Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 10 Science Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. HBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2024. Haryana Board Class 10th Science Solved Question Paper 2024. HBSE Class 10 Question Paper 2024 PDF Download. HBSE Science Solved Question Paper 2024 Class 10. HBSE 10th Science Solved Question Paper 2024. HBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper Download 2024. HBSE Class 10 Science Solved Question Paper 2024.
HBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (Physics)
1. किसी गोलीय दर्पण तथा किसी पतले गोलीय लेंस दोनों की फोकस दूरियाँ –15 सेमी है। दर्पण तथा लेंस संभवतः है : (1 Mark)
(a) दोनों अवतल
(b) दोनों उत्तल
(c) दर्पण अवतल और लेंस उत्तल
(d) दर्पण उत्तल और लेंस अवतल
उत्तर – (a) दोनों अवतल
A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens each have a focal length of –15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be :
(a) both concave
(b) both convex
(c) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex and the lens is concave
Answer – (a) both concave
2. निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा पद विद्युत परिपथ में विद्युत शक्ति को निरूपित नहीं करता? (1 Mark)
(a) I2R
(b) IR2
(c) VI
(d) V2/R
उत्तर – (b) IR2
Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
(a) I2R
(b) IR2
(c) VI
(d) V2/R
Answer – (b) IR2
3. विद्युत धारा का SI मात्रक ……….. है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – एम्पियर
The SI unit of electric current is ………
Answer – Ampere
4. सूर्योदय के समय सूर्य रक्ताभ क्यों प्रतीत होता है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – प्रकाश के प्रकीर्णन के कारण
Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer – Due to scattering of light
5. अभिकथन (A) : कभी-कभी बारिश के मौसम में आसमान में इंद्रधनुष तभी दिखाई देता है, जब पर्यवेक्षक की पीठ सूर्य की ओर होती है। (1 Mark)
कारण (R) : पानी की बूदों में आंतरिक परावर्तन के कारण फैलाव होता है और अंतिम किरणें पीछे की ओर होती हैं।
(a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(b) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, परन्तु (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(c) (A) सत्य है, परन्तु (R) असत्य है।
(d) (A) असत्य है, परन्तु (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
Assertion (A) : A rainbow is sometimes seen in the sky in rainy season only when observer’s back is towards the sun.
Reason (R) : Internal reflection in the water droplets causes dispersion and the final rays are in backward direction.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
6. निम्नलिखित की परिभाषा दीजिए : (2 Marks)
Define the following :
(a) प्रकाश का प्रकीर्णन
उत्तर – प्रकाश का प्रकीर्णन वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा प्रकाश जिस माध्यम से यात्रा करता है उसमें छोटे कणों, अणुओं या अनियमितताओं के साथ संपर्क के कारण दिशा बदल जाती है। इस घटना के कारण प्रकाश फैलता है और विभिन्न दिशाओं में बिखर जाता है।
Scattering of light
Answer – Scattering of light is the process by which light changes direction due to interaction with small particles, molecules, or irregularities in the medium through which it travels. This phenomenon causes light to spread out and scatter in different directions.
(b) वायुमंडलीय अपवर्तन
उत्तर – वायुमंडलीय अपवर्तन, प्रकाश (या किसी विद्युत चुम्बकीय तरंग) का झुकना है क्योंकि यह विभिन्न घनत्वों के साथ पृथ्वी के वायुमंडल की परतों से गुजरता है। यह भिन्नता इसलिए होती है क्योंकि तापमान, दबाव और हवा की संरचना में अंतर के कारण वायुमंडल का अपवर्तनांक ऊंचाई के साथ बदलता है।
Atmospheric refraction
Answer – Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light (or any electromagnetic wave) as it passes through layers of the Earth’s atmosphere with varying densities. This variation occurs because the refractive index of the atmosphere changes with altitude due to differences in air temperature, pressure, and composition.
7. विद्युत लैम्पों के तंतुओं के निर्माण में प्रायः एकमात्र टंगस्टन का ही उपयोग क्यों किया जाता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – टंगस्टन का गलनांक एवं प्रतिरोधकता बहुत अधिक होती है। यह उच्च तापमान पर आसानी से नहीं जलता। बिजली के लैंप बहुत ऊंचे तापमान पर चमकते हैं। इसलिए, टंगस्टन का उपयोग लगभग विशेष रूप से विद्युत लैंप के फिलामेंट के लिए किया जाता है।
Why is tungsten used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps?
