Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 10 Science Question Paper 2025 with a fully solved answer key. Students can use this HBSE Class 10 Science Solved Paper to match their responses and understand the question pattern. This BSEH Science Answer Key 2025 is based on the latest syllabus and exam format to support accurate preparation and revision for the board exams.
HBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2025 Answer Key
SECTION – A
भौतिक विज्ञान (PHYSICS)
1. किसी दर्पण से आप चाहे कितनी ही दूरी पर खड़े हों, आपका प्रतिबिंब सदैव सीधा ही प्रतीत होता है। संभवतः दर्पण है : (1 Mark)
(A) केवल समतल
(B) केवल अवतल
(C) केवल उत्तल
(D) या तो समतल अथवा उत्तल
उत्तर – (D) या तो समतल अथवा उत्तल
No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be :
(A) only plane
(B) only concave
(C) only convex
(D) either plane or convex
Answer – (D) either plane or convex
2. किसी विद्युत बल्ब का अनुमतांक 220 V तथा 100 W है। जब इसे 110 V पर प्रचालित करते हैं, तब इसके द्वारा उपयुक्त शक्ति कितनी होती है? (1 Mark)
(A) 100 W
(B) 75 W
(C) 50 W
(D) 25 W
उत्तर – (D) 25 W
प्रतिरोध, R = V2/P = (220)2/100 = 484 Ω
110 V पर खपत होने वाली शक्ति, P’ = (V’)2/R = (110)2/484 = 25 W
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be :
(A) 100 W
(B) 75 W
(C) 50 W
(D) 25 W
Answer – (D) 25 W
Resistance, R = V2/P = (220)2/100 = 484 Ω
Power at 110 V, P’ = (V’)2/R = (110)2/484 = 25 W
3. …………… शक्ति का छोटा मात्रक है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – वाट
…………. is the small unit of electric power.
Answer – Watt
4. बल्बों में कौन-सी गैस भरी जाती है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – आर्गन
Which gas is filled in electric bulbs?
Answer – Argon
5. निम्नलिखित प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं : (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : नेत्र लेंस में अपनी फोकल लंबाई को समायोजित करके रेटिना पर स्पष्ट रूप से फोकस करने की क्षमता होती है।
कारण (R) : इस घटना को समायोजन की शक्ति के रूप में जाना जाता है।
(A) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(B) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, लेकिन (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(C) (A) सत्य है, लेकिन (R) असत्य है।
(D) (A) असत्य है, लेकिन (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (A) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
The question below consists of two statements :
Assertion (A) : The eyelens has the ability to focus clearly on the retina by adjusting its focal length.
Reason (R) : This phenomenon is known as power of accommodation.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
6. किसी अंतरिक्ष यात्री को आकाश नीले की अपेक्षा काला क्यों प्रतीत होता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – वायुमंडल की अनुपस्थिति के कारण प्रकाश का प्रकीर्णन नहीं होता है।
Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
Answer – Due to absence of atmosphere, no scattering of light occurs.
7. किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध किन कारकों पर निर्भर करता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – चालक की लंबाई, अनुप्रस्थ काट का क्षेत्रफल, पदार्थ की प्रकृति, और तापमान।
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depends?
Answer – Length of the conductor, area of cross-section, nature of material, and temperature.
8. ओम के नियम को परिभाषित कीजिए। प्रतिरोध का SI मात्रक बताइये। ओम के नियम के अनुसार निम्न में से प्रतिरोध का सही समीकरण चुनें : (3 Marks)
(A) R = V/I
(B) R = I/V
उत्तर – (A) R = V/I
ओम का नियम कहता है कि किसी चालक में प्रवाहित होने वाली विद्युत धारा (I) उसके सिरों के बीच लगाए गए विभवांतर (V) के सीधे समानुपाती होती है, बशर्ते चालक की भौतिक अवस्थाएँ, विशेषकर तापमान, स्थिर रहें। इस संबंध को V ∝ I या V = IR के रूप में व्यक्त किया जाता है, जहाँ R चालक का प्रतिरोध है। प्रतिरोध का SI मात्रक ओम (Ω) होता है।
Define Ohm’s law. State SI unit of resistance. Select the correct equation of resistance in accordance to Ohm’s law from below options :
(A) R = V/I
(B) R = I/V
Answer – (A) R = V/I
Ohm’s Law states that the electric current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (V) across it, provided the physical conditions, especially temperature, remain constant. This relationship is written as V ∝ I or V = IR, where R is the resistance of the conductor. The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω).
9. (a) किसी छड़ चुंबक के चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ खींचिए। (1 Mark)
Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
Answer –
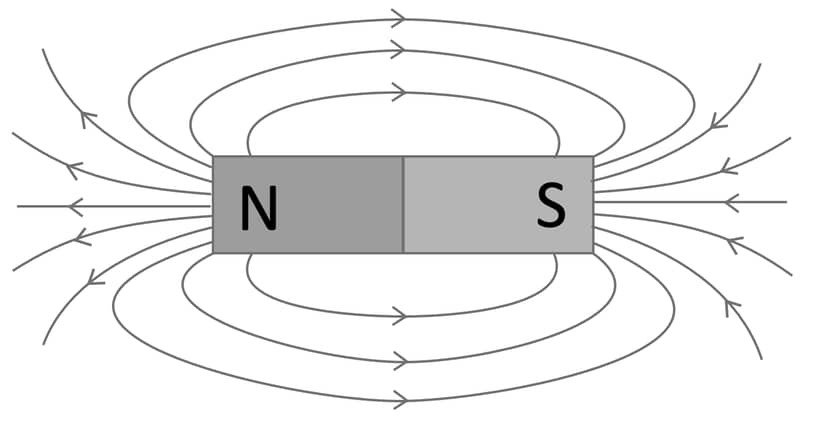
(b) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाओं के कोई दो गुण लिखिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – (i) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ सदैव उत्तर ध्रुव से निकलकर दक्षिण ध्रुव में प्रवेश करती हैं और चुंबक के भीतर दक्षिण से उत्तर की ओर जाती हैं, इस प्रकार ये बंद वक्र बनाती हैं।
(ii) दो चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ कभी एक-दूसरे को नहीं काटतीं।
Write any two properties of magnetic field lines.
