Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 11 Maths Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. BSEH (Board of School Education Haryana) Class 11 Math Answer Key 2024. HBSE (Haryana Board of School Education) Class 11 Math Solved Question Paper 2024. BSEH Class 11 Mathematics Paper 2024 Solution. Download PDF and check accurate answers carefully prepared through my personal understanding, subject knowledge, and dedication to help students based on the syllabus and exam pattern.
HBSE Class 11 Maths Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (1 Mark)
1. If A = {3, 5, 7, 9, 11}, B = {7, 9, 11, 13}, C = {11, 13, 15} and D = {15, 17}, find (A ∪ D) ∩ (B ∪ C) :
(a) {3, 5, 9}
(b) {7, 11, 15}
(c) {7, 9, 11, 15}
(d) Φ
Answer : (c) {7, 9, 11, 15}
A ∪ D = {3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 15, 17}
B ∪ C = {7, 9, 11, 13, 15}
(A ∪ D) ∩ (B ∪ C) = {7, 9, 11, 15}
2. Let U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, A = {1, 2, 3, 4}, B = {2, 4, 6, 8} and C = {3, 4, 5, 6} find (B – C)’ :
(a) {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9}
(b) {1, 4, 7, 8, 9}
(c) {3, 4, 6, 8}
(d) {2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
Answer : (a) {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9}
B – C = {2, 8}
(B – C)’ = U – (B – C) = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {2, 8} = {1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9}
3. Let A = {x, y , z) and B = {1, 2}, then number of relations from A into B will be :
(a) 6
(b) 9
(c) 24
(d) 64
Answer : (d) 64
m = 3 (number of elements in A)
n = 2 (number of elements in B)
Number of subsets or relations = 2mn = 23×2 = 26 = 64
4. In which quadrant do the angle –1930° lie :
(a) 1st quadrant
(b) 2nd quadrant
(c) 3rd quadrant
(d) 4th quadrant
Answer : (c) 3rd quadrant
= – 1930° + 360° × 6 = – 1930°+ 2160° = 230°
5. Write (5 – 3i)3 in the form of a + ib :
(a) 0 + 0i
(b) – 10 + 198i
(c) 10 – 198i
(d) – 10 – 198i
Answer : (d) – 10 – 198i
Using identity, (a – b)3 = a3 – b3 – 3ab(a – b)
(5 – 3i)3 = (5)3 – (3i)3 – 3(5)(3i)(5 – 3i)
= 125 – 27i3 – 225i + 135i²
= 125 – 27(–i) – 225i + 135(–1)
= 125 + 27i – 225i – 135
= – 10 – 198i = a + bi
6. The longest side of a triangle is 3 times the shortest side and the third side is 2 cm shorter than the longest side. If the perimeter of the triangle is atleast 61 cm. Find the minimum length of the shortest side :
(a) 9 cm
(b) 6 cm
(c) 4 cm
(d) 10 cm
Answer : (a) 9 cm
Let smallest side = x
Longest side = 3x
Third side = 3x – 2
Perimeter ≥ 61
x + 3x + 3x – 2 ≥ 61
7x ≥ 61 + 2
7x ≥ 63
x ≥ 9
7. If nP5 = 42 nP3, n > 4, the value of n is :
(a) 10
(b) 6
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer : (a) 10
nP5 = 42 nP3
n! / (n – 5)! = 42 n! / (n – 3)!
(n – 3)! = 42 (n – 5)!
(n – 3)(n – 4)(n – 5)! = 42 (n – 5)!
(n – 3)(n – 4) = 42
n2 – 4n – 3n + 12 – 42 = 0
n2 – 7n – 30 = 0
n2 – 10n + 3n – 30 = 0
n(n – 10) + 3(n – 10) = 0
(n – 10)(n + 3) = 0
n = 10 (we reject n = –3)
8. Find 5th term in binomial expansion of (x/3 – 3y)7 :
(a) 105 x4y3
(b) 105 x3y4
(c) 105 xy6
(d) 105 x6y
Answer : (b) 105 x3y4
The general term in a binomial expansion of (a + b)n is Tr+1 = nCr(a)n–r(b)r
T5 = T4+1 = 7C4(x/3)7–4(–3y)4
= (7×6×5×4 / 4×3×2×1) (x3/27) (81y4)
