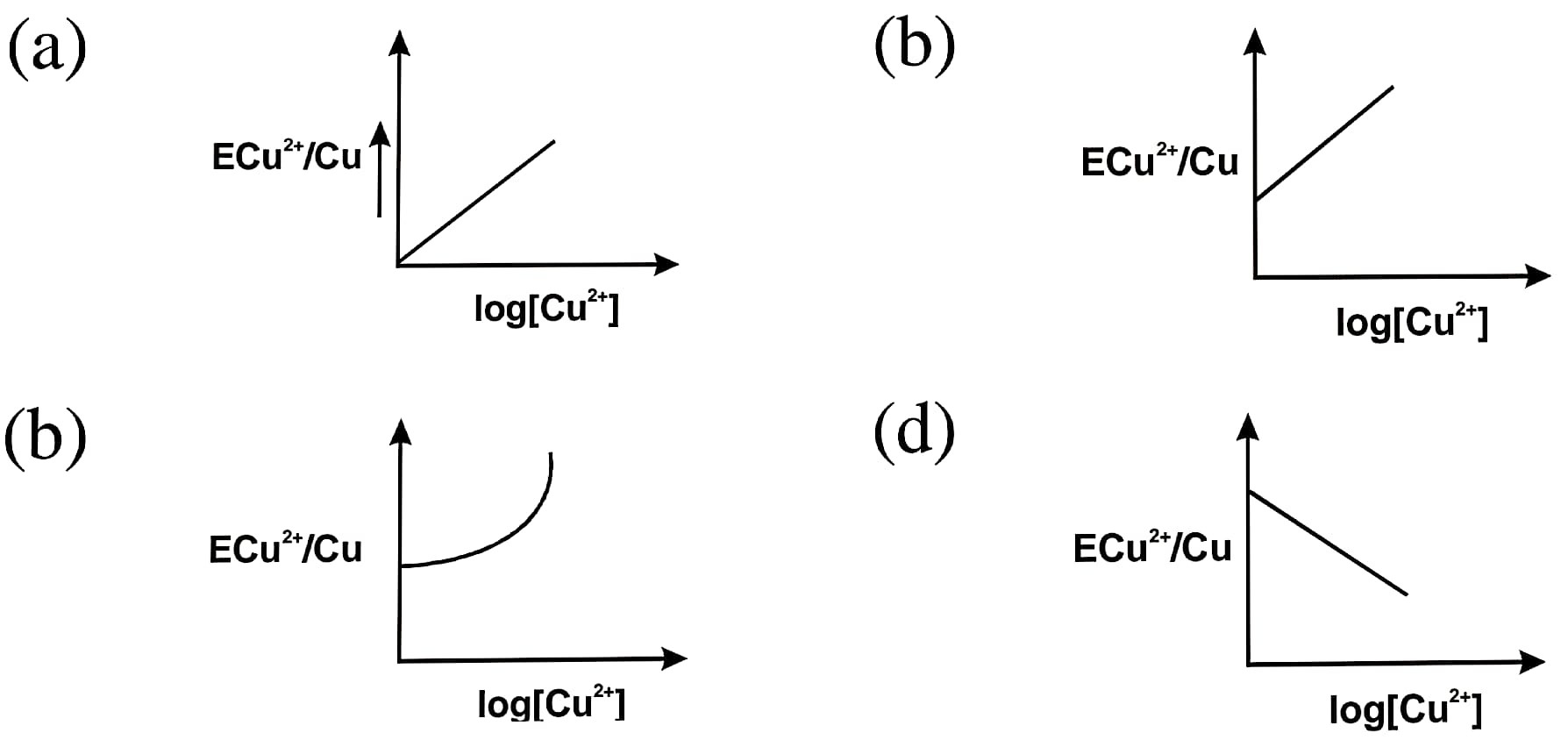
Answer – Option (b)
60. For a first order reaction, the time taken to reduce the initial concentration by a factor of 1/4th is 20 minutes. The time required to reduce initial concentration by a factor of 1/16th is
(a) 20 min
(b) 10 min
(c) 80 min
(d) 40 min
Answer – (d) 40 min
The time required to reduce the initial concentration to a factor 1/4th is 20 min.
So, half life of the reaction is (t½) = 10 min.
The time required to reduce the initial concentration to a factor 1/16th i.e. 4 half lives is (10 × 4) min = 40 min
61. Glucose on treatment with sodium amalgam gives :
(a) n-heptanoic acid
(b) Sorbitol
(c) Gluconic acid
(d) Glucaric acid
Answer – (b) Sorbitol
62. The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic KOH and p-toluidine forms.

Answer – Option (a)
63. When 1 mol CrCl3.6H2O is treated with excess of AgNO3, 3 mol of AgCl are obtained. The Formula of Complex is
(a) [CrCl3(H2O)3].3H2O
(b) [CrCl3(H2O)4]Cl.2H2O
(c) [CrCl(H2O)5]Cl2.H2O
(d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
Answer – (d) [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
64. Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH yield.
(a) o-cresol
(b) m-cresol
(c) 2,4-dihydroxy toluene
(d) Benzyl alcohol
Answer – (d) Benzyl alcohol
65. At pH = 11, Cr2O7²- ion changes to :
(a) CrO3
(b) CrO4²-
(c) Cr³+
(d) CrO2²+
Answer – (b) CrO4²-
66. Ethanol on warming with conc. H2SO4 at 413 K gives :
(a) Ethene
(b) Diethyl ether
(c) Dimethyl ether
(d) Ethyl hydrogen sulphate
Answer – (b) Diethyl ether
67. Which of the following compound will dissolve in an alkali solution after it undergoes reaction with Hinsberg’s reagent.