Answer – (i) Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole and enter the south pole outside the magnet and form closed loops inside the magnet.
(ii) No two magnetic field lines intersect each other.
10. (a) अवतल दर्पण के मुख्य फोकस की परिभाषा लिखिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – अवतल दर्पण का मुख्य फोकस वह बिंदु है जिस पर प्रधान अक्ष के समानांतर आने वाली प्रकाश किरणें दर्पण से परावर्तन के बाद वास्तव में एकत्रित हो जाती हैं।
Define the principal focus of a concave mirroг.
Answer – The principal focus of a concave mirror is the point on the principal axis where rays of light parallel to the principal axis actually meet after reflection from the mirror.
(b) उस दर्पण का नाम बताइये जो बिंब का सीधा तथा आवर्धित प्रतिबिंब बना सके। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – अवतल दर्पण
Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer – Concave mirror
(c) हम वाहनों में उत्तल दर्पण को पश्च दृश्य दर्पण के रूप में वरीयता क्यों देते हैं? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – वाहनों में उत्तल दर्पण को पश्च दृश्य दर्पण के रूप में इसलिए वरीयता दी जाती है क्योंकि यह हमेशा सीधा और आभासी प्रतिबिंब बनाता है तथा इसका दृष्टि क्षेत्र अधिक होता है। इससे चालक को पीछे की अधिक वस्तुएँ एक साथ दिखाई देती हैं।
Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
Answer – A convex mirror is preferred as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because it always forms an erect and virtual image and provides a wider field of view. This enables the driver to see a larger area behind the vehicle.
OR
(a) किसी लेंस की 1 डाइआप्टर क्षमता को परिभाषित कीजिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – एक डाइआप्टर (D) किसी लेंस की वह क्षमता होती है, जिसकी फोकस दूरी 1 मीटर हो। लेंस की क्षमता का सूत्र P = 1/f होता है, जहाँ P क्षमता (डाइआप्टर में) तथा f फोकस दूरी (मीटर में) होती है।
Define 1 dioptre of power of a Lens.
Answer – One dioptre (D) is the power of a lens whose focal length is 1 metre. The power of a lens is given by P = 1/f, where P is measured in dioptres and f in metres.
(b) 2 m फोकस दूरी वाले अवतल लेंस की क्षमता ज्ञात कीजिए। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – अवतल लेंस के लिए फोकस दूरी ऋणात्मक होती है।
यहाँ, f = – 2 m
लेंस की क्षमता, P = 1/f = 1/(–2) = – 0.5 D
Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2 m.
Answer – For a concave lens, the focal length is taken as negative.
Here, f = – 2 m
Power of lens, P = 1/f = 1/(–2) = – 0.5 D
(c) निम्न सूत्र लिखें : (2 Marks)
Write the following formulas :
(i) लेंस सूत्र
उत्तर : 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
Lens formula
Answer : 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
(ii) दर्पण सूत्र
उत्तर : 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
Mirror formula
Answer : 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
SECTION – B
रसायन विज्ञान (CHEMISTRY)
11. लौह चूर्ण पर तनु हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल डालने से क्या होता है? सही उत्तर को चुनिए : (1 Mark)
(A) हाइड्रोजन गैस एवं आयरन क्लोराइड बनता है।
(B) क्लोरीन गैस एवं आयरन हाइड्रॉक्साइड बनता है।
(C) कोई अभिक्रिया नहीं होती।
(D) आयरन लवण व जल बनता है।
उत्तर – (A) हाइड्रोजन गैस एवं आयरन क्लोराइड बनता है।
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron filling? Choose the correct answer :
(A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(B) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(C) No reaction takes place.
(D) Iron salt and water are produced.
Answer – (A) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
12. नमकीन को पैकेट से निकालने के उपरांत विकृतगंधिता से बचाने हेतु आप क्या उपाय करेंगे? (1 Mark)
(A) प्रति ऑक्सीकारक मिलायेंगे
(B) नाइट्रोजन गैस भरेंगे
(C) वायुरोधी बर्तन में रखेंगे
(D) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर – (C) वायुरोधी बर्तन में रखेंगे
What measures will you take to prevent the ‘Namkeen’ from getting rancid after removing it from the packet?
(A) Add anti-oxidant
(B) Fill Nitrogen gas
(C) Store in an air-tight container
(D) All of the above
Answer – (C) Store in an air-tight container
13. ………….. सबसे अधिक आघातवर्ध्य धातु है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – सोना
………….. is the most malleable metal.
Answer – Gold
14. आयनिक यौगिकों का गलनांक उच्च क्यों होता है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – आयनिक यौगिकों में धनायन और ऋणायन के बीच प्रबल वैद्युत आकर्षण बल होता है, इसलिए उन्हें तोड़ने के लिए अधिक ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है और उनका गलनांक उच्च होता है।
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Answer – Ionic compounds have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between positive and negative ions, so a large amount of energy is required to break them, resulting in high melting points.