Answer – The melting point and resistivity of tungsten are very high. It does not burn readily at a high temperature. The electric lamps glow at very high temperatures. Hence, tungsten is used almost exclusively for filament of electric lamps.
OR
जब कोई विद्युत हीटर विद्युत स्रोत से 4 A विद्युत धारा लेता है, तब उसके टर्मिनलों के बीच विभवांतर 60 V है। उस समय विद्युत हीटर कितनी विद्युत धारा लेगा, जब विभवांतर को 120 V तक बढ़ा दिया जायेगा?
उत्तर – यहां, V = 60 V, I = 4 A
R = V/I = 60/4 = 15 Ω
यदि V’ = 120 V
तो I’ = V’/R = 120/15 = 8 A
The potential difference between the terminals of an electric heater is 60 V, when it draws a current of 4 A from the source. What current will the heater draw if the potential difference is increased to 120 V ?
Answer – Here, V = 60 V, I = 4 A
R = V/I = 60/4 = 15 Ω
If V’ = 120 V
Then I’ = V’/R = 120/15 = 8 A
8. प्रतिरोध क्या है? इसका SI मात्रक बताइए। किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध किन कारकों पर निर्भर करता है? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – प्रतिरोध किसी चालक का वह गुण है जो उसमें से विद्युत धारा के प्रवाह का विरोध करता है। इसे R द्वारा निरूपित किया जाता है और ओम के नियम द्वारा V = IR के रूप में दिया जाता है। प्रतिरोध की SI इकाई ओम (Ω) है। किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध लंबाई, तापमान, अनुप्रस्थ काट के क्षेत्र और पदार्थ की प्रकृति पर निर्भर करता है।
What is resistance? State its SI unit. On which factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
Answer – Resistance is the property of a conductor that opposes the flow of electric current through it. It is denoted by R and is given by Ohm’s Law as V = IR. The SI unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω). The resistance of a conductor depends on length, temperature, area of cross section and nature of material.
9. (a) किसी चुंबकीय क्षेत्र में स्थित विद्युत धारावाही चालक पर आरोपित बल कब अधिकतम होता है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – जब चालक चुंबकीय क्षेत्र के लंबवत होता है।
When is the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
Answer – When the conductor is perpendicular to the magnetic field.
(b) दो चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ एक-दूसरे को प्रतिच्छेद क्यों नहीं करती? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – दो चुंबकीय बल रेखाएं कभी भी एक-दूसरे को नहीं काटती हैं, क्योंकि यदि वे ऐसा करती हैं, तो इसका मतलब यह होगा कि प्रतिच्छेदन के बिंदु पर, एक ही स्थान पर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र की दो अलग-अलग दिशाएं होंगी, जो संभव नहीं है।
Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other?
Answer – Two magnetic lines of force never intersect each other because if they did, it would mean that at the point of intersection, there would be two different directions of the magnetic field at the same location, which is not possible.
OR
भूसंपर्क तार का क्या कार्य है? धातु के आवरण वाले विद्युक्त साधित्रों को भूसंपर्कित करना क्यों आवश्यक है? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – भूसंपर्क तार अतिरिक्त विद्युत धारा को जमीन तक प्रवाहित करने के लिए एक सुरक्षित मार्ग प्रदान करके लोगों को बिजली के झटके से बचाता है। बिजली के झटके और उपकरण को होने वाली क्षति से बचाने के लिए धातु के आवरण वाले विद्युक्त साधित्रों को भूसंपर्कित करना आवश्यक है।
What is the function of an earthwire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Answer – An earth wire protects people from electric shock by providing a safe path for excess electrical current to flow to the ground. It’s necessary to earth metallic appliances to prevent electrical shock and damage to the appliance.
10. (a) प्रकाश का अपवर्तन क्या है? अपवर्तन के नियम लिखिये। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – जब प्रकाश एक पारदर्शी माध्यम से दूसरे पारदर्शी माध्यम में जाता है तो उसकी दिशा में परिवर्तन की घटना को अपवर्तन कहते हैं।
अपवर्तन के नियम : (i) आपतित किरण, अपवर्तित किरण और सतह का अभिलंब आपतन बिंदु पर एक ही तल में होते हैं। (ii) मीडिया के दिए गए जोड़े के लिए आपतन कोण की ज्या और अपवर्तन कोण की ज्या का अनुपात एक स्थिरांक है। इस नियम को स्नेल के अपवर्तन के नियम के रूप में भी जाना जाता है अर्थात sini/sinr = n
What is refraction of light? Write down the laws of refraction.