(a) CH3NH2
(b) (CH3)2NH
(c) C6H5NHC6H5
(d) (CH3)3N
Answer – (a) CH3NH2
68. The end product (D) in the following sequence is
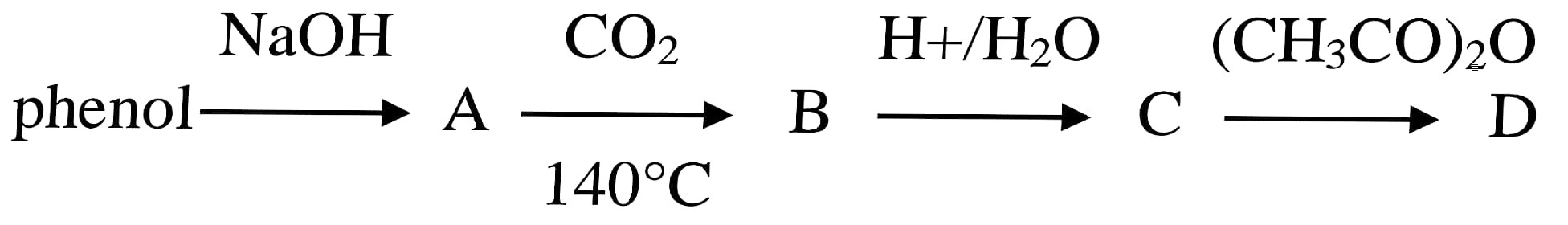
(a) Salicylic Acid
(b) Salicylaldehyde
(c) Phenyl acetate
(d) Aspirin
Answer – (d) Aspirin
69. Aniline on oxidation with Na2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 gives :
(a) Benzoic acid
(b) m-amino benzoic acid
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) p-Benzoquinone
Answer – (d) p-Benzoquinone
70. We are having three aqueous solutions of K2SO4 labelled as ‘X’, ‘Y’ and ‘Z’ with the concentration of 0.001 M, 0.01 M, 0.1 M respectively. The value of Van’t Hoff factor for these solutions will be in the order
(a) ix < iy < iz
(b) ix > iy > iz
(c) ix = iy = iz
(d) ix < iy > iz
Answer – (c) ix = iy = iz
Assertion-Reason Based Questions
The questions below consists of two statements : Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer the question by selecting the appropriate option given below.
1. Assertion (A) : Study of actinoids is difficult than the study of lanthanoids.
Reason (R) : Actinoids are radioactive elements.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
2. Assertion (A) : Thiocyanate ligand can cause linkage isomerism.
Reason (R) : Ambidentate ligands results in linkage isomerism in coordination compounds.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
3. Assertion (A) : Alcohols are readily soluble in water.
Reason (R) : Alcohols form hydrogen bonding with water.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
4. Assertion (A) : When nucleotide is linked to phosphoric acid, we get a nucleoside.
Reason (R) : Nucleotides are joined together by phosphodiester linkage.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
5. Assertion (A) : Mercury cell is a primary cell.
Reason (R) : In primary battery reaction occurs only once and cannot be reused again.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
6. Assertion (A) : Half-life of a first order reaction is variable.
Reason (R) : For first order reaction, half-life is independent of initial concentration of reactant.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
7. Assertion (A) : Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic addition reactions.
Reason (R) : Aldehydes give positive Tollen’s test.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
8. Assertion (A) : Carbylamine reaction is shown by secondary amines.
Reason (R) : Carbylamines are foul smelling substances.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
9. Assertion (A) : Testosterone is the major sex hormone produced in males.
Reason (R) : Testosterone participates in the control of menstrual cycle.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (c) A is true but R is false.
10. Assertion (A) : Reaction of propene with HCl yields Chloropropane as major product.
Reason (R) : Addition of HCl to propene follows Markonikov’s rule.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
11. Assertion (A) : Unit of rate constant for a radioactive decay is time-¹.
Reason (R) : Radioactive decay is a pseudo first order reaction.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (c) A is true but R is false.
12. Assertion (A) : Air is an ideal solution.
Reason (R) : The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
13. Assertion (A) : Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Reason (R) : Aniline being basic forms salt with aluminium chloride.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
14. Assertion (A) : o-Nitrophenol is more acidic than m-Nitrophenol.
Reason (R) : Nitro group is an electron releasing group.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (c) A is true but R is false.
15. Assertion (A) : Tetrahedral complexes show Geometric isomerism.
Reason (R) : Geometric isomerism arises due to different possible geometric arrangements of the ligands.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
16. Assertion (A) : The conductance of electricity by ions present in the solutions is called ionic conductance.
Reason (R) : Ionic conductance decreases with increase in temperature.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (c) A is true but R is false.
17. Assertion (A) : For CH3COOH the Molar conductance of 0.1 M CH3COOH and equivalent conductance of 0.1 N CH3COOH is same.
Reason (R) : These do not depend upon concentration.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (c) A is true but R is false.
18. Assertion (A) : For an exothermic reaction, activation energy for the backward reaction is more than the activation energy of the forward reaction.
Reason (R) : If the activation energy is high, the reaction is slow.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
19. Assertion (A) : Lanthanoids show a limited number of oxidation states where as Actinoids show a large number of oxidation states.
Reason (R) : Energy gap between 4f, 5d and 6s subshell is small where as that between 5f, 6d and 7s subshell in large.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer –(c) A is true but R is false.
20. Assertion (A) : Aniline is more basic than ethylamine.
Reason (R) : The lone pair on N atom is present in Conjugation with benzene ring and becomes less available for protonation because of resonance.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer – (d) A is false but R is true.
Subjective Questions
1. What are isotonic solutions?
Answer – Two solutions having the same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
2. Write full form of DNA.
Answer – Deoxyribo Nucleic acid
3. What is the name of the linkage joining two amino acids?
Answer – Peptide bond
4. What are polypeptides?
Answer – If more than ten α-amino acids are joined together by peptide bond the structure thus formed is called Polypeptides.
5. Give an example of non-essential amino acid.
Answer – Glycine / Proline
6. Write a note on Wurtz reaction.
Answer – Alkyl halides react with sodium in dry ether to give hydrocarbons containing double the number of carbon atoms present in the halide. This reaction is known as Wurtz reaction.