15. निम्नलिखित प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं : (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : हमारा उदर हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल उत्पन्न करता है।
कारण (R) : हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल लाल लिटमस को नीला कर देता है।
(A) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(B) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, लेकिन (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(C) (A) सत्य है, लेकिन (R) असत्य है।
(D) (A) असत्य है, लेकिन (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (C) (A) सत्य है, लेकिन (R) असत्य है।
(कारण असत्य है क्योंकि HCl एक अम्ल है, जो नीले लिटमस को लाल करता है, ना कि लाल लिटमस को नीला)
The question below consists of two statements :
Assertion (A) : Our stomach produces hydrochloric acid.
Reason (R) : Hydrochloric acid turns red litmus blue.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(reason is false because HCl is an acid, it turns blue litmus red, not red litmus blue)
16. संयोजन अभिक्रिया से आप क्या समझते हैं? रासायनिक समीकरण सहित एक उदाहरण दीजिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – संयोजन अभिक्रिया वह रासायनिक अभिक्रिया है, जिसमें दो या दो से अधिक पदार्थ आपस में मिलकर एक ही पदार्थ का निर्माण करते हैं।
उदाहरण: CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
What is combination reaction? Give one example with chemical equation.
Answer – A combination reaction is a chemical reaction in which two or more substances combine to form a single product.
Example: CaO + H2O → Ca(OH)2
17. विरंजक चूर्ण का रासायनिक सूत्र और उसके दो उपयोग लिखें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – विरंजक चूर्ण का रासायनिक सूत्र CaOCl2 है।
इसके दो उपयोग निम्नलिखित हैं :
(i) पीने के पानी को कीटाणुरहित (शुद्ध) करने के लिए।
(ii) सूती कपड़ों और लिनन की विरंजन (सफेदी) के लिए।
Write the chemical formula and two uses of bleaching powder.
Answer – The chemical formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl2.
Two uses of bleaching powder are :
(i) It is used to disinfect drinking water.
(ii) It is used for bleaching cotton and linen clothes.
OR
(a) जल की अनुपस्थिति में अम्ल, अम्लीय व्यवहार क्यों नहीं दिखाते हैं? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – अम्ल जल में घुलने पर ही आयनीकरण करके हाइड्रोजन आयन (H+) उत्पन्न करते हैं। जल के अभाव में अम्ल आयनीकरण नहीं कर पाते, इसलिए वे अम्लीय व्यवहार प्रदर्शित नहीं करते।
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer – Acids ionize and produce hydrogen ions (H+) only in the presence of water. In the absence of water, acids do not ionize and therefore do not show acidic behaviour.
(b) उदासीनीकरण अभिक्रिया क्या है? एक उदाहरण दीजिए। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – उदासीनीकरण अभिक्रिया वह रासायनिक अभिक्रिया है, जिसमें अम्ल और क्षार आपस में अभिक्रिया करके लवण और जल बनाते हैं।
उदाहरण: HCl (अम्ल) + NaOH (क्षार) → NaCl (लवण) + H2O (जल)
What is neutralization reaction? Give an example.
Answer – A neutralization reaction is a chemical reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water.
Example: HCl (acid) + NaOH (base) → NaCl (salt) + H2O (water)
OR
योग्यता आधारित प्रश्न (Competency Based) :
लोहे की कॉपर सल्फेट विलयन के साथ अभिक्रिया में Fe + CuSO4 → Cu + FeSO4, दी गई टेबल में कौन-सा विकल्प ऑक्सीकृत और अपचायक ऐजेन्ट को सही ढंग से दर्शाता है? (2 Marks)
| विकल्प | पदार्थ ऑक्सीकृत | पदार्थ अपचायक |
| A | Fe | Fe |
| B | Fe | FeSO4 |
| C | Cu | Fe |
| D | CuSO4 | Fe |
उत्तर – विकल्प A
In the reaction of Iron with Copper Sulphate solution (CuSO4) :
Fe + CuSO4 → Cu + FeSO4
Which option in the given table correctly represent the substance oxidized and reducing agent?
| Option | Substance Oxidized | Substance Reduced |
| A | Fe | Fe |
| B | Fe | FeSO4 |
| C | Cu | Fe |
| D | CuSO4 | Fe |
Answer – Option A
18. निम्न अभिक्रिया के लिये पहले शब्द-समीकरण लिखिए तथा उसके बाद संतुलित समीकरण लिखिए, जब : (3 Marks)
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place, when :
(a) तनु सल्फ्यूरिक अम्ल दानेदार जिंक के साथ अभिक्रिया करता है।
उत्तर – जिंक + सल्फ्यूरिक अम्ल → जिंक सल्फेट + हाइड्रोजन
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
Dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
Answer – Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(b) तनु हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल मैग्नीशियम पट्टी के साथ अभिक्रिया करता है।
उत्तर – मैग्नीशियम + हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल → मैग्नीशियम क्लोराइड + हाइड्रोजन
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
Answer – Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) तनु हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल लौह के रेतन के साथ अभिक्रिया करता है।
उत्तर – लौह + हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल → लौह (II) क्लोराइड + हाइड्रोजन
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron fillings.