Answer – The phenomenon of change in the direction of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another is called refraction.
Laws of refraction : (i) The incident ray, refracted ray, and normal to the interface lie in the same plane at the point of incidence. (ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction i.e. sini/sinr = n
(b) हम वाहनों में पश्च दर्पण के रूप में कौन-से दर्पण का उपयोग करते हैं और क्यों? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – उत्तल दर्पण को हम वाहनों में पश्च दर्पण के रूप में उपयोग करते हैं क्योंकि यह व्यापक दृश्य क्षेत्र के साथ दूर की वस्तुओं की सीधी, आभासी और पूर्ण आकार की छोटी छवि देता है।
Which mirror do we use as a rear-view mirror in vehicles and why?
Answer – Convex mirror is used as a rear-view mirror in vehicles because it gives an erect, virtual and full size diminished image of distant objects with a wider field of view.
OR
(a) किसी अवतल लेंस की फोकस दूरी 15 सेमी है। बिंब को लेंस से कितनी दूरी पर रखें कि इसके द्वारा बिंब का लेंस से 10 सेमी दूरी पर प्रतिबिंब बने? (3 Marks)
उत्तर : यहां, f = –15 cm, v = –10 cm
लेंस सूत्र का प्रयोग, 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
1/u = 1/v – 1/f
1/u = 1/(–10) – 1/(–15)
1/u = –1/10 + 1/15
1/u = –1/30
u = – 30 cm
इस प्रकार वस्तु को लेंस से 30 सेमी की दूरी पर रखा जाना चाहिए।
A concave lens has a focal length of 15 cm. At what distance should the object from the lens be placed so that it forms an image at 10 cm from the lens?
Answer : Here, f = –15 cm, v = –10 cm
Using lens formula, 1/f = 1/v – 1/u
1/u = 1/v – 1/f
1/u = 1/(–10) – 1/(–15)
1/u = –1/10 + 1/15
1/u = –1/30
u = – 30 cm
Thus the object should be placed at a distance of 30 cm from the lens.
(b) दर्पण सूत्र लिखिए। (1 Mark)
उत्तर : 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
Write the mirror formula.
Answer : 1/f = 1/v + 1/u
(c) उस दर्पण का नाम बताइए जो बिंब का सीधा तथा आवर्धित प्रतिबिंब बना सके? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – अवतल दर्पण
Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer – Concave mirror
SECTION – B (Chemistry)
11. निम्न में से किसके विलयन का उपयोग दीवारों पर सफेदी करने के लिये किया जाता है? (1 Mark)
(a) सोडियम हाइड्रोक्साइड
(b) कैल्सियम हाइड्रोक्साइड
(c) मैग्निशियम हाइड्रोक्साइड
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर – (b) कैल्सियम हाइड्रोक्साइड
Which of the following solutions was used to white wash walls?
(a) Sodium hydroxide
(b) Calcium hydroxide
(c) Magnesium hydroxide
(d) All of the above
Answer – (b) Calcium hydroxide
12. CaOCl2 का प्रचलित नाम क्या है? (1 Mark)
(a) जिप्सम
(b) विरंजक चूर्ण
(c) बेकिंग सोडा
(d) धावन सोडा
उत्तर – (b) विरंजक चूर्ण
What is the common name of CaOCl2?
(a) Gypsum
(b) Bleaching Powder
(c) Baking Soda
(d) Washing Soda
Answer – (b) Bleaching Powder
13. …………. एक धातु है, जो कमरे के ताप पर द्रव होती है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – मर्करी (पारा)
…………. is a metal, which is a liquid at room temperature.
Answer – Mercury
14. आयनिक यौगिकों का गलनांक उच्च क्यों होता है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – आयनिक यौगिकों का गलनांक उच्च होता है क्योंकि उनके विपरीत आवेशित आयनों के बीच मजबूत इलेक्ट्रोस्टैटिक बलों को तोड़ने के लिए बड़ी मात्रा में ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है।
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Answer – Ionic compounds have high melting points because of the large amount of energy required to break the strong electrostatic forces between their oppositely charged ions.