2CH3Br + 2Na + dry ether → CH3CH3 + 2NaBr
7. What is aldol?
Answer – Aldehydes and having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy aldehydes, this is known as Aldol.
8. What is electrolysis?
Answer – The process in which external source of voltage is used to bring about a chemical reaction.
9. What is an electrochemical cell?
Answer – An electrochemical cell converts the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy.
10. How can you convert an electrochemical cell to an electrolytic cell?
Answer – By applying external voltage more than emf of electrochemical cell.
11. Write the products of electrolysis of molten NaCl.
Answer – Sodium metal and Cl2 gas.
12. Write one use of electrolysis.
Answer – Electrorefining of metals / electroplating of metals / extraction of metals like Na, Mg, Al.
13. What is the name of the linkage joining two nucleotides?
Answer – Phosphodiester bond
14. What is ‘r’ in r-RNA?
Answer – ribosomal
15. How many oxygen atoms are present in 2-deoxyribose sugar?
Answer : 4
16. Which type of hybridisation is found in [Co(NH3)6]³+ ?
Answer – d²sp³
17. What is magnetic nature of [CoF6]³- ?
Answer – Paramagnetic
18. What is geometry of [CoF6]³- ?
Answer – Octahedral
19. How many unpaired electrons are present in central atom of [Co(NH3)6]³+ ?
Answer : zero
20. What is pseudo first order reaction? Give an example.
Answer – The reaction which is not of first order but behaves like first order is called pseudo first order reaction.
Example: acid hydrolysis of ethyl acetate or inversion of cane sugar.
21. What is meant by ‘disproportionation’?
Answer – When a particular oxidation state becomes less stable relative to other oxidation states, one lower, one higher, it is said to undergo disproportionation.
22. Why amino acids show amphoteric behaviour?
Answer – Amino acids have amino (−NH2) group, basic in nature and accepts a proton and COOH group loses a proton forming a dipolar ion, called the Zwitter ion. In this form, amino acids behave both as acids and bases, so they are amphoteric in nature.
23. Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
Answer – Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is present in primary amines but not in tertiary amines (H-atom absent in amino group) so primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines.
24. Why are aliphatic amines stronger bases than aromatic amines?
Answer – In aromatic amines, the (−NH2) group is attached to a (−C6H5) group, which is an electron withdrawing group. So, the availability of a lone pair of electrons on N is decreased. Therefore, aliphatic amines are more basic than aromatic amines.
25. List the factors affecting the rate of reaction.
Answer – Concentration of reactants & pressure in case of gases, temperature, and catalyst.
26. What are alloys? Name an important alloy which contains some of the lanthanoid metals.
Answer – An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of a metal with other metal or non-metals. An important alloy containing some of the lanthanoid metal is mischmetal.
27. Write increasing order of reactivity four isomers of bromobutane for SN² reaction.
Answer : tert-butyl bromide < sec-butyl bromide < isobutyl bromide < n-butyl bromide
28. What is decarboxylation? Give an example.
Answer – Carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with sodalime (NaOH and CaO in the ratio of 3:1). The reaction is known as decarboxylation.
CH3COONa + NaOH + Cao + ∆ → CH4 + Na2CO3
29. What is cyanohydrin?
Answer – Addition products formed by the reaction of aldehydes and ketones with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) are known as cyanohydrins.
30. What are azeotropes?
Answer – Azeotropes are binary mixtures having the same composition in liquid and vapour phase and boil at a constant temperature.
31. Arrange the following in increasing order of basic strength :
Aniline, p-nitroaniline and p-toluidine
Answer : p-nitroaniline < Aniline < p-toluidine
32. Give one structural difference between amylose and amylopectin.
Answer – Amylose is water soluble linear polymer of α-D glucose whereas amylopectin is water insoluble branched (C1–C6) glycosidic linkage carrying branched polymer.
33. Give the uses of freon-12, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Answer – (i) Freon-12 is used for aerosol propellants, refrigeration and air conditioning purposes.
(ii) Carbon tetrachloride is used in the synthesis of chlorofluorocarbons and other chemicals, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and general solvent use.
(iii) Iodoform can be used as antiseptic.
34. Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is not. Give Explaination.
Answer – Ethylamine is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with water as it is soluble but in aniline the bulk carbon prevents the formation of effective hydrogen bonding and is not soluble.
35. Account for the following :
(a) Aniline does not undergo Friedal craft reaction.
Answer – Aniline being lewis base react with Anhydrous AlCl3 which is lewis acid to form salt.
(b) Methylamine is water reacts with ferric chloride to precipitate hydrated ferric oxide.
Answer – Methylamine accept proton from water and liberate OH- ion which combine with Fe³+ ion to form hydrated ferric oxide Fe(OH)3 or Fe2O3.3H2O
36. Why Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions?
Answer – Because Grignard reagent reacts with moisture and form Alkane.
37. Define Denaturation.
Answer – When protein in native form is subjected to physical changes like change in temperature or pH then hydrogen bonds are broken, it looses its biological activity and all structures are destroyed and only primary structure remain intact.
38. Define Primary structure.
Answer – It is the sequence in which various α-amino acids present in a protein are linked to one another.
39. Why the dipole moment of chloro benzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride?
Answer : C–Cl bond in chloro benzene acquire some double bond character due to delocalization of ions pair on chlorine so bond length decreases.
40. Aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction. Give Explaination.
Answer – A Friedel-Crafts reaction is carried out in the presence of AlCl3. But AlCl3 is acidic in nature, while aniline is a strong base. Thus, aniline reacts with AlCl3 to form a salt and benzene ring is deactivated. Hence, aniline does not undergo the Friedel-Crafts reaction.
41. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is preferred for synthesising primary amines. Give Explaination.
Answer – Gabriel phthalimide reaction gives pure primary amines without any contamination of secondary and tertiary amines. Therefore, it is preferred for synthesising primary amines.
42. Define colligative properties. Give examples.
Answer – The properties which depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution are called colligative properties. Examples: relative lowering of vapour pressure of the solvent, depression of freezing point of the solvent.