Answer – Iron + Hdrochloric acid → Iron chloride + Hydrogen
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
19. सोडियम, ऑक्सीजन एवं मैग्नीशियम के लिये इलेक्ट्रॉन बिंदु संरचना लिखिए। (3 Marks)
Write electron dot structure for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
Answer –
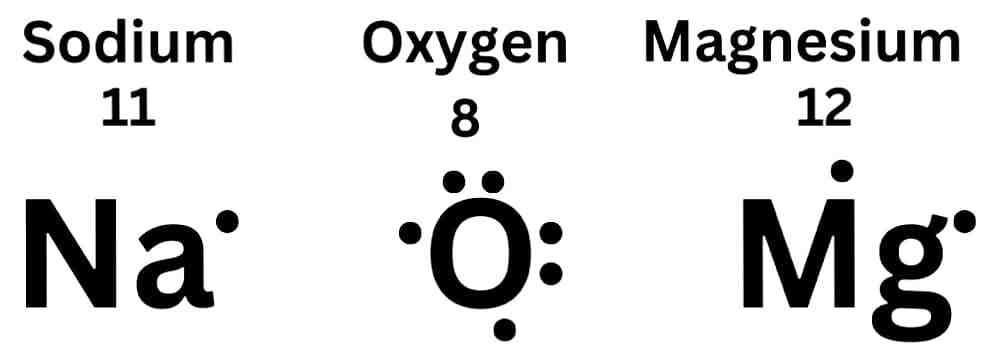
OR
रासायनिक गुणधर्मों के आधार पर धातुओं एवं अधातुओं में कोई तीन अंतर बताइये। (3 Marks)
उत्तर –
| धातु | अधातु |
| 1. धातुएँ क्षारीय ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं। | 1. अधातुएँ अम्लीय या उदासीन ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं। |
| 2. धातुएँ अपचायक होती हैं। | 2. अधातुएँ उपचायक होती हैं। |
| 3. धातुएँ जल (या भाप) से हाइड्रोजन को विस्थापित कर देती हैं। | 3. अधातुएँ जल से या भाप से अभिक्रिया नहीं करती हैं। अतः H2 को जल से विस्थापित नहीं करती हैं। |
| 4. धातुएँ इलेक्ट्रॉन त्याग कर धनात्मक आयन बनाती हैं। | 4. अधातुएँ इलेक्ट्रॉन ग्रहण कर ऋणात्मक आयन बनाती हैं। |
Write any three differences between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Answer –
| Metals | Non-Metals |
| 1. Metals form basic oxides. | 1. Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| 2. Metals are reducing in nature. | 2. Non-metals are oxidising in nature. |
| 3. Metals displace hydrogen from water (or steam). | 3. Non-metals do not react with water (or steam). Therefore, H2 is not displaced from water. |
| 4. Metals lose electrons to form positive ions. | 4. Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. |
20. (a) कार्बन के दो गुणधर्म कौन-से हैं, जिनके कारण हमारे चारों ओर कार्बन यौगिकों की विशाल संख्या दिखाई देती है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – (i) श्रृंखला निर्माण : कार्बन परमाणु आपस में जुड़कर लंबी, शाखित तथा वलयाकार शृंखलाएँ बनाता है।
(ii) चतुष्संयोजकता : कार्बन के चार संयोजक इलेक्ट्रॉन होते हैं, इसलिए यह चार सहसंयोजक बंध बनाता है।
What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer – (i) Catenation : Carbon atoms link with each other to form long chains, branched chains and rings.
(ii) Tetravalency : Carbon has four valence electrons, so it forms four covalent bonds.
(b) भौतिक एवं रासायनिक गुणधर्मों के आधार पर एथेनॉल एवं एथेनोइक अम्ल में आप कैसे अंतर करेंगे? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – भौतिक गुणधर्म :
गंध : एथेनॉल में हल्की मादक गंध होती है, जबकि एथेनोइक अम्ल में सिरके जैसी तीखी गंध होती है।
स्वाद : एथेनॉल का स्वाद कड़वा होता है, जबकि एथेनोइक अम्ल का स्वाद खट्टा होता है।
• रासायनिक गुणधर्म :
लिटमस परीक्षण : एथेनॉल लिटमस पर कोई प्रभाव नहीं डालता, जबकि एथेनोइक अम्ल नीले लिटमस को लाल कर देता है।
सोडियम बाइकार्बोनेट के साथ अभिक्रिया : एथेनॉल के साथ कोई अभिक्रिया नहीं होती, जबकि एथेनोइक अम्ल के साथ CO2 गैस निकलती है।
How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer – Physical properties :
Smell : Ethanol has a pleasant alcoholic smell, whereas ethanoic acid has a strong vinegar-like smell.
Taste : Ethanol has a bitter taste, whereas ethanoic acid has a sour taste.
• Chemical properties :
Litmus test : Ethanol shows no change with litmus paper, whereas ethanoic acid turns blue litmus red.
Reaction with sodium bicarbonate : Ethanol does not react with sodium bicarbonate, whereas ethanoic acid reacts to produce carbon dioxide gas.
OR
(a) हाइड्रोजनीकरण क्या है? इसका औद्योगिक अनुप्रयोग क्या है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – हाइड्रोजनीकरण वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें असंतृप्त कार्बनिक यौगिकों में हाइड्रोजन गैस को निकेल (Ni) उत्प्रेरक की उपस्थिति में मिलाकर उन्हें संतृप्त यौगिकों में परिवर्तित किया जाता है।
हाइड्रोजनीकरण का प्रमुख औद्योगिक उपयोग वनस्पति तेलों को वनस्पति घी (मार्जरीन) में बदलने के लिए किया जाता है।
What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer – Hydrogenation is the process in which hydrogen gas is added to unsaturated organic compounds in the presence of a nickel (Ni) catalyst to convert them into saturated compounds.
The main industrial application of hydrogenation is the conversion of vegetable oils into vanaspati ghee (margarine).