= 105 x3y4
9. Which term of the G.P. 1/3, 1/9, 1/27, ……. is 1/19683 ?
(a) 7th
(b) 5th
(c) 9th
(d) 4th
Answer : (c) 9th
Here a = 1/3, r = 1/9 ÷ 1/3 = 1/3
nth term of G.P., an = arn–1
an = (1/3)(1/3)n–1 = 19683
(1/3)n = (1/3)9
n = 9
10. Find the sum of 17 terms of the A.P. 5, 9, 13, 17, ………. :
(a) 629
(b) 529
(c) 615
(d) 0
Answer : (a) 629
Here a = 5, d = 9 – 5 = 4
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
S17 = 17/2 [2(5) + 16(4)]
= 17/2 [10 + 64] = 17/2 (74) = 629
11. If A.M. and G.M. of roots of a quadratic equation are 8 and 5, respectively, then obtain the quadratic equation.
Answer : AM = (α + β)/2 = 8
α + β = 16 ……..(i)
GM = √(αβ) = 5
αβ = 25 ……..(ii)
Quadratic equation = x2 – (α + β)x + αβ
x2 – 16x + 25 = 0
12. Write equation of directrix of an ellipse x2/a2 + y2/b2 = 1 (a > b)
Answer : x = ± a/e
13. limx→0 (ax – 1)/x = ?
Answer : log a
14. Find the derivative of cosec x.
Answer : –cosecx.cotx
15. Find the mean of first n natural numbers.
Answer : Mean = Total sum / Total numbers = [n(n+1)/2] / n = (n+1)/2
16. A die is thrown, find the probability that a number less than 3 will appear.
Answer : Total possible outcomes = 6 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Favorable outcomes = 2 {1, 2}
Probability = Favorable outcomes / Total possible outcomes
P(E) = 2/6 = 1/3
17. If an event is impossible, then what will be its probability?
Answer : Zero
18. Given P(A) = 3/5 and P(B) = 1/5, find P(A or B), if A and B are mutually exclusive events.
Answer : For mutually exclusive events A and B then P(A ∩ B) = 0
P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) – P(A ∩ B)
P(A or B) = P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) = 3/5 + 1/5 = 4/5
P(A or B) = 4/5
19. Assertion (A) : If (4x + 3, y) = (3x + 5, –2) then x = 2 and y = –2.
Reason (R) : If A = {–1, 3, 4}, then A × A is {(–1, –1), (–1, 3), (–1, 4), (3, –1), (4, –1), (3, 4)}
(a) (A) is true, (R) is true; (R) is correct explanation of (A).
(b) (A) is true, (R) is true; (R) is not a correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, (R) is true.
Answer : (c) (A) is true, (R) is false.
20. Assertion (A) : The collection of all natural numbers less than 100 is a set.
Reason (R) : A set is a well defined collection of the distinct objects
(a) (A) is true, (R) is true; (R) is correct explanation of (A).
(b) (A) is true, (R) is true; (R) is not a correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, (R) is true.
Answer : (a) (A) is true, (R) is true; (R) is correct explanation of (A).
SECTION – B (2 Marks)
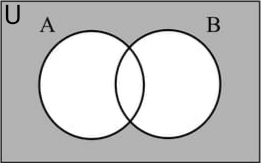
21. Draw appropriate Venn diagram for each of following :
(i) (A ∪ B)’
(ii) A’ ∩ B’
Answer : Both (i) & (ii) have same venn diagram because (A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
22. Solve :
– x2 + x – 2 = 0
Answer : –x2 + x – 2 = 0
x2 – x + 2 = 0
Here a = 1, b = –1, c = 2
x = [–b ± √b2–4ac] / 2a
= [–(–1) ± √(–1)2–4(1)(2)] / 2(1)
= [1 ± √1–8] / 2
= [1 ± √–7] / 2
= [1 ± √7i] / 2
x = [1+√7i] / 2 and [1+√7i] / 2
OR
Simplify : [(1/3 + i 7/3) + (4 + i 1/3)] – (– 4/3 + i)
Answer : 1/3 + i 7/3 + 4 + i 1/3 + 4/3 – i
= (1/3 + 4 + 4/3) + i(7/3 + 1/3 – 1)
= 17/3 + i 5/3
23. Solve : (5 – 2x)/3 ≤ x/6 – 5
Answer : (5 – 2x)/3 ≤ x/6 – 5
Multiply both sides of the inequality by 6,
2(5 – 2x) ≤ x – 30
10 – 4x ≤ x – 30
– 4x – x ≤ – 30 – 10
–5x ≤ –40
5x ≥ 40
x ≥ 8
x ∈ [8, ∞)
24. How many terms of the G.P. 3, 3/2, 3/4,
……… are needed to give the sum 3069/512 ?