43. Write chemical reaction of aniline with benzoyl chloride and write the name of the product obtained.
Answer : C6H5NH2 + C6H5COCl → C6H5NHCOC6H5 + HCl
Name of the product obtained is N Methylbenzamide.
44. What is reverse osmosis?
Answer – If a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side, the pure solvent flows out of the solution through the semi permeable membrane. This phenomenon is called reverse osmosis.
45. What is meant by ‘doping’ in a semiconductor?
Answer – Addition of a suitable impurity to a semiconductor to increase its conductivity is called doping.
46. Write one application of osmosis in food preservation.
Answer – The preservation of meat by salting or the preservation of fruits by adding sugar.
47. What type of bonding help in stabilising the α-helix structure of proteins?
Answer – Hydrogen bonds, disulphide linkages, van der Waals and electrostatic forces of attraction.
48. Write down the IUPAC name of following :
(i) K4[Mn(CN)6]
Answer : Potassium hexacyanomanganate (II)
(ii) (CH3)3N
Answer : N,N-Dimethylmethanamine
(iii) C6H5NHCH3
Answer : N-Methylaniline
(iv) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(NO2)]
Answer : Diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum (II)
(v) K3[Cr(C2O4)3]
Answer : Potassium trioxalatochromate (III)
(vi) [Co(NH3)5(CO3)]Cl
Answer : Pentaamminecarbonatocobalt (III) chloride
49. Complete the following reactions :
(i) C6H5NH2 + (CH3CO)2O → C6H5NHCOCH3
(ii) C6H5SO2Cl + CH3NH2 → C6H5SO2NHCH3
(iii) C6H5NH2 + CHCl3 + alc. KOH → C6H5NC
50. What are ambident nucleophiles? Give an example.
Answer – Groups which possess two different nucleophilic centres are called ambident nucleophiles.
Nitrite ion represents an ambident nucleophile with two different points of linkage. The linkage through oxygen results in alkyl nitrites while through nitrogen atom, it leads to nitroalkanes.
51. Which metal in the first series of transition metals exhibits +1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
Answer – In the first transition series, Cu (Copper) exhibits +1 oxidation state very frequently. It is because Cu (+1) has an electronic configuration of [Ar] 3d¹⁰. The completely filled d-orbital makes it highly stable.
52. Explain with at least three reasons why transition metals act as good catalyst.
Answer – (i) ability to adopt multiple oxidation states
(ii) ability to form complexes
(iii) transition metals utilise outer d and s electrons for bonding. This has the effect of increasing the concentration of the reactants at the catalyst surface and also weakening of the bonds in the reacting molecules.
53. Actinoid contraction is greater from element to element than lanthanoid contraction. Why?
Answer – The shielding effect of 5f orbitals is poorer than the shielding effect of 4f orbitals.
Due to this, the valence shell electrons of actinide experience greater effective nuclear charge than that experienced by lanthanides. Hence, actinoid contraction is greater than lanthanoid contraction.
54. What are lanthanoids? Write their general electronic configuration. What is lanthanoid contraction?
Answer – The elements of the first series of the inner transition metals; 4f (Ce to Lu) are known as lanthanoids.
General electronic configuration for lanthanoids is: (n-2)f¹-¹⁴(n-1)⁰-¹ns² where n = 6.
The steady decrease in the atomic and ionic radii of lanthanide elements with increasing atomic number is called Lanthanide contraction.
55. State Faraday’s law of electrolysis.
Answer : First Law – The amount of chemical reaction which occurs at any electrode during electrolysis by a current is proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte.
• Second Law – The amounts of different substances liberated by the same quantity of electricity passing through the electrolytic solution are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights.
56. What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals?
Answer – Interstitial compounds are those which are formed when small atoms like H, C or N are trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals.
Interstitial compounds are well known for transition compounds due to their closed crystalline structure with voids in them. The atomic size of transition metals is very large hence have large voids to occupy these small atoms.
57. Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reactions involved.
Answer – The Hinsberg test is used for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Benzenesulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl), which is also known as Hinsberg’s reagent, reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. Tertiary amines do not react with Hinsberg’s reagent.
58. Why are amines less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses?
Answer – Amines undergo protonation to give amide ion. Similarly, alcohol loses a proton to give alkoxide ion.
In an amide ion, the negative charge is on the N-atom whereas in alkoxide ion, the negative charge is on the O-atom. Since O is more electronegative than N, O can accommodate the negative charge more easily than N. As a result, the amide ion is less stable than the alkoxide ion. Hence, amines are less acidic than alcohols of comparable molecular masses.
59. Which of the 3d series of the transition metals exhibits the largest number of oxidation states and why?
Answer – Manganese (Z=25) shows maximum number of oxidation states. This is because its electronic configuration is 3d⁵4s². As 3d and 4s are close in energy, it has maximum number of electrons to lose or share (as all the 3d electrons are unpaired).
60. Describe aldol condensation.
Answer – Aldehydes and ketones having at least one α-hydrogen undergo a reaction in the presence of dilute alkali as catalyst to form β-hydroxy aldehydes (aldol) or β-hydroxy ketones (ketol), respectively. This is known as Aldol reaction. The aldol and ketol readily lose water to give α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds which are aldol condensation products, and the reaction is called Aldol condensation.
61. Expan Kolbe’s reaction with example.
Answer – Phenoxide ion generated by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide is even more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. Hence, it undergoes electrophilic substitution with carbon dioxide, a weak electrophile. Ortho hydroxybenzoic acid is formed as the main reaction product.
62. Explain Reimer-Tiemann reaction with example.
Answer – On treating phenol with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide, a –CHO group is introduced at ortho position of benzene ring. The intermediate substituted benzal chloride is hydrolysed in the presence of alkali to produce salicylaldehyde.
63. What is a colligative property? Which colligative property is considered the best to determine the molar mass of solute?
Answer – The properties which depend on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution are called colligative properties.
Osmotic pressure is considered the best to determine the molar mass of solute.