15. अभिकथन (A) : सफेद सिल्वर क्लोराइड सूरज की रोशनी में ग्रे हो जाता है। (1 Mark)
कारण (R) : सूर्य के प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में सिल्वर क्लोराइड का अपघटन सिल्वर धातु और क्लोरीन गैस बनाने के लिये होता है।
(a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(b) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, परन्तु (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(c) (A) सत्य है, परन्तु (R) असत्य है।
(d) (A) असत्य है, परन्तु (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
Assertion (A) : White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight.
Reason (R) : Decomposition of silver chloride in presence of sunlight takes place to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
16. विस्थापन अभिक्रिया क्या है? एक उदाहरण दीजिए।
उत्तर – विस्थापन प्रतिक्रिया एक रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया है जिसमें अधिक प्रतिक्रियाशील तत्व अपने यौगिक से कम प्रतिक्रियाशील तत्व को विस्थापित करता है। विस्थापन प्रतिक्रियाओं में धातु और अधातु दोनों भाग लेते हैं।
जैसे: Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
What is displacement reaction? Give an example.
Answer – Displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound. Both metals and non-metals take part in displacement reactions.
e.g. Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
17. जल की अनुपस्थिति में अम्ल का व्यवहार अम्लीय क्यों नहीं होता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – जल की अनुपस्थिति में अम्ल का व्यवहार अम्लीय नहीं होता क्योंकि उन्हें आयनित करने और हाइड्रोजन आयन (H+) छोड़ने के लिए पानी की आवश्यकता होती है, जो उनके अम्लीय गुणों के लिए जिम्मेदार हैं। जल के बिना, यह आयनीकरण नहीं होता है, और एसिड H+ आयन नहीं छोड़ सकता है, जिसका अर्थ है कि यह अम्लीय व्यवहार प्रदर्शित नहीं करता है।
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer – Acids do not show acidic behavior in the absence of water because they need water to ionize and release hydrogen ions (H+), which are responsible for their acidic properties. Without water, this ionization does not occur, and the acid cannot release H+ ions, meaning it does not exhibit acidic behavior.
18. आपके पास दो विलयन ‘A’ व ‘B’ हैं। विलयन ‘A’ के pH का मान 6 है एवं विलयन ‘B’ के pH का मान 8 है। किस विलयन में हाइड्रोजन आयन की सांद्रता अधिक हैं? इनमें से कौन अम्लीय है तथा कौन क्षारकीय? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – विलयन ‘A’ में हाइड्रोजन आयन की सांद्रता अधिक है। विलयन ‘A’ अम्लीय है और विलयन ‘B’ क्षारकीय है।
You have two solutions ‘A’ and ‘B’. The pH of solution ‘A’ is 6 and pH of solution ‘B’ is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of these is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer – Solution ‘A’ has more hydrogen ion concentration. Solution ‘A’ is acidic and solution ‘B’ is basic.
19. रासायनिक गुणधर्मों के आधार पर धातुओं एवं अधातुओं में विभेद कीजिए।
उत्तर –
| धातु | अधातु |
| 1. धातुएँ क्षारीय ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं। | 1. अधातुएँ अम्लीय या उदासीन ऑक्साइड बनाती हैं। |
| 2. धातुएँ तनु HCI या तनु H2SO4 से अभिक्रिया कर H2 गैस मुक्त करती हैं, क्योंकि हाइड्रोजन को विस्थापित कर देती हैं। | 2. अधातुएँ तनु HCI या तनु H2SO4 से अभिक्रिया नहीं करती हैं, क्योंकि हाइड्रोजन को विस्थापित नहीं करती हैं। |
| 3. धातुएँ अपचायक होती हैं। | 3. अधातुएँ उपचायक होती हैं। |
| 4. धातुएँ जल (या भाप) से हाइड्रोजन को विस्थापित कर देती हैं। | 4. अधातुएँ जल से या भाप से अभिक्रिया नहीं करती हैं। अतः H2 को जल से विस्थापित नहीं करती हैं। |
| 5. धातुएँ इलेक्ट्रॉन त्याग कर धनात्मक आयन बनाती हैं। | 5. अधातुएँ इलेक्ट्रॉन ग्रहण कर ऋणात्मक आयन बनाती हैं। |
| 6. सभी धातुएँ H2 से संयोग कर हाइड्राइड नहीं बनाती हैं। | 6. सभी अधातुएँ H2 से संयोग कर हाइड्राइड बनाती हैं। |
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of chemical properties.