Answer : a = 3, r = (3/2) / 3 = 1/2, Sn = 3069/512
Sn = a(1 – rn) / (1 – r) = 3069 / 512
3[1 – (1/2)n] / (1 – 1/2) = 3069 / 512
6[1 – (1/2)n] = 3069 / 512
1 – (1/2)n = 3069 / 3072
1 – 3069/3072 = (1/2)n
3/3072 = (1/2)n
1/1024 = (1/2)n
(1/2)10 = (1/2)n
n = 10
Therefore, 10 terms of the given GP are needed to give the sum 3069/512.
25. Find the equation of parabola with vertex at the origin, passing through (2, 3) and axis along x-axis.
Answer : y2 = 4ax
(3)2 = 4a(2)
9 = 8a
a = 9/8
y2 = 4ax
y2 = 4(9/8)x
y2 = 9/2 x
2y2 = 9x
Now, equation is 2y2 = 9x
OR
Find the coordinates of focus and equation of directrix of parabola x2 = –16y.
Answer : Compare x2 = –16y with x2 = 4ax
4a = –16
a = –4
Focus is (0, –a) = (0, –4)
Directrix is y = a, so y = 4
SECTION – C (3 Marks)
26. In a group of 65 people, 40 like cricket, 10 like both cricket and tennis. How many like tennis only and not cricket? How many like tennis?
Answer : n(C ∪ T) = 65, n(C) = 40, n(C ∩ T) = 10
n(C ∪ T) = n(C) + n(T) – n(C ∩ T)
n(T) = n(C ∪ T) + n(C ∩ T) – n(C)
= 65 + 10 – 40
= 75 – 40
= 35
The number of people like tennis only and not cricket = n(T – C)
n(T) = n(T – C) + n(C ∩ T)
n(T – C) = n(T) – n(C ∩ T)
= 35 – 10
= 25
Therefore, 35 people like tennis and 25 people like tennis only and not cricket.
27. Find domain and range of real function f(x) = – | x |. Also find value of function at x = – 5.
Answer : Domain of f(x) = All real number (-∞, ∞)
Range is of f(x) = (-∞, 0]
The value of the function at x = –5 is f(–5) = – |–5| = – 5
28. Using principle of mathematical induction, prove that for all n ∈ N :
1 + 2 + 3 + …….. + n < 1/8 (2n + 1)2
Answer : Let P (n) be the given statement.
P(n) : 1 + 2 + 3 + …. + n < 1/8 (2n + 1)2
P(1) : 1 < 1/8 (2.1 + 1)2
1 < 9/8, which is true.
P(k) : 1 + 2 + 3 + …. + k < 1/8 (2k + 1)2 ……(i)
P(k + 1) is true whenever P(k) is true.
Now, we have
1 + 2 + 3 + ….. + k < 1/8 (2k + 1)2
= 1 + 2 + 3 + ….. + k + (k + 1)
< 1/8 (2k + 1)2 + (k + 1) ……[from (i)]
< 1/8 [(2k + 1)2 + 8(k + 1) ]
< 1/8 [4k2 + 4k + 1+ 8k + 8]
< 1/8 [4k2 + 12k + 9]
< 1/8 [2k + 3]2
< 1/8 [2(k + 1) + 1]2
Thus P(k + 1) is true, whenever P (k) is true.