64. State Henry’s law. Write its two applications.
Answer – The partial pressure of the gas in vapour phase (p) is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas (x) in the solution.
Applications : (i) To increase the solubility of CO2 in soft drinks and soda water, the bottle is sealed under high pressure.
(ii) To avoid bends the tanks used by scuba divers are filled with air diluted with helium.
(iii) At high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at the ground level. This leads to low concentrations of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitudes or climbers.
65. State Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions. Write its two applications.
Answer – The law states that limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be represented as the sum of the individual contributions of the anion and cation of the electrolyte.
Applications : (i) to calculate limiting molar conductivity of any electrolyte.
(ii) to calculate the degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte.
(iii) to calculate dissociation constant of weak electrolyte.
66. Differentiate between ideal and non-ideal solutions.
Answer –
| Ideal Solutions | Non-ideal solutions |
| 1. Those liquid-liquid solutions which obey Raoults’ law at each concentration. | 1. Those liquid-liquid solutions which do not obey Raoults’ law at each concentration. |
| 2. The molecular interactions of solution is same as that of solute and solvent. | 2. The molecular interactions of solution is not same as that of solute and solvent. |
| 3. ∆Vmix = 0 | 3. ∆Vmix ≠ 0 |
| 4. ∆Hmix = 0 | 4. ∆Hmix ≠ 0 |
67. Differentiate between two types of Non-ideal solutions.
Answer –
| Positive Deviation Non-ideal Solutions | Negative Deviation Non-ideal solutions |
| 1. Those liquid-liquid solutions which has vapour pressure more than expectations from Raoults’ law. | 1. Those liquid-liquid solutions which has vapour pressure less than expectations from Raoults’ law. |
| 2. The molecular interactions of solution is weaker than that of solute and solvent. | 2. The molecular interactions of solution is stronger than that of solute and solvent. |
| 3. ∆Vmix > 0 | 3. ∆Vmix < 0 |
| 4. ∆Hmix > 0 | 4. ∆Hmix < 0 |
| 5. They form minimum boiling azeotrops. | 5. They form maximum boiling azeotrops. |
68. Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins.
Answer –
| Globular proteins | Fibrous Proteins |
| 1. In this chains of polypeptides coil around to give a spherical shape. | 1. In this polypeptide chains run parallel and fibre like structure is formed. |
| 2. These are usually soluble in water. | 2. These are usually insoluble in water. |
69. Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6-trimethylcyclohexanone does not. Give explaination.
Answer – In 2,2,6-trimethyl cyclohexanone, three methyl groups are presents at α −position with respect to the ketonic (>C=O) group. Therefore, these groups cause steric hindrance during the nucleophilic attack of CN− ion so cyanohydrin is not formed. Due to the absence of methyl groups in cyclohexanone, there is no steric hindrance and cyanohydrin is formed.
70. There are two –NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. Give explaination.
Answer – Semicarbazide has two amino (NH2) groups, out of which one is involved in resonance. Electron-density on this (NH2) decreases and it does not act as a nucleophile. But the other (NH2) group (attached to NH) has a lone pair of electrons which are not involved in resonance. So, this pair is available for the nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group (>C=O) of aldehydes and/or ketones.
71. What is quaternary structure of proteins? Give an example.
Answer – Quaternary structure of proteins: Some of the proteins are composed of two or more polypeptide chains referred to as sub-units. The spatial arrangement of these subunits with respect to each other is known as quaternary structure. Example: Haemoglobin, which has four polypeptide chains around a haeme group.
72. Define molar conductivity for the solution of an electrolyte. How does it vary with concentration for a weak electrolyte?
Answer – Molar conductivity of a solution at a given concentration is the conductance of volume V of a solution containing one mole of electrolyte kept between two electrodes with an area of crosssection A and distance of unit length.
Molar conductivity increases with a decrease in concentration. This is because the total volume V of the solution containing mole of the electrolyte increases on dilution. For weak electrolytes, molar conductivity increases steeply on dilution, especially near lower concentrations.
73. Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Ethanal and Propanone
Answer – Tollen’s test / Fehling’s test (Ethanal gives the test while propanone does not)
(ii) Propanal and Benzaldehyde
Answer – Fehling’s test (Propanal gives the test while benzaldehyde does not)
74. Calculate the ‘spin only’ magnetic moment of M²+ (aq) ion (Z = 27).
Answer – Number of unpaired electrons in M²+ = 3
μ = √n(n+2) = √3(3+2) = √15 = 3.87 BM
75. Calculate the amount of benzoic acid (C6H5COOH) required for preparing 250 mL of 0.15 M solution in methanol.
Answer – Given molarity (M) = 0.15 M
Volume (V) = 250 mL
Molar mass of solute (M2) = 122 g/mol
Mass of solute (w2) = ?
w2 = (M×M2×V) ÷ 1000 = (122×250×0.15) ÷ 1000
w2 = 4.575 g
76. How much electricity in term of Faraday is required to produce 40g of Al from molten Al2O3?
Answer – Given
Production of Al from Al2O3 has a reaction as following : Al³+ + 3e- → Al
i.e. production of 1 mole of Al (27 g) from Al2O3 requires electricity = 3 F
or production of 1 g of Al from Al2O3 requires electricity = 3/27 F
So, production of 40 g of Al from Al2O3 requires electricity = 40/9 F = 4.44 F
77. A solution of Ni(NO3)2 is electrolysed between platinum electrodes using a current of 5 amperes for 20 minutes. What mass of Ni is deposited at the cathode?
Answer – The reactions occurring in cell is as following :
Ni²+ + 2e- → Ni
Given, I = 5 A, T = 20 minutes = 1200 s
Q = It = 1200 x 5 C = 6000 C
2 × 96500 C charge deposits Ni = 59 g
1 C charge deposits Ni = 59 ÷ (2×96500)
6000 C charge deposits Ni = (59×6000) ÷ (2×96500) g = 1.83 g
78. Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [COCl2(en)2]+.