Answer –
| Metals | Non-Metals |
| 1. Metals form basic oxides. | 1. Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| 2. Metals react with diluted HCI or dilute H2SO4 to release H2 gas, as they displace hydrogen. | 2. Non-metals do not react with dilute HCI or dilute H2SO4, because they do not displace hydrogen. |
| 3. Metals are reducing in nature. | 3. Non-metals are oxidising in nature. |
| 4. Metals displace hydrogen from water (or steam). | 4. Non-metals do not react with water (or steam). Therefore, H2 is not displaced from water. |
| 5. Metals lose electrons to form positive ions. | 5. Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions. |
| 6. Not all metals combine with H2 to form hydrides. | 6. All non-metals combine with H2 to form hydrides. |
OR
उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड क्या होते हैं? दो उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइडों का उदाहरण दीजिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड धातु ऑक्साइड होते हैं जो अम्ल और क्षार दोनों के साथ प्रतिक्रिया करके पानी और लवण उत्पन्न कर सकते हैं। इनमें अम्लीय और क्षारीय दोनों गुण होते हैं। जैसे: Al2O3, ZnO
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer – Amphoteric oxides are metal oxides that can react with both acids and bases to produce water and salts. They have both acidic and basic properties. e.g. Al2O3, ZnO
20. (a) एथेनॉल से एथेनॉइक अम्ल में परिवर्तन को ऑक्सीकरण अभिक्रिया क्यों कहते हैं? अभिक्रिया भी लिखिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – एथेनॉल का एथेनॉइक एसिड में रूपांतरण एक ऑक्सीकरण प्रतिक्रिया माना जाता है क्योंकि इस प्रक्रिया के दौरान, एथेनॉल अणु में एक ऑक्सीजन परमाणु जोड़ा जाता है, जो ऑक्सीकरण प्रतिक्रिया की परिभाषित विशेषता है। रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया है:
CH3CH2OH + [O] (ऑक्सीकरण एजेंट) → CH3COOH + H2O
Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction? Write the reaction also.
Answer – The conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid is considered an oxidation reaction because during this process, an oxygen atom is added to the ethanol molecule, which is the defining characteristic of an oxidation reaction. The chemical reaction is:
CH3CH2OH + [O] (oxidizing agent) → CH3COOH + H2O
(b) समजातीय श्रेणी क्या है? उदाहरण के साथ समझाइए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – समजातीय श्रेणी समान सामान्य सूत्र और समान रासायनिक और भौतिक गुणों वाले कार्बनिक यौगिकों का एक समूह है। एक समजातीय श्रेणी में यौगिक एक पैरामीटर द्वारा एक दूसरे से भिन्न होते हैं, आमतौर पर मेथिलीन –CH2 समूह। जैसे: मीथेन, ईथेन।
What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer – A homologous series is a group of organic compounds with the same general formula and similar chemical and physical properties. The compounds in a homologous series differ from each other by a single parameter, usually a methylene –CH2 group. e.g. methane, ethane.
OR
(a) इलेक्ट्रॉन बिन्दु संरचना बनाइये : (3 Marks)
Draw the electron dot structures for :
(i) Ethanoic acid
Answer –

(ii) H2S
Answer –

(iii) Propanone
Answer –

(b) कार्बन एवं उसके यौगिकों का उपयोग अधिकतर अनुप्रयोगों में ईंधन के रूप में क्यों किया जाता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – कार्बन एवं उसके यौगिकों का उपयोग अधिकतर अनुप्रयोगों में ईंधन के रूप में किया जाता है क्योंकि जलने पर वे बड़ी मात्रा में गर्मी और प्रकाश पैदा करते हैं और उनका कैलोरी मान उच्च होता है। इन्हें संभालना भी आसान है और इनका दहन नियंत्रित होता है।
Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer – Carbon and its compounds are used as fuels because they produce a large amount of heat and light when burned, and have high calorific values. They are also easy to handle and have a controlled combustion.
SECTION – C (Biology)
21. निम्न में से कौन आहार श्रृंखला का निर्माण करते हैं? (1 Mark)
(a) घास, गेहूँ तथा आम
(b) घास, बकरी तथा मानव
(c) बकरी, गाय तथा हाथी
(d) घास, मछली तथा बकरी
उत्तर – (b) घास, बकरी तथा मानव
Which of the following constitute a food chain?