Hence, from the principle of mathematical induction, the statement P(n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n ∈ N.
OR
Prove the following by using the principle of mathematical induction, for all n ∈ N :
1² + 3² + 5² + ………. + (2n – 1)2 = n(2n – 1)(2n + 1)/3
Answer : Let P (n) be the given statement.
P(n) : 12 + 32 + 52 + …. + (2n – 1)2 = [n(2n – 1)(2n + 1)]/3
P(1) : 12 = [1(2.1 – 1)(2.1 + 1)]/3
1 = 1.1.3/3
1 = 1, which is true.
P(k) : 12 + 32 + 52 + …. + (2k – 1)2 = [k(2k – 1)(2k + 1)]/3 ……(i)
P(n + 1) : 12 + 32 + 52 + …. + (2(k + 1) – 1)2
= 12 + 32 + 52 + …. + (2k + 1)2
= [12 + 32 + 52 + …. + (2k – 1)2] + (2k + 1)2
= [k(2k – 1)(2k + 1)]/3 + (2k + 1)2 ….[from (i)]
= [k(2k – 1)(2k + 1) + 3(2k + 1)2]/3
= (2k + 1) [k(2k – 1) + 3(2k + 1)]/3
= (2k + 1) [2k2 – k + 6k + 3]/3
= (2k + 1) [2k2 + 5k + 3]/3
= (2k + 1) [2k2 + 2k + 3k + 3]/3
= (2k + 1) [2k (k + 1) + 3(k + 1)]/3
= [(2k + 1)(k + 1)(2k + 3)]/3
= (k + 1) [2(k + 1) – 1] [2(k + 1) + 1]/3
Thus P(k + 1) is true, whenever P(k) is true.
Hence, from the principle of mathematical induction, the statement P (n) is true for all natural numbers i.e., n ∈ N.
29. Find the value of x for which the points (x, –1), (2, 1) and (4, 5) are collinear.
Answer : If points A( x, –1), B(2, 1) and C(4, 5) are collinear,
Then, Slope of AB = Slope of BC
Slope, m = (y2–y1)/(x2–x1)
[1 – (–1)]/(2 – x) = (5 – 1)/(4 – 2)
(1 + 1)/(2 – x) = 4/2
2/(2 – x) = 2
2 = 4 – 2x
2x = 4 – 2
2x = 2
x = 1
Thus, the required value of x = 1.
30. Find : limx→1 f(x) where :
f(x) = {x² – 1, x ≤ 1 and –x2 – 1, x > 1}
Answer : The given function is f(x) = {x2 – 1, x ≤ 1 and –x2 – 1, x > 1}
Now,
limx→1– f(x) = limx→1 [x2 – 1] (as x < 1)
= 12 – 1
= 1 – 1
= 0
limx→1+ f(x) = limx→1 [– x2 – 1] (as x > 1)
= – 12 – 1
= – 1 – 1
= – 2
It is observed that limx→1– f(x) ≠ limx→1+ f(x)
Hence the given limit limx→1 f(x) does not exist.
OR
Find the derivative of (5x3 + 3x – 1)(x – 1).