(b) साबुन की सफाई प्रक्रिया की क्रियाविधि समझाइये। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – साबुन की सफाई प्रक्रिया में साबुन के अणु एक लंबी हाइड्रोकार्बन श्रृंखला (कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल भाग) और एक आयनिक सिरा (COO– Na+) रखते हैं, जिससे उनमें एक जलरागी तथा एक जलविरागी सिरा होता है। पानी में घुलने पर ये अणु मिलकर मिसेल नामक गोलाकार संरचना बनाते हैं, जिसमें जलरागी सिरे बाहर पानी की ओर रहते हैं, जबकि जलविरागी पूँछें अंदर की ओर मुड़कर तेल या गंदगी में फँस जाती हैं। इस प्रकार गंदगी मिसेल के भीतर बंद होकर पानी में निलंबित हो जाती है और धुलाई के समय पानी के साथ बह जाती है, जिससे कपड़े साफ हो जाते हैं।
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer – In the cleaning action of soap, soap molecules consist of a long hydrocarbon chain (carboxylic acid part) and an ionic end (COO– Na+), due to which each molecule has one hydrophilic and one hydrophobic end. When soap dissolves in water, the molecules form micelles, with hydrophilic ends facing water and hydrophobic tails embedded in oil or dirt. Thus, the dirt gets trapped inside the micelles, remains suspended in water, and is washed away during rinsing, leaving the clothes clean.
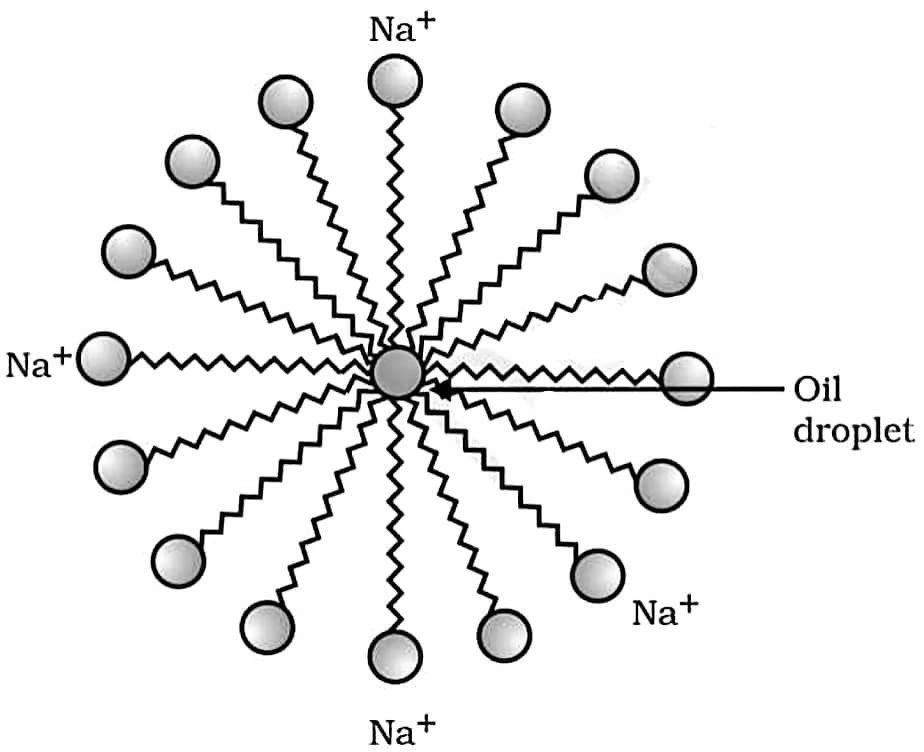
OR
योग्यता आधारित प्रश्न (Competency Based Question) :
नीचे दी गई तालिका स्रोत द्वारा दिये गये संकेत दर्शाती है :
| क्रम संख्या | संकेत |
| 1. | यौगिक “A” का व्यापक रूप में अचार में परिरक्षक के रूप में उपयोग किया जाता है। |
| 2. | “A” एथेनॉल के साथ अभिक्रिया करके मीठी गंध वाला यौगिक “B” बनाता है। |
उपरोक्त संकेतों के आधार पर निम्न प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए :
(i) यौगिक “A” तथा यौगिक “B” को पहचानें। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – यौगिक “A” एथेनोइक अम्ल (एसीटिक अम्ल) है।
यौगिक “B” एथाइल एथेनोएट (एक एस्टर) है, जिसकी गंध मीठी होती है।
(ii) जब यौगिक “A” वाशिंग सोडा के साथ अभिक्रिया करता है, तो कौन-सी गैस उत्पन्न होगी? रासायनिक समीकरण लिखें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – जब यौगिक “A” (एथेनोइक अम्ल) की वाशिंग सोडा (सोडियम कार्बोनेट) से अभिक्रिया होती है, तो कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (CO2) गैस उत्पन्न होती है।
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
(iii) एथेनॉल के दो उपयोग लिखें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – एथेनॉल का उपयोग औषधियों, इत्र और वार्निश में विलायक के रूप में किया जाता है।
एथेनॉल का उपयोग ईंधन के रूप में किया जाता है, जैसे स्पिरिट लैम्प में तथा पेट्रोल के साथ जैव-ईंधन के रूप में।
The table given below shows the hints given by source :
| Sr. No. | Hints |
| 1. | Compound “A” is widely used as preservative in pickles. |
| 2. | “A” reacts with Ethanol to form a sweet smelling compound “B”. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions :
(i) Identify the compound “A” and compound “B”.
Answer – Compound “A” is Ethanoic acid (Acetic acid).
Compound “B” is Ethyl ethanoate (an ester), which has a sweet smell.
(ii) Which gas is produced when compound “A” reacts with washing soda? Write chemical equation.
Answer – When compound “A” (ethanoic acid) reacts with washing soda (sodium carbonate), carbon dioxide (CO2) gas is produced.
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
(iii) Write two uses of Ethanol.
Answer – Ethanol is used as a solvent in medicines, perfumes, and varnishes.
It is also used as a fuel (spirit lamps and blended with petrol as bio-fuel).
SECTION – C
जीव विज्ञान (LIFE SCIENCE)
21. निम्न में से कौन मानव में नर जनन तंत्र का भाग है? (1 Mark)
(A) अंडाशय
(B) गर्भाशय
(C) शुक्रवाहिका
(D) डिंबवाहिनी
उत्तर – (C) शुक्रवाहिका
Which of the following is a part of the male reproductive system in human beings?