(a) Grass, Wheat and Mango
(b) Grass, Goat and Human
(c) Goat, Cow and Elephant
(d) Grass, Fish and Goat
Answer – (b) Grass, Goat and Human
22. निम्न में से कौन मानव में नर जनन तंत्र का भाग है? (1 Mark)
(a) अंडाशय
(b) गर्भाशय
(c) शुक्रवाहिका
(d) डिंबवाहिनी
उत्तर – (c) शुक्रवाहिका
Which of the following is a part of male reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopean tube
Answer – (c) Vas deferens
23. वायुमंडल में ओजोन परत के क्षय का मुख्य कारक ………… का बढ़ना है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – क्लोरोफ्लोरोकार्बन
The main reason for the loss of ozone layer in atmosphere is the increase in ………..
Answer – Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
24. मानव में अवटु ग्रंथि द्वारा थायरॉक्सिन के संश्लेषण के लिये क्या अनिवार्य है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – आयोडीन
What is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine by the thyroid gland in human?
Answer – Iodine
25. अभिकथन (A) : विभिन्न जीवन प्रक्रियाओं को पूरा करने के लिये ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है। (1 Mark)
कारण (R) : माइटोकांड्रिया में ऊर्जा एटीपी के रूप में प्राप्त होती है।
(a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
(b) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं, परन्तु (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं है।
(c) (A) सत्य है, परन्तु (R) असत्य है।
(d) (A) असत्य है, परन्तु (R) सत्य है।
उत्तर – (a) (A) व (R) दोनों सत्य हैं तथा (R), (A) की सही व्याख्या है।
Assertion (A) : Energy is required to carry out different life processes.
Reason (R) : Energy is obtained in the form of ATP in the mitochondria.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
(d) (A) is false, but (R) is true.
Answer – (a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
26. ऐसे पादप हार्मोन का नाम बतायें, जो : (2 Marks)
Name such plant hormone, which :
(a) कोशिका विभाजन को प्रेरित करता है
उत्तर – साइटोकाइनिन
Induces cell division
Answer – Cytokinin
(b) वृद्धि का संदमन करता है
उत्तर – एब्सिसिक अम्ल
Inhibits growth
Answer – Abscisic acid
27. मानव में वृषण के क्या कार्य हैं? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – मनुष्य में वृषण दो मुख्य कार्य करते हैं: शुक्राणु उत्पादन और टेस्टोस्टेरोन उत्पादन।
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
Answer – The testis in human beings perform two main functions: sperm production & testosterone production.
28. पुष्प की अनुदैर्ध्य काट का नामांकित चित्र बनायें। (3 Marks)
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer –

29. मेंडल के प्रयोगों से कैसे पता चला कि विभिन्न लक्षण स्वतंत्र रूप से वंशानुगत होते हैं?
उत्तर – मटर के पौधों के साथ मेंडल के प्रयोगों से पता चला कि लक्षण पृथक्करण और स्वतंत्र वर्गीकरण की प्रक्रिया के माध्यम से स्वतंत्र रूप से विरासत में मिले हैं। उन्होंने लंबे और छोटे जैसे अलग-अलग लक्षणों वाले मटर के पौधों को क्रॉस किया और देखा कि संतानों को प्रत्येक गुण के लिए प्रत्येक माता-पिता से एक एलील विरासत में मिला है। इसे पृथक्करण के नियम के रूप में जाना जाता है। फिर उन्होंने दो अलग-अलग लक्षणों, जैसे कि बीज का रंग और बीज के आकार, के साथ मटर के पौधों को क्रॉस किया और देखा कि एक गुण की विरासत दूसरे लक्षण की विरासत को प्रभावित नहीं करती है। इसे स्वतंत्र वर्गीकरण के नियम के रूप में जाना जाता है। कुल मिलाकर, मेंडल के प्रयोगों से पता चला कि लक्षण एक-दूसरे से स्वतंत्र रूप से विरासत में मिले हैं, जिसे अब स्वतंत्र वर्गीकरण के सिद्धांत के रूप में जाना जाता है।
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits are inherited independently?