Answer –
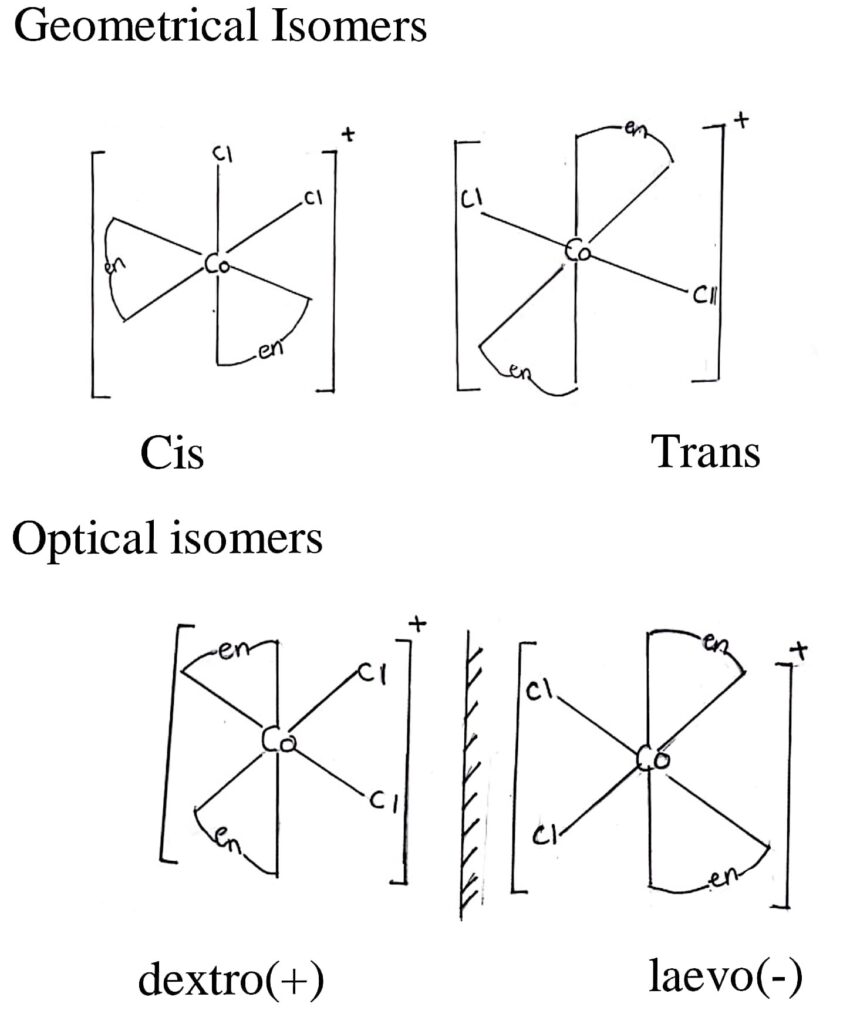
79. Derive an integrated rate equation for a first-order reaction.
Answer –

80. A first order reaction takes 40 min for 30% decomposition. Calculate t½.
Answer –

81. Write five examples of electrophilic substitution of haloarenes.
Answer –
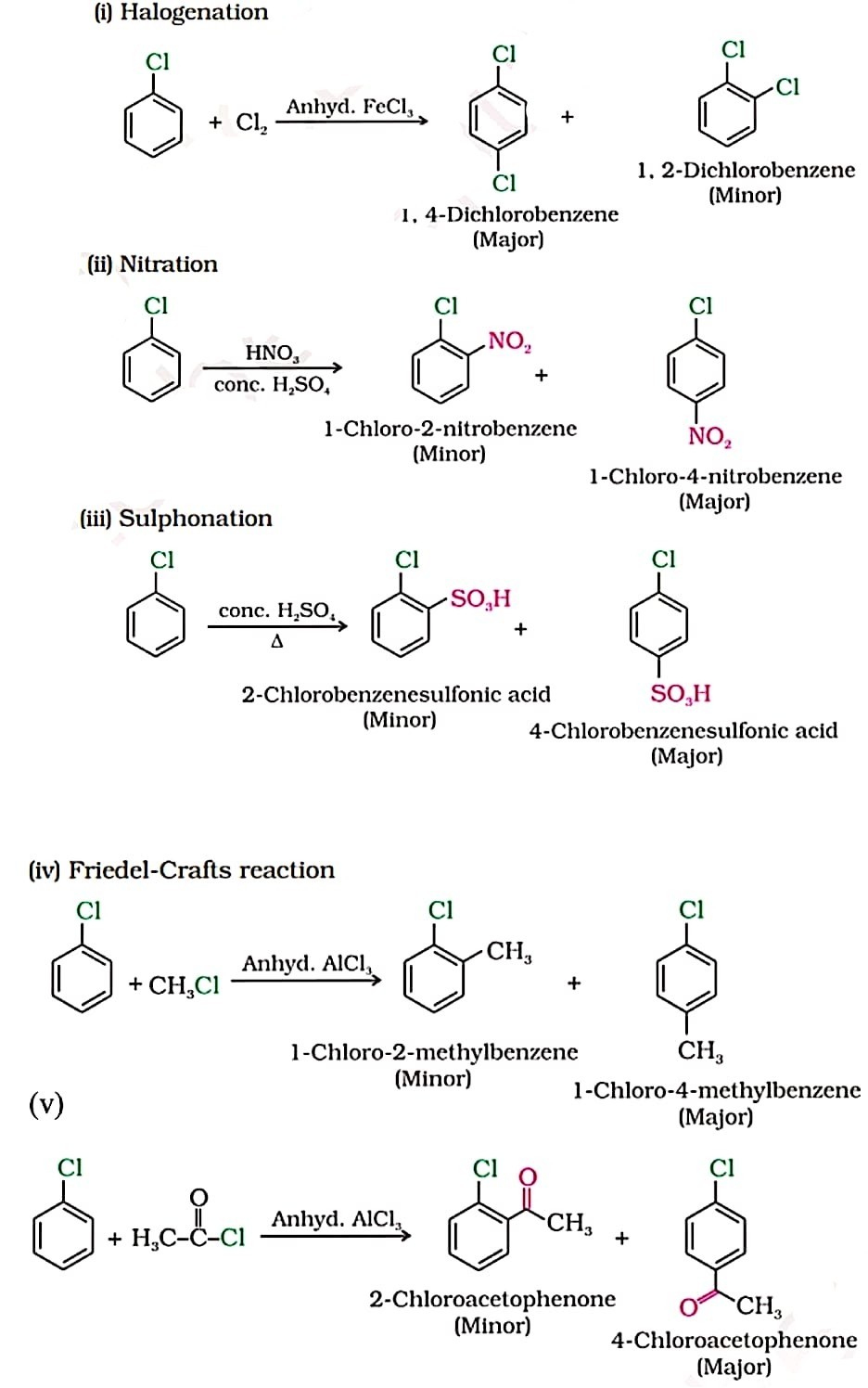
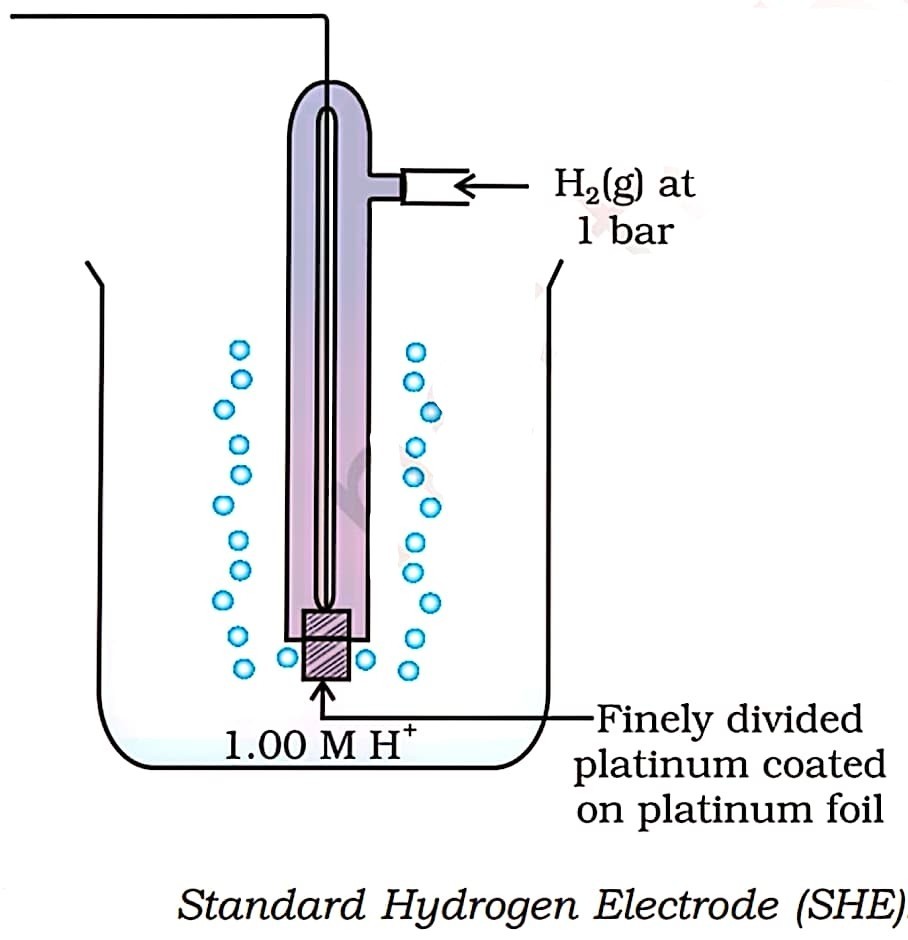
82. Draw a labelled diagram of standard hydrogen electrode.
Answer –
Case Study Based Questions
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C6H6O gives a characteristic colour with aqueous FeCl3 solution. (A) on treatment with CO2 and NaOH at 400 K under pressure gives (B), which on acidification gives a compound (C). The compound (C) reacts with acetyl chloride to give (D) which is a popular analgesic.
Questions :
(i) What is compound (A)?
Answer – Phenol
(ii) What is the number of carbon atoms in compound (D)?
Answer : 8
OR
Write the name of compound (C).
Answer – Salicylic Acid
(iii) What is the name of the conversion reaction of compound (A) to (C)?
Answer – Reimer-Tiemann reaction
(iv) Write one use of compound (D).
Answer – Aspirin possesses analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic properties.
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Proteins are the most abundant biomolecules of the living system. The chief sources of proteins are milk, cheese, pulses, fish, meat, peanuts, etc. They are found in every part of the body and form a fundamental basis of the structure and functions of life. These are also required for the growth and maintenance of the body. The word protein is derived from the Greek word, ‘proteios’ meaning ‘primary’ or of ‘prime importance’. Chemically, proteins are the polymers in which the monomeric units are the α-amino acids. Amino acids contain an amino (-NH2) and carboxylic (-COOH) functional groups. Amino acids which are synthesised by the body are called non-essential amino acids. On the other hand, those amino acids which cannot be synthesized in the human body and are supplied in the form of diet (because they are required for proper health and growth) are called essential amino acids.
Questions :
(i) Why amino acids show amphoteric behaviour?
Answer – Amino acids have amino (−NH2) group, basic in nature and accepts a proton and COOH group loses a proton forming a dipolar ion, called the Zwitter ion. In this form, amino acids behave both as acids and bases, so they are amphoteric in nature.
(ii) What is the name of the linkage joining two amino acids?
Answer – Peptide bond
(iii) What are polypeptides?
Answer – If more than ten α-amino acids are joined together by peptide bond the structure thus formed is called Polypeptides.
(iv) Give an example of non-essential amino acid.
Answer – Glycine / Glutamic acid / Proline
OR
How many types of amino acids are found in proteins?