Answer : Let f(x) = (5x3 + 3x – 1)(x – 1)
Use differentiation rule, d/dx (uv) = u’v + uv’
f'(x) = (5x3 + 3x – 1) d/dx (x – 1) + (x – 1) d/dx (5x3 + 3x – 1)
= (5x3 + 3x – 1)(1) + (x – 1)(5.3x2 + 3 – 0)
= (5x3 + 3x – 1) + (x – 1)(15x2 + 3)
= 5x3 + 3x – 1 + 15x3 + 3x – 15x2 – 3
= 20x3 – 15x2 + 6x – 4
31. If E and F are events such that P(E) = 1/4, P(F) = 1/2 and P(E and F) = 1/8, find :
(i) P(E or F)
Answer : P(E or F) = P(E) + P(F) – P (E and F)
P(E or F) = 1/4 + 1/2 – 1/8 = 5/8
(ii) P(not E and not F)
Answer : From (i), P(E or F) = P (E ∪ F) = 5/8
By De Morgan’s law,
(E’ ∩ F’) = (E ∪ F)’
P(E’ ∩ F’) = P (E υ F)’
= 1 – P(E ∪ F)
= 1 – 5/8 [From (i)]
= 3/8
SECTION – D (5 Marks)
32. Prove that :
(i) cos4x = 1 – 8sin2x cos2x
Answer : LHS = cos4x
= cos2(2x)
= 1 – 2sin22x [By double angle formula, cos 2A = 1 – 2sin2A]
= 1 – 2(2sinx cosx)2 [By double angle formulas, sin2A = 2sinAcosA]
= 1 – 2(4sin2x cos2x)
= 1 – 8sin2x cos2x
= RHS
(ii) cos2(2x) – cos2(6x) = sin4x sin8x
Answer : LHS = cos22x – cos26x
= (cos2x + cos6x)(cos2x – cos6x)
[Using a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a – b) formula]
= [2cos {(2x + 6x) / 2} cos {(2x – 6x) / 2}] × [–2 sin{(2x + 6x) / 2} sin{(2x – 6x) / 2}]
{Since cosA + cosB = 2cos [(A + B) / 2] cos [(A – B) / 2] and cos A – cos B = –2sin [(A + B) / 2] sin [(A – B) / 2]}
= [2cos4x cos(–2x)] × [–2sin4x sin(–2x)]
= [2cos4x cos2x] × [–2sin4x (–sin2x)]
[By trigonometric formula, cos (–A) = cosA and sin(–A) = –sinA]
= [2cos4x cos2x] × [2sin4x sin2x]
= [2cos4x sin4x] × [2cos2x sin2x]
= [sin(4x + 4x) – sin (4x – 4x)] × [sin(2x + 2x) – sin(2x – 2x)]
[Since, 2cosA sinB = sin(A + B) – sin(A – B)]
= [sin8x + sin0] × [sin4x + sin0]
= sin8x × sin4x
[by trigonometric table sin 0 = 0]
= sin4x sin8x
= RHS
33. Using binomial theorem, find (a + b)4 – (a – b)4. Hence evaluate (√3 + √2)4 – (√3 – √2)4.
Answer : Using binomial theorem, we will evaluate the expressions (a + b)4 and (a – b)4.
(a + b)4 = 4C0 a4 + 4C1 a3b + 4C2 a2b2 + 4C3 ab3 + 4C4 b4
(a – b)4 = 4C0 a4 – 4C1 a3b + 4C2 a2b2 – 4C3 ab3 + 4C4 b4
Therefore,
(a + b)4 – (a – b)4 = [(4C0 a4 + 4C1 a3b + 4C2 a2b2 + 4C3 ab3 + 4C4 b4) – (4C0 a4 – 4C1 a3b + 4C2 a2b2 – 4C3 ab3 + 4C4 b4)]
= 2(4C1 a3b + 4C3 ab3)
= 2(4a3b + 4ab3)
= 8ab(a2 + b2)
Putting a = √3 and b = √2
(√3 + √2)4 – (√3 – √2)4 = 8(√3)(√2)[(√3)2 + (√2)2]
= 8√6 [3 + 2]
= 40√6
OR
Find the sum of n terms of the sequence 8, 88, 888, 8888, ………
Answer : The given sequence is 8, 88, 888, …. n terms .
Sn = 8 + 88 + 888 + …. n terms
= 8 [9 + 99 + 999 + …. terms]
= 8/9 [(10 – 1) + (100 – 1) + (1000 – 1) + …. n terms]
= 8/9 [(10 + 102 + 103 + …. n terms) – (1 + 1 + 1 + …. n terms)]
Using, Sn = a(rn – 1)/(r – 1)
= 8/9 [10(10n – 1)/(10 – 1) – n]
= 8/9 [10(10n – 1)/9 – n]
= 80/81 (10n – 1) – 8/9 n
34. The vertices of a ∆POR are P(2, 1), Q(–2, 3) and R(4, 5). Find equation of the median through the vertex R and Q.
Answer : It is given that the vertices of ΔPQR are P (2, 1), Q (–2, 3) and R (4, 5). Let RL be the median through vertex R.