Answer – Mendel’s experiments with pea plants showed that traits are inherited independently through the process of segregation and independent assortment. He crossed pea plants with different traits, such as tall and short, and observed that the offspring inherited one allele from each parent for each trait. This is known as the law of segregation. Then he crossed pea plants with two different traits, such as seed color and seed shape, and observed that the inheritance of one trait did not affect the inheritance of the other trait. This is known as the law of independent assortment. Overall, Mendel’s experiments demonstrated that traits are inherited independently of each other, which is now known as the principle of independent assortment.
OR
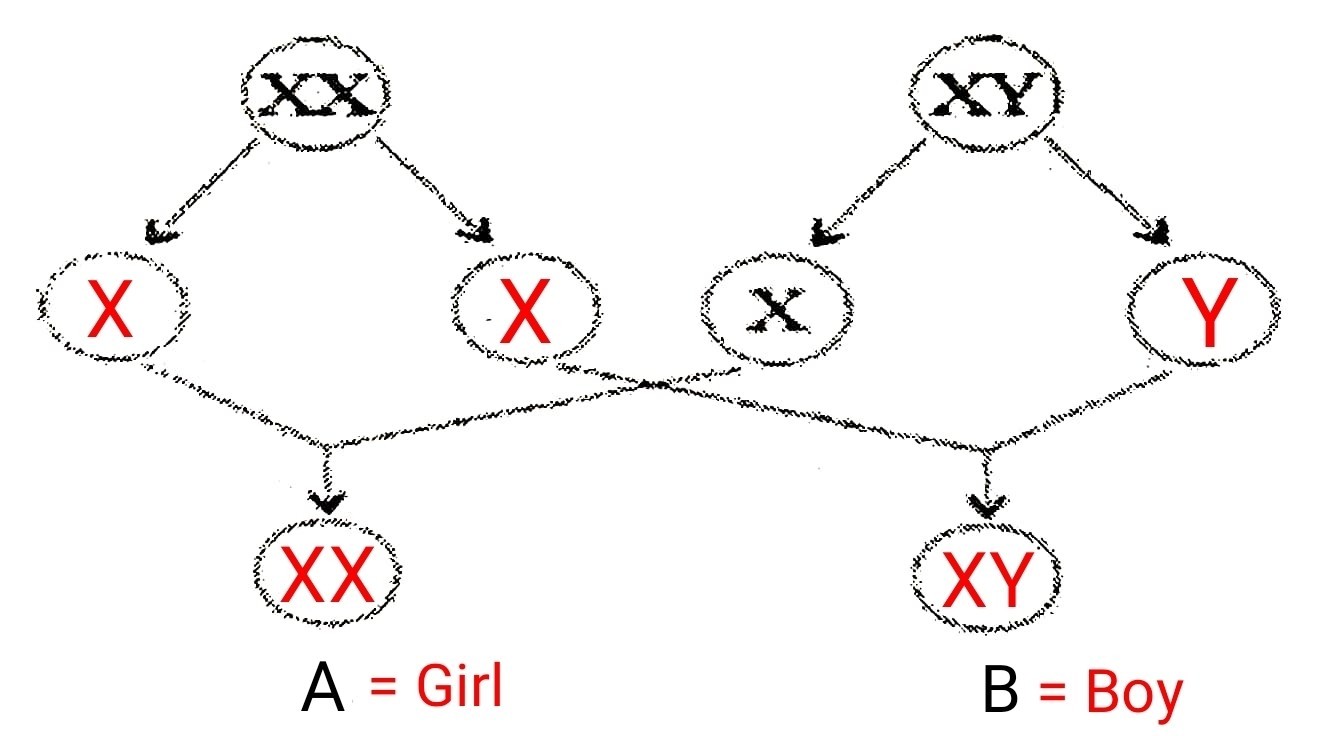
मानव में बच्चे का लिंग निर्धारण कैसे होता है? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – मनुष्य में लिंग का निर्धारण विशिष्ट लिंग गुणसूत्रों के आधार पर होता है। पुरुषों में XY गुणसूत्र होते हैं और महिलाओं में XX गुणसूत्र होते हैं। इससे स्पष्ट है कि स्त्री में Y गुणसूत्र नहीं होता। जब नर-मादा संयोजन से संतान उत्पन्न होती है, तो मादा किसी भी अवस्था में नर शिशु पैदा करने में सक्षम नहीं हो सकती है क्योंकि नर शिशु में XY गुणसूत्र होना आवश्यक है। निषेचन में, यदि पुरुष का X गुणसूत्र महिला के X गुणसूत्र के साथ जुड़ जाता है, तो यह एक XX जोड़ी बनाता है अत: संतान लड़की के रूप में होगी। लेकिन जब पुरुष का Y गुणसूत्र महिला के गुणसूत्र X से जुड़ता है तो XY बनता है इससे पुत्र का जन्म होगा।
How is the sex of the child determined in human beings?