(A) Ovary
(B) Uterus
(C) Vas Deferens
(D) Fallopian tube
Answer – (C) Vas Deferens
22. निम्न में से कौन पर्यावरण मित्र नहीं है? (1 Mark)
(A) कागज का लिफाफा
(B) लकड़ी की डण्डी
(C) गुब्बारा
(D) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर – (C) गुब्बारा
Which of the following is not environment friendly?
(A) Paper bag
(B) Wooden stick
(C) Balloon
(D) All of the above
Answer – (C) Balloon
23. क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन (CFC) जैसे रसायन …………… परत को नुकसान पहुँचाते हैं। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – ओजोन परत
Chemicals like CFC harms the ……………. layer.
Answer – Ozone layer
24. कौन-सी ग्रंथि को हॉर्मोन बनाने के लिये आयोडीन की आवश्यकता होती है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – थायरॉयड ग्रंथि
Which gland requires iodine to produce hormones?
Answer – Thyroid gland
25. निम्नलिखित प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं : (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : पादप में तने की वृद्धि का कारण हॉर्मोन होते हैं।
कारण (R) : जिब्बेरेलिन एक पादप हॉर्मोन है, जो तने की वृद्धि में सहायक है।
(A) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(B) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, लेकिन (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(C) (A) सत्य है, लेकिन (R) असत्य है।
(D) (A) असत्य है, लेकिन (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (A) (A) और (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
The question below consists of two statements :
Assertion (A) : Hormones are responsible for the growth of stem in plants.
Reason (R) : Gibberelin is a plant hormone which helps in stem growth.
(A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(B) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(C) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(D) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (A) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
26. प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की क्या भूमिका है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की सीधी भूमिका नहीं होती है। इस प्रकार की क्रिया का नियंत्रण मुख्य रूप से मेरुरज्जु द्वारा किया जाता है, ताकि शरीर किसी अचानक होने वाली उत्तेजना, जैसे गर्म वस्तु को छूने पर, तुरंत प्रतिक्रिया कर सके। मस्तिष्क को इस क्रिया की सूचना बाद में मिलती है, जिससे वह स्थिति को समझ सके और भविष्य में सावधानी बरती जा सके।
What is the role of brain in reflex action?
Answer – In a reflex action, the brain does not play a direct role. The action is mainly controlled by the spinal cord, which enables the body to give an immediate and automatic response to sudden stimuli such as touching a hot object. The brain receives the information afterward to understand the event and help in taking precautions in the future.
OR
हम एक अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता कैसे लगाएंगे? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – हम अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता अपनी नाक में मौजूद घ्राण रिसेप्टर्स की सहायता से लगाते हैं। जब अगरबत्ती जलती है, तो उससे निकलने वाले सुगंधित अणु प्रसरण द्वारा हवा में फैलते हुए नाक में प्रवेश करते हैं। ये अणु घ्राण रिसेप्टर्स को उत्तेजित करते हैं, जिससे तंत्रिका संकेत उत्पन्न होते हैं। ये संकेत मस्तिष्क के अग्र मस्तिष्क तक पहुँचते हैं, जहाँ इन्हें एक विशिष्ट गंध के रूप में पहचाना जाता है।
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti?
Answer – We detect the smell of an agarbatti with the help of olfactory receptors present in our nose. When an agarbatti burns, aromatic molecules released spread through air by diffusion and enter the nose. These molecules stimulate the olfactory receptors, generating nerve impulses. The impulses are transmitted to the forebrain, where they are interpreted as a specific smell.
27. शुक्राशय एवं प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि की क्या भूमिका है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – शुक्राशय शुक्राणुओं के लिए एक पोषक द्रव का स्राव करते हैं, जिसमें मुख्य रूप से फ्रक्टोज होता है। यह द्रव शुक्राणुओं को ऊर्जा प्रदान करता है तथा उनके परिवहन में सहायता करता है।
प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि एक हल्का क्षारीय द्रव स्रावित करती है, जो शुक्राणुओं की गतिशीलता को बढ़ाता है और स्त्री जनन मार्ग के अम्लीय वातावरण से उनकी रक्षा करता है।
इन दोनों ग्रंथियों के स्राव आपस में मिलकर वीर्य का निर्माण करते हैं।
What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer – The seminal vesicles secrete a nutritive fluid rich in fructose, which provides energy to sperms and helps in their transport.
The prostate gland secretes a slightly alkaline fluid that increases sperm mobility and protects sperms from the acidic environment of the female reproductive tract.
The secretions of both glands together form semen.