Accordingly, L is the midpoint of PQ.
By midpoint formula, the coordinates of point L are given by [(2 – 2)/2, (1 + 3)/2] = (0, 2)
Therefore, the equation of the line passing through points (4, 5) and (0, 2) is
(y – y1)/(x – x1) = (y2 – y1)/(x2 – x1)
(y – 5)/(x – 4) = (2 – 5)/(0 – 4)
(y – 5)/(x – 4) = (–3)/(–4)
4(y – 5) = 3(x – 4)
4y – 20 = 3x – 12
3x – 4y + 8 = 0
Thus, the equation of the median through vertex R is 3x – 4y + 8 = 0.
OR
Find the distance between the parallel lines 15x + 8y – 34 = 0 and 15x + 8y + 31 = 0.
Answer : Here, A = 15, B = 8, C1 = –34 and C2 = 31
Therefore, the distance between the parallel lines is d = |C2–C1| / √A2+B2
d = |31–(–34)| / √(15)2+(8)2
= |65| / √289
= 65/17 units
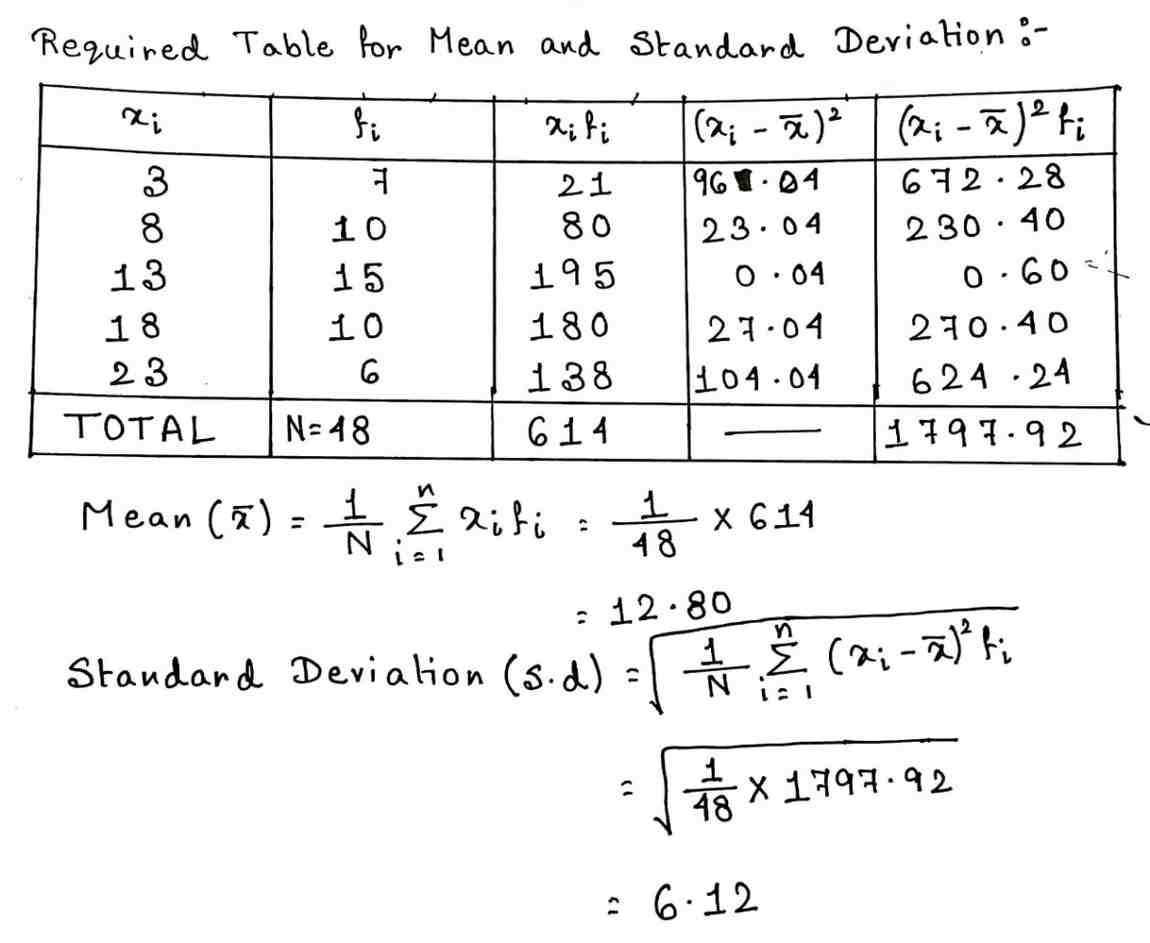
35. Calculate standard deviation for the following data :
| xi | 3 | 8 | 13 | 18 | 23 |
| fi | 7 | 10 | 15 | 10 | 6 |
Answer :
SECTION – E (4 Marks : CASE STUDY)
36. A civil engineer is given a work of renovating a semi-elliptical bridge. This bridge is 10 m wide at the base and 3 m high at the centre.

Answer the following questions :
(i) What could be the equation of the elliptical curve showing in the figure?
Answer : The base width is 2a = 10m, so a = 5 m
The height at center is b = 3 m
The standard equation of the ellipse centered at the origin is :
x2/a2 + y2/b2 = 1
x2/(5)2 + y2/(3)2 = 1
x2/25 + y2/9 = 0
(ii) At what distance from the centre, the height of the bridge would be 2 m ?
Answer : Substitute y = 2 into the above equation,
x2/25 + 22/9 = 1
x2/25 + 4/9 = 1
x2/25 = 5/9
x2 = 125/9
x = ± 5√5 / 3
37. A coach is training 3 players. He observes that player A can hit a target 4 times in 5 shots, player B can hit 3 times in 4 shots and player C can hit 2 times in 3 shots.
From this situation answer the following questions :
(i) Probability that A, B and C all will hit target.
Answer : Probability of A hitting the target = 4/5
Probability of B hitting the target = 3/4
Probability of C hitting the target = 2/3
Since the events are independent, multiply the probabilities:
P(all hit) = (4/5) × (3/4) × (2/3) = 2/5
(ii) What is probability that B, C will hit and A will lose?
Answer : Probability of A missing the target = 1 – 4/5 = 1/5
Probability of B hitting the target = 3/4
Probability of C hitting the target = 2/3
Since the events are independent, multiply the probabilities:
P( B and C will hit and A will lose) = (1/5) × (3/4) × (2/3) = 1/10
38. A submarine is moving in such a way that at a particular moment of time its angle of elevation for two ships, situated at different positions on the surface of water is α and β respectively, if cosec α = √3 and sec β = 2.
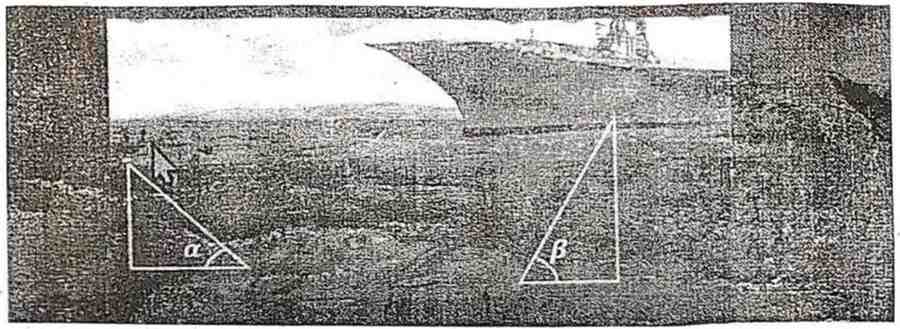
Answer the following questions:
(i) What will be the value of sec α ?
Answer : cosec α = √3
sin α = 1/√3
cos α = √(2/3) [using sin2α + cos2α = 1]
sec α = 1/cos α = √3/√2 = √6/2
(ii) What will be the measure of the angle β ?
Answer : sec β = 2
cos β = 1/2 = cos 60°
β = 60° = π/3
(iii) What will be the value tan α ?
Answer : sin α = 1/√3, cos α = √2/√3
tan α = sin α / cos α = (1/√3) / (√2/√3) = 1/√2 = √2/2