Answer – In human beings, sex is determined on the basis of specific sex chromosomes. Males have XY chromosomes and females have XX chromosomes. It is clear from this that the female does not have the Y chromosome. When offspring are produced by male-female combination, the female may not be able to produce a male infant at any stage because the male infant must have XY chromosomes. In fertilization, if the X chromosome of a man is fused with the X chromosome of the woman, then it will form an XX pair, hence the child will be in the form of a girl. But when a man’s Y chromosome combines with the female’s chromosome X, XY will be formed, this will lead to the birth of a boy.
30. (a) वायवीय और अवायवीय श्वसन के बीच तीन अंतर लिखिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर –
| वायवीय श्वसन | अवायवीय श्वसन |
| 1. जब इस प्रकार का श्वसन होता है तो ऑक्सीजन मौजूद होती है। | 1. इस प्रकार की श्वसन प्रक्रिया में ऑक्सीजन अनुपस्थित होती है। |
| 2. श्वसन के इस रूप में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान होता है। | 2. श्वसन के इस रूप में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान नहीं होता है। |
| 3. यह साइटोप्लाज्म और माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया में पाया जा सकता है। | 3. यह केवल कोशिका द्रव्य में पाया जा सकता है। |
| 4. ग्लूकोज कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और पानी में टूट जाता है। | 4. ग्लूकोज एथिल अल्कोहल, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और ऊर्जा में टूट जाता है। |
| 5. स्तनधारियों जैसे सभी उच्च जीवों में इस प्रकार की श्वसन क्रिया होती है। | 5. निचले जीव जैसे बैक्टीरिया और यीस्ट इस प्रकार का उपयोग करते हैं। अन्य जीवों में यह भारी गतिविधियों के दौरान होता है। |
Write three differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration in human beings.
Answer –
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1. Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. | 1. Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. |
| 2. Gases are exchanged in this form of respiration. | 2. Gases are not exchanged in this form of respiration. |
| 3. It can be found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. | 3. It can be found only in the cytoplasm. |
| 4. Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. | 4. Glucose breaks down into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy. |
| 5. All higher organisms such as mammals have this type of respiration. | 5. Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast use this type. In other organisms, it occurs during heavy activities. |
(b) भोजन के पाचन में लार की क्या भूमिका है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – लार का स्राव जीभ के नीचे स्थित लार ग्रंथियों द्वारा होता है। लार में विशेष एंजाइम होते हैं जो आपके भोजन में मौजूद स्टार्च को पचाने में मदद करते हैं। एमाइलेज़ नामक एंजाइम स्टार्च (जटिल कार्बोहाइड्रेट) को शर्करा में तोड़ देता है, जिसे आपका शरीर अधिक आसानी से अवशोषित कर सकता है।
What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Answer – Saliva is secreted by the salivary glands located under the tongue. Saliva contains special enzymes that help digest the starches in your food. An enzyme called amylase breaks down starches (complex carbohydrates) into sugars, which your body can more easily absorb.
OR
(a) मानव पाचन तंत्र का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए। (3 Marks)
Draw a well labelled diagram of the human digestive system.
Answer –

(b) स्वपोषी पोषण के लिये आवश्यक परिस्थितियाँ कौन-सी हैं? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – स्वपोषी पोषण वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा जीव अकार्बनिक पदार्थों से अपना भोजन स्वयं बनाते हैं। इस प्रक्रिया को प्रकाश संश्लेषण कहा जाता है। कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, जल, क्लोरोफिल वर्णक और सूर्य का प्रकाश स्वपोषी पोषण के लिए आवश्यक आवश्यक शर्तें हैं। कार्बोहाइड्रेट (भोजन) और O2 प्रकाश संश्लेषण के उप-उत्पाद हैं।
What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition?
Answer – Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which organisms make their own food from inorganic materials. The process is called photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll pigment, and sunlight are the necessary conditions required for autotrophic nutrition. Carbohydrates (food) and O2 are the by-products of photosynthesis.