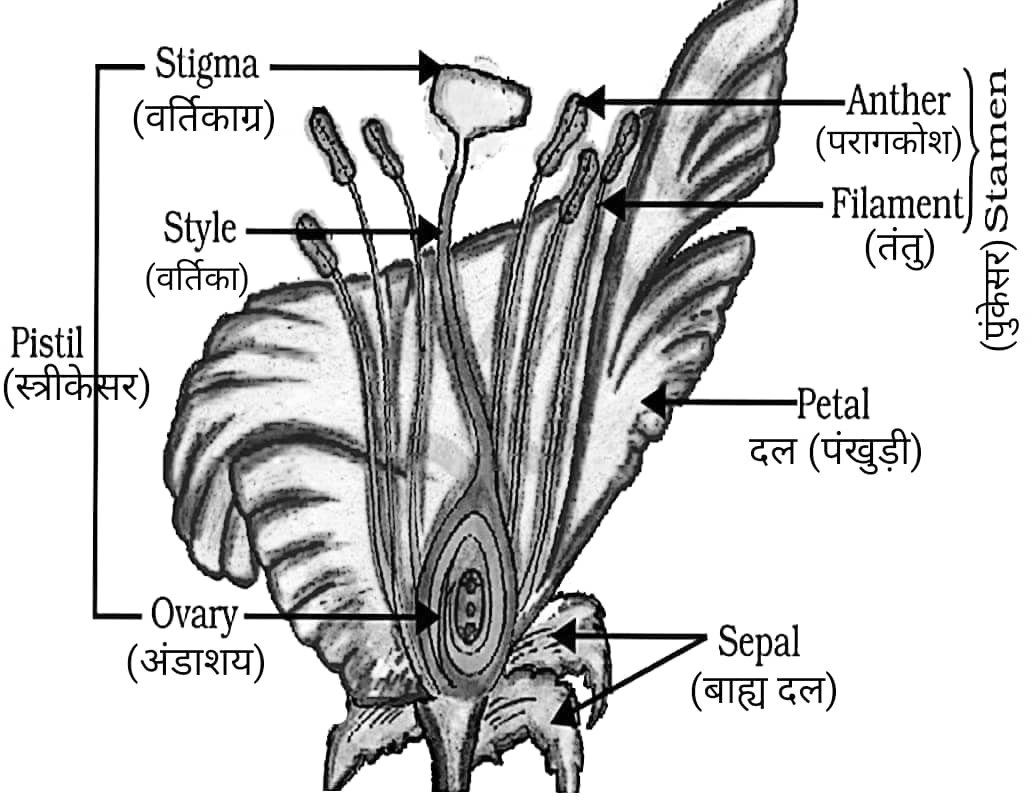
28. पुष्प की अनुदैर्ध्य काट का नामांकित चित्र बनायें। (3 Marks)
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer –
29. मेंडल के प्रयोगों से कैसे पता चलता है कि विभिन्न लक्षण स्वतंत्र रूप से वंशानुगत होते हैं? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – मेंडल के प्रयोगों से यह स्पष्ट होता है कि विभिन्न लक्षण स्वतंत्र रूप से वंशानुगत होते हैं। उन्होंने मटर के पौधों पर द्विलक्षणी संकरण किया, जिसमें एक साथ दो लक्षण, बीज का आकार (गोल / झुर्रीदार) और बीज का रंग (पीला / हरा) का अध्ययन किया। F2 पीढ़ी में उन्हें 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 का अनुपात प्राप्त हुआ, जिसमें कुछ नए लक्षण-संयोजन भी दिखाई दिए जो जनक पीढ़ी में नहीं थे। इससे यह सिद्ध हुआ कि एक लक्षण की वंशागति दूसरे लक्षण को प्रभावित नहीं करती। अतः मेंडल ने निष्कर्ष निकाला कि लक्षण स्वतंत्र वर्गीकरण के नियम के अनुसार वंशानुगत होते हैं।
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer – Mendel showed that traits are inherited independently through his dihybrid cross experiments on pea plants. He studied two traits together, such as seed shape (round / wrinkled) and seed colour (yellow / green). In the F2 generation, he obtained a 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 ratio, including new combinations not present in the parental generation. This proved that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another. Hence, Mendel proposed the Law of Independent Assortment, which states that traits are inherited independently of each other.
OR
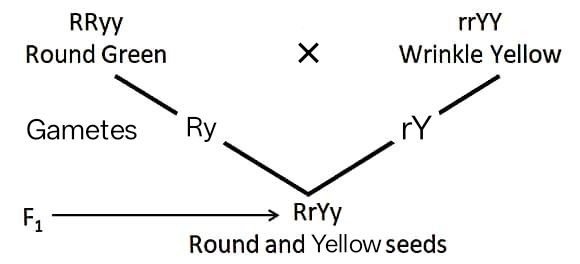
गोल, हरे बीज वाले पौधे का संकरण झुर्रीदार पीले बीज वाले पौधे से कराया गया :
Plant with round, green seeds was crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeds plant :
(a) प्रथम संतति में बीज की आकृति व रंग कैसा होगा? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – गोल, हरे बीज वाले पौधे का संकरण झुर्रीदार, पीले बीज वाले पौधे से कराने पर F1 पीढ़ी में सभी बीज गोल और पीले होंगे, क्योंकि गोल और पीला लक्षण प्रभावी होते हैं।
What will be the shape and colour of seeds in F1 generation?
Answer – When a plant with round, green seeds is crossed with a plant having wrinkled, yellow seeds, all seeds in the F1 generation will be round and yellow, because round shape and yellow colour are dominant traits.
(b) संकरण सचित्र दर्शायें। (1 Mark)
Show the crossing with diagram.
Answer –
30. (a) स्वयंपोषी पोषण एवं विषमपोषी पोषण में क्या अंतर है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर –
| स्वयंपोषी पोषण | विषमपोषी पोषण |
| 1. यह वह पोषण विधि है जिसमें जीव कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और जल जैसे सरल अकार्बनिक पदार्थों से अपना भोजन स्वयं बनाते हैं। | 1. यह वह पोषण विधि है जिसमें जीव अपना भोजन स्वयं नहीं बना सकते और भोजन के लिए अन्य जीवों पर निर्भर रहते हैं। |
| 2. इस पोषण में जीव सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में प्रकाश-संश्लेषण द्वारा भोजन बनाते हैं, इसलिए भोजन के लिए स्वतंत्र होते हैं। | 2. इस पोषण में प्रकाश-संश्लेषण नहीं होता तथा जीव पौधों या अन्य जीवों से भोजन प्राप्त करते हैं। |
| 3. इस प्रकार के जीव उत्पादक कहलाते हैं, जैसे हरे पौधे, शैवाल तथा कुछ जीवाणु। | 3. इस प्रकार के जीव उपभोक्ता कहलाते हैं, जैसे पशु, कवक तथा अन्य गैर-प्रकाशसंश्लेषी जीव। |
What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and heterotrophic nutrition?