Answer : 20
3. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
A compound (A) containing C, H and O is unreactive towards sodium. It also does not react with Schiff’s reagent. On refluxing with an excess of hydroiodic acid, (A) yields only one organic product (B). On hydrolysis, (B) yields a new compound (C) which can be converted into (B) by reaction with red phosphorous and iodine. The compound (C) on oxidation with potassium permanganate gives a carboxylic acid (D). The equivalent weight of this acid is 60.
Questions :
(i) What is compound (A)?
Answer – ether or C2H5OC2H5
(ii) What is the number of carbon atoms in compound (D)?
Answer : 2
OR
Write the name of compound (D).
Answer – Ethanoic acid
(iii) What is compound (C)?
Answer : C2H5OH
(iv) Draw structure of compound (B).
Answer : CH3CH2I
4. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Nucleic acids are the polymers of nucleotides which in turn consist of a base, a pentose sugar and phosphate moiety. Nucleic acids are responsible for the transfer of characters from parents to offsprings. There are two types of nucleic acids – DNA and RNA. DNA contains a five-carbon sugar molecule called 2-deoxyribose whereas RNA contains ribose. Both DNA and RNA contain adenine, guanine and cytosine. The fourth base is thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA. The structure of DNA is a double strand whereas RNA is a single strand molecule. DNA is the chemical basis of heredity and have the coded message for proteins to be synthesised in the cell. There are three types of RNA – mRNA, rRNA and tRNA which actually carry out the protein synthesis in the cell.
Questions :
(i) Write full form of DNA.
Answer – Deoxyribo Nucleic acid
(ii) What is the name of the linkage joining two nucleotides?
Answer – Phosphodiester bond
(iii) What is ‘r’ in r-RNA?
Answer – ribosomal
(iv) How many hydrogen bonds are formed by cytosine with guanine in DNA?
Answer : 3
OR
How many oxygen atoms are present in 2-deoxyribose sugar?
Answer : 4
5. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the type of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert (e.g., platinum or gold), it does not participate in the chemical reaction and acts only as source or sink for electrons. On the other hand, if the electrode is reactive, it participates in the electrode reaction. Thus, the products of electrolysis may be different for reactive and inert electrodes. The products of electrolysis depend on the different oxidising and reducing species present in the electrolytic cell and their standard electrode potentials.
Questions :
(i) What is electrolysis?
Answer – The process in which external source of voltage is used to bring about a chemical reaction.
(ii) What is an electrochemical cell?
Answer – An electrochemical cell converts the chemical energy of a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy.
OR
How can you convert an electrochemical cell to an electrolytic cell?
Answer – By applying external voltage more than emf of electrochemical cell.
(iii) Write the products of electrolysis of molten NaCl.
Answer – Sodium metal and Cl2 gas
(iv) Write one use of electrolysis.
Answer – Electrorefining of metals / electroplating of metals / extraction of metals like Na, Mg, Al.
6. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
To explain bonding in coordination compounds various theories were proposed. One of the important theories was valence bond theory. According to that, the central metal ion in the complex makes available a number of empty orbitals for the formation of coordination bonds with suitable ligands. The appropriate atomic orbitals of the metal hybridise to give a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry. The d-orbitals involved in the hybridisation may be either inner d-orbitals i.e., (n-1)d or outer d-orbitals i.e., nd. For example, CO³+ forms both inner orbital and outer orbital complexes, with ammonia it forms [Co(NH3)6]³+ and [CoF6]³- complex ion.
Questions :
(i) Which of the above-mentioned complexes is inner orbital complex?
Answer – [Co(NH3)6]³+
(ii) Which type of hybridisation is found in [Co(NH3)6]³+ ?
Answer – d²sp³
(iii) What is magnetic nature of [CoF6]³- ?
Answer – Paramagnetic
(iv) What is geometry of [CoF6]³- ?
Answer – Octahedral
OR
How many unpaired electrons are present in central atom of [Co(NH3)6]³+ ?
Answer : zero
7. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
The spontaneous flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a pure solvent to solution or from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution is called osmosis. The phenomenon of osmosis can be demonstrated by taking two eggs of the same size. In an egg, the membrane below the shell and around the egg material is semi-permeable. The outer hard shell can be removed by putting the egg in dilute hydrochloric acid. After removing the hard shell, one egg is placed in distilled water and the other in a saturated salt solution. After some time, the egg placed in distilled water swells-up while the egg placed in salt solution shrinks. The external pressure applied to stop the osmosis is termed as osmotic pressure which is a colligative property.
Questions :
(i) What is reverse osmosis?
Answer – If a pressure larger than the osmotic pressure is applied to the solution side, the pure solvent flows out of the solution through the semi permeable membrane. This phenomenon is called reverse osmosis.
(ii) What would happen if red blood corpuscles were placed in 0.5% NaCl solution?
Answer – Red blood corpuscles will swell up
OR
What are isotonic solutions?
Answer – Two solutions having the same osmotic pressure at a given temperature are called isotonic solutions.
(iii) Write one application of osmosis in food preservation.
Answer – The preservation of meat by salting or the preservation of fruits by adding sugar.
(iv) Out of 1 M KCl and 1 M urea, which will have higher osmotic pressure?
Answer – 1 M KCl
8. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions :
Primary alkyl halide C4H9Br (A) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (B). Compound (B) is reacted with HBr to give (C) which is an isomer of (A). When (A) is reacted with sodium metal it gives compound (D), C8H18 which is different from the compound formed when n-butyl bromide is reacted with sodium.
Questions :
(i) Which type of isomerism is present between compounds (A) and (C)?
Answer – Position isomerism
(ii) Write IUPAC name of compound (D).
Answer : 2,5-Dimethylhexane
(iii) Draw structure of compound (B).
Answer : (CH3)2C=CH2
(iv) How will you convert compound (B) to (A)?
Answer : (CH3)2C=CH2 + HBr + peroxide → (CH3)2CHCH2Br
OR
What is the name of the reaction in which compound (A) is converted to compound (D).
Answer – Wurtz reaction