Answer –
| Autotrophic Nutrition | Heterotrophic Nutrition |
| 1. It is the mode of nutrition in which organisms prepare their own food from simple inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water. | 1. It is the mode of nutrition in which organisms cannot prepare their own food and depend on other organisms for nourishment. |
| 2. In this mode, organisms prepare food by photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight and therefore are independent for food. | 2. In this mode, photosynthesis does not occur, and organisms obtain food from plants or other organisms. |
| 3. Organisms following this mode of nutrition are called producers, such as green plants, algae, and some bacteria. | 3. Organisms following this mode of nutrition are called consumers, such as animals, fungi, and other non-photosynthetic organisms. |
(b) मानव पाचन तंत्र का चित्र बनाइये। (3 Marks)
Draw the labelled diagram of human digestive system.
Answer –

OR
(a) हमारे आमाशय में अम्ल की क्या भूमिका होती है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – आमाशय में उपस्थित हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल (HCl) भोजन के साथ आने वाले हानिकारक जीवाणुओं को नष्ट करता है तथा भोजन को अम्लीय माध्यम प्रदान करता है, जिससे पाचक एंज़ाइम (जैसे पेप्सिन) सक्रिय होकर प्रोटीन के पाचन में सहायता करते हैं।
What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Answer – The acid present in our stomach, mainly hydrochloric acid (HCl), kills harmful bacteria present in food and provides an acidic medium required for the activation of digestive enzymes like pepsin, which helps in protein digestion.
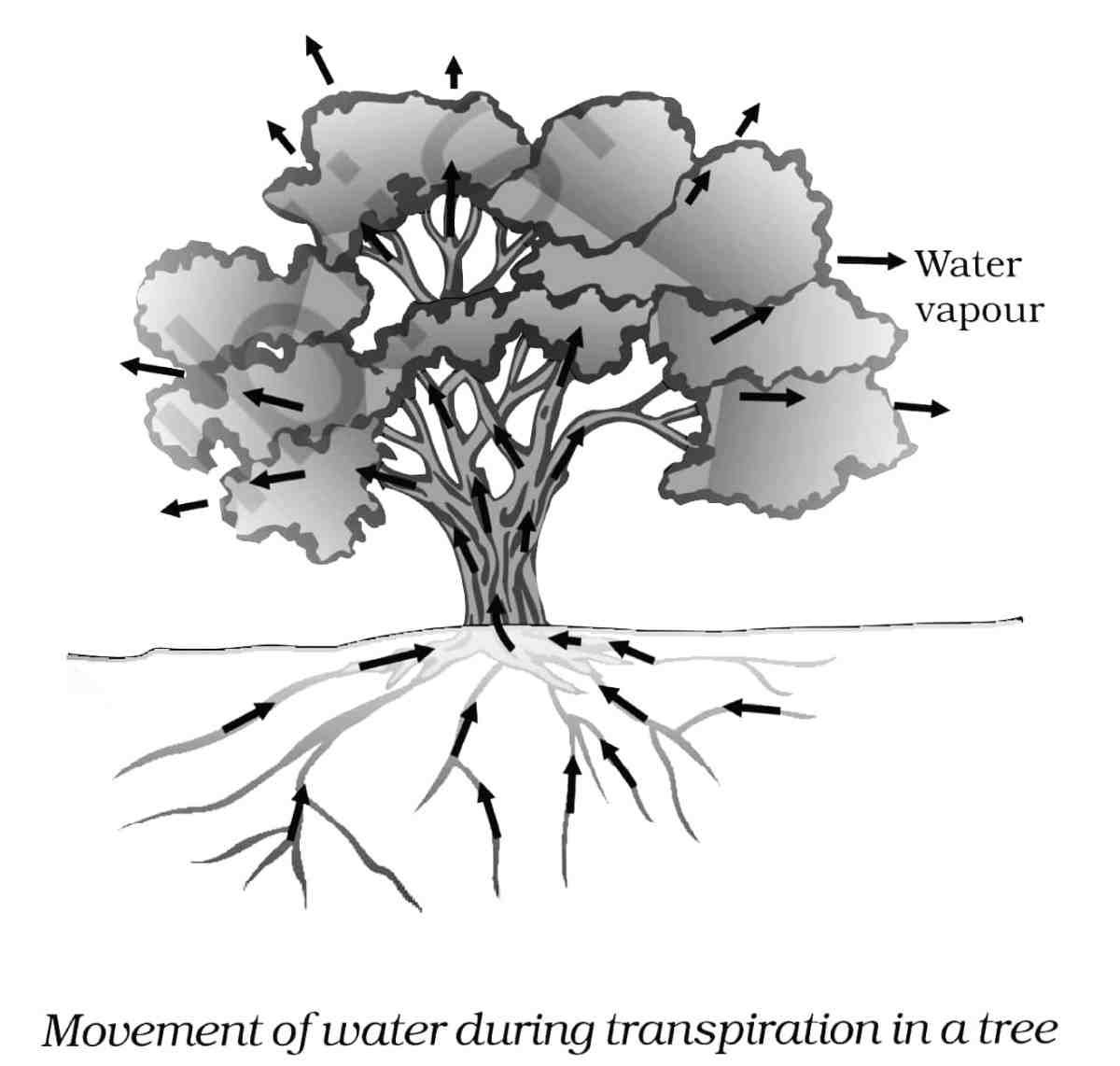
(b) नामांकित चित्र की सहायता से वृक्ष में वाष्पोत्सर्जन के समय जल की गति दर्शाइये। (3 Marks)
Show the movement of water during transpiration in a tree with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer –