Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. HBSE Class 10 Mathematics Question Paper 2024. Haryana Board Class 10th Math Solved Question Paper 2024. HBSE Class 10 Question Paper 2024 PDF Download. HBSE Maths Solved Question Paper 2024 Class 10. HBSE 10th Mathematics Solved Question Paper 2024. HBSE Class 10 Mathematics Question Paper Download 2024. HBSE Class 10 Maths Solved Question Paper 2024.
HBSE Class 10 Maths (Basic) Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (1 Mark)
1. 72 और 120 का म० स० अ० (HCF) है :
The HCF of 72 and 120 is :
(a) 12
(b) 24
(c) 36
(d) 72
Answer : (b) 24
72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
HCF = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 = 24
2. निम्नलिखित में कौन-सी अपरिमेय संख्या है?
Which of the following is an irrational number?
(a) √36
(b) √25
(c) 6√3
(d) 5√4
Answer : (c) 6√3
3. द्विघात बहुपद 2x2 – 8x + 6 के शून्यकों का योगफल होगा :
The sum of zeroes of quadratic polynomial 2x2 – 8x + 6 will be :
(a) 4
(b) –4
(c) 3
(d) 1/3
Answer : (a) 4
α + β = –b/a = –(–8)/2 = 4
4. A.P. 3, 1, –1, 3 …….. का सार्व अंतर ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the common difference of the A.P. 3, 1, –1, –3, ……..
Answer : d = 1 – 3 = –2
5. निम्नलिखित में से द्विघात समीकरण कौन-सी है?
Which of the following is a quadratic equation?
(a) (x + 1)2 = 2(x – 3)
(b) (x – 2)(x + 1) = (x – 1)(x + 3)
(c) (x + 2)3 = 2x(x2 – 1)
(d) x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2
Answer : (a) (x + 1)2 = 2(x – 3)
x2 + 2x + 1 = 2x – 6
x2 + 2x – 2x + 1 + 6 = 0
x2 + 7 = 0
6. बिन्दुओं (–2, 7) और (4, 3) को मिलाने वाले रेखाखण्ड का मध्य बिन्दु है :
Coordinates of mid point of line joining two points (–2, 7) and (4, –3) is :
(a) (–1, –2)
(b) (–2, –4)
(c) (2, 4)
(d) (1, 2)
Answer : (d) (1, 2)
Here x1 = –2, y1 = 7, x2 = 4, y2 = –3
Coordinates of mid point M(x, y) is [(x1+x2)/2, (y1+y2)/2] = [(–2+4)/2, (7–3)/2] = (1, 2)
7. सभी वर्ग ………. होते हैं। (समरूप, सर्वांगसम)
All squares are ………… (Similar, Congruent)
Answer : Similar
8. वृत्त के किसी बिन्दु पर स्पर्श रेखा, स्पर्श बिन्दु से जाने वाली त्रिज्या के बीच का कोण होता है :
The tangent at any point of a circle makes an angle to the radius through the point of contact is :
(a) 180°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 60°
Answer : (c) 90°
9. किसी वृत्त की स्पर्श रेखा उसे कितने बिन्दुओं पर स्पर्श करती है?
At how many points a tangent to a circle intersect it?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) Infinite
Answer : (a) 1
10. sin60°sec30° का मान होगा :
The value of sin60°sec30° will be :
(a) √3/4
(b) 3/2
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer : (c) 1
sin60°sec30° = √3/2 × 2/√3 = 1
11. यदि tanθ = 4/3 हो, तो sinθ का मान होगा :
If tanθ = 4/3, then the value of sinθ will be :
(a) 3/4
(b) 3/5
(c) 5/3
(d) 4/5
Answer : (d) 4/5
tanθ = P/B = 4/3
P = 4, B = 3, H = √P2+B2 = √42+32 = √16+9 = √25 = 5
sinθ = P/H = 4/5
12. 9 sec2A – 9 tan2A बराबर है :
9 sec2A – 9 tan2A is equals to :
(a) –9
(b) 9
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer : (b) 9
9 sec2A – 9 tan2A = 9(sec2A – tan2A) = 9(1) = 9
13. वृत्त की परिधि और व्यास का अनुपात है :
The ratio of circumference to diameter is :
(a) π : 1
(b) 2π : 1
(c) π : r
(d) 1 : π
Answer : (a) π : 1
Circumference : Diameter = 2πr : 2r = π : 1
14. किसी वृत्त के त्रिज्याखण्ड का क्षेत्रफल जिसकी त्रिज्या 6 सेमी और कोण 30° है, होगा :
Area of the sector of a circle with radius 6 cm and angle 30° will be :
(a) 2π cm2
(b) 7π cm2
(c) 3π cm2
(d) 5π cm2
Answer : (c) 3π cm2
Area of sector of a circle = θ/360° × πr2 = 30°/360° × π(6)2 = 3π cm2
15. गोले का पृष्ठीय क्षेत्रफल जिसकी त्रिज्या 3 सेमी है, होगा :
The surface area of sphere whose radius is 3 cm, will be :
(a) 3/4π cm2
(b) 4/3π cm2
(c) 18π cm2
(d) 36π cm2
Answer : (d) 36π cm2
Surface area of sphere = 4πr2 = 4π(3)2 = 36π cm2
16. निम्नलिखित बारंबारता बंटन का बहुलक वर्ग होता है :
The modal class for the following frequency distribution :
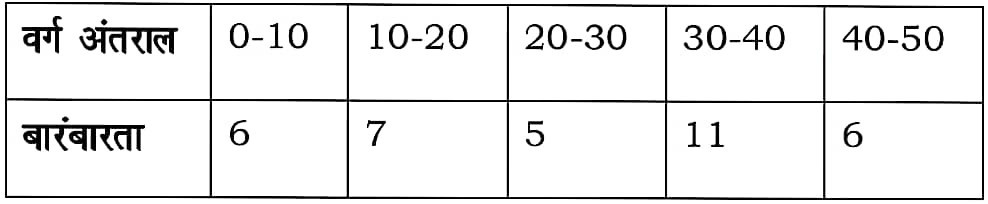
(a) 0-10
(b) 40-50
(c) 30-40
(d) 10-20
Answer : (c) 30-40
17. केन्द्रीय प्रवृत्ति के मापकों में एक आनुभविक सम्बन्ध क्या है?
(a) 3 माध्यक = बहुलक + 2 माध्य
(b) माध्यक = 3 बहुलक + 2 माध्य
(c) माध्यक = 2 बहुलक + 3 माध्य
(d) 3 माध्यक = बहुलक – 2 माध्य
उत्तर : (a) 3 माध्यक = बहुलक + 2 माध्य
What is the empirical relationship between the three measures of central tendency?
(a) 3 Median = Mode + 2 Mean
(b) Median = 3 Mode + 2 Mean
(c) Median = 2 Mode + 3 Mean
(d) 3 Median = Mode – 2 Mean
Answer : (a) 3 Median = Mode + 2 Mean
18. यदि P(E) = 0.07 है, तो P(E नहीं) का मान होगा :
If P(E) = 0.07, then P(not E) will be :
(a) 0.7
(b) 0.3
(c) 0.03
(d) 0.93
Answer : (d) 0.93
P(E) + P(not E) = 1
P(not E) = 1 – P(E) = 1 – 0.07 = 0.93
19. अभिकथन (A) : 5 एक परिमेय संख्या है।
तर्क (R) : सभी धनात्मक पूर्णांकों के वर्गमूल अपरिमेय संख्याएँ हैं।
(a) अभिकथन (A) और तर्क (R) दोनों सही हैं और तर्क (R) अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या करता है।
(b) अभिकथन (A) और तर्क (R) दोनों सही हैं और तर्क (R) अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं करता है।
(c) अभिकथन (A) सही है, लेकिन तर्क (R) गलत है।
(d) अभिकथन (A) गलत है, लेकिन तर्क (R) सही है।
उत्तर : (c) अभिकथन (A) सही है, लेकिन तर्क (R) गलत है।
Assertion (A) : 5 is a rational number.
Reason (R) : The square root of all positive integers is an irrational number.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer : (c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
20. अभिकथन (A) : बिन्दुओं (1, –3) और (4, 1) के बीच की दूरी 5 इकाई है।
तर्क (R) : बिन्दु A(x1, y1) और B(x2, y2) के बीच की दूरी, AB = √(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2
(a) अभिकथन (A) और तर्क (R) दोनों सही हैं और तर्क (R) अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या करता है।
(b) अभिकथन (A) और तर्क (R) दोनों सही हैं और तर्क (R) अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं करता है।
(c) अभिकथन (A) सही है, लेकिन तर्क (R) गलत है।
(d) अभिकथन (A) गलत है, लेकिन तर्क (R) सही है।
उत्तर : (a) अभिकथन (A) और तर्क (R) दोनों सही हैं और तर्क (R) अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या करता है।
Assertion (A) : The distance between points (1, –3) and (4, 1) is 5 units.
Reason (R) : The distance between A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) is AB = √(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer : (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is correct explanation of Assertion (A).
SECTION – B (2 Marks)
21. k के किस मान के लिए, निम्न रैखिक समीकरणों के युग्म अपरिमित रूप से अनेक हल होंगे?
For what values of k will the following pair of linear equations have infinitely many solutions?
kx + 3y – (k–3) = 0
12x + ky – k = 0
Answer : Equations have infinitely many solutions
a1/a2 = b1/b2 = c1/c2
k/12 = 3/k = –(k–3)/(–k)
k2 = 36
k = ±6
22. आकृति में DE || BC है। AD ज्ञात कीजिए।
In Fig. DE || BC, then find AD.
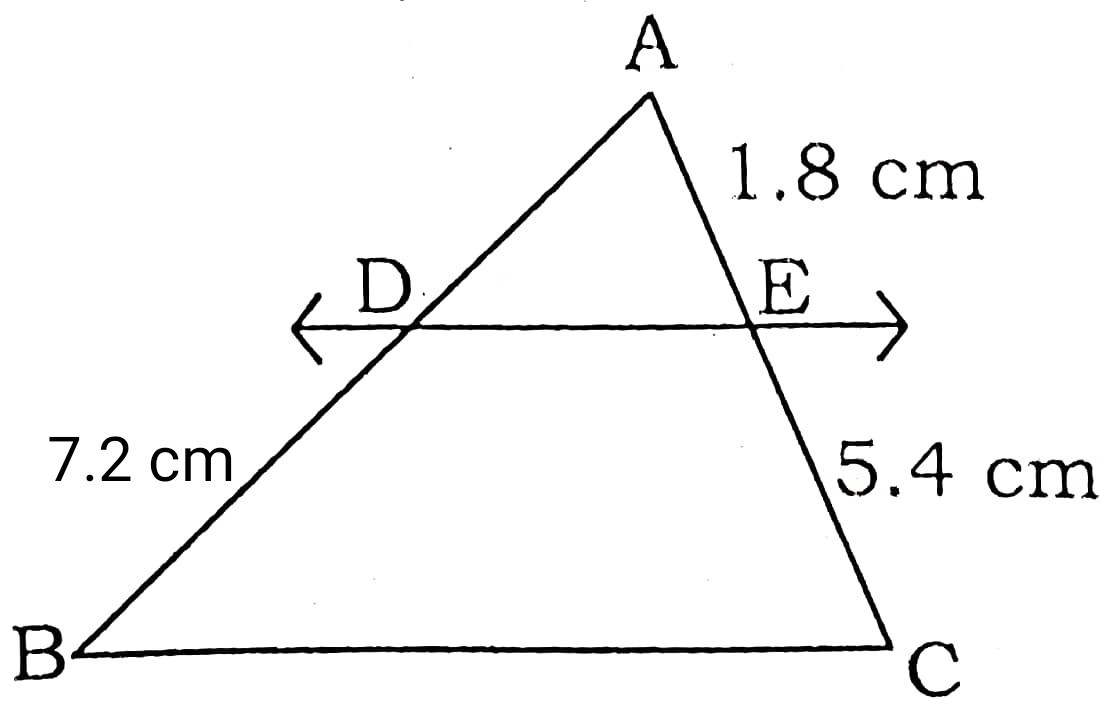
Answer : By basic proportionality theorem which states that if a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio.
AD/DB = AE/EC
AD/7.2 = 1.8/5.4
AD = 2.4 cm
23. एक बिन्दु A से, जो एक वृत्त के केन्द्र से 5 सेमी दूरी पर है, वृत्त पर स्पर्श रेखा की लंबाई 4 सेमी है। वृत्त की त्रिज्या ज्ञात कीजिए।
The length of a tangent from a point A at distance 5 cm from the centre of the circle is 4 cm. Find the radius of the circle.
Answer :
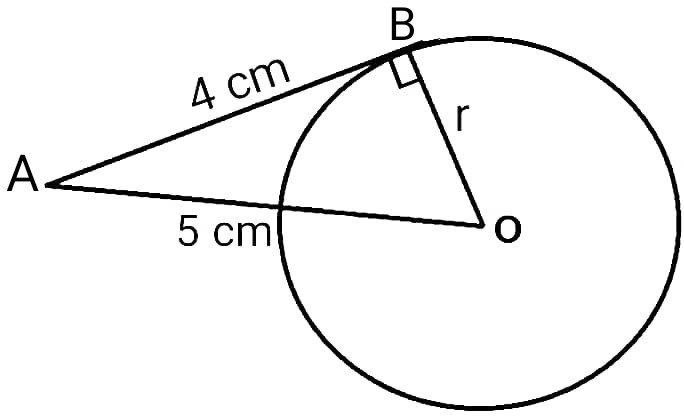
Here AO = 5 cm, AB = 4 cm, ∠ABO = 90° (BO⊥AB)
Using Pythagoras theorem, H2 = P2 + B2
AO2 = AB2 + BO2
BO2 = AO2 – AB2
BO2 = 52 – 42
BO2 = 25 – 16
BO2 = 9
BO = √9
BO = 3 cm
Radius of circle (BO) = 3 cm
24. यदि sin(A – B) = 1/2, cos(A + B) = 1/2, 0° < A + B ≤ 90°, A > B, तो A और B ज्ञात कीजिए।
If sin(A – B) = 1/2, cos(A + B) = 1/2, 0° < A + B ≤ 90°, A > B, then find the value of A and B.
Answer :
sin(A – B) = 1/2 = sin30°
A – B = 30° ………(i)
cos(A + B) = 1/2 = cos60°
A + B = 60° ………(ii)
Add eqn.(i) and (ii), we get
2A = 90°
A = 45°
Put A = 45° in eqn.(i), we get
45° – B = 30°
B = 15°
Hence, the value of A = 45° and B = 15°.
OR
यदि tan(A + B) = √3 और tan(A – B) = 1/√3; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°, A > B, तो A और B का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
If tan(A + B) = √3 and tan(A – B) = 1/√3; 0° < A + B ≤ 90°, A > B then find the value of A and B.
Answer :
tan(A + B) = √3 = tan60°
A + B = 60° ………(i)
tan(A – B) = 1/√3 = tan30°
A – B = 30° ………(ii)
Add eqn.(i) and (ii), we get
2A = 90°
A = 45°
Put A = 45° in eqn.(i), we get
45° + B = 60°
B = 15°
Hence, the value of A = 45° and B = 15°.
25. किसी कार के दो वाइपर हैं, परस्पर कभी आच्छादित नहीं होते हैं। प्रत्येक वाइपर की पत्ती की लम्बाई 25 सेमी है और 115° के कोण तक घूमकर सफाई कर सकता है। पत्तियों की प्रत्येक फुहार के साथ जितना क्षेत्रफल साफ हो जाता है, वह ज्ञात कीजिए।
A car has two wipers which do not overlap. Each wiper has a blade of length 25 cm sweeping through an angle of 115°. Find the total area cleaned at each sweep of the blades.
Answer : Total area for both wipers = 2 × Area of each wiper
Area = 2 × θ/360° × πr2 = 2 × 115°/360° × 22/7 × (25)2 = 1254.96 cm2
SECTION – C (3 Marks)
26. सिद्ध कीजिए कि √5 एक अपरिमेय संख्या है।
Prove that √5 is an irrational number.
Answer : Let us assume that √5 is a rational number.
Now √5 = p/q where p and q are co-prime integers and q ≠ 0
p = √5q
Squaring both sides, we get
p2 = 5q2 ……..(i)
5 divides p2, then 5 also divides p
Put p = 5m in eqn.(i),
(5m)2 = 5q2
25m2 = 5q2
5m2 = q2
5 divides q2 then 5 also divides q
Here p, q have a common factor is 5. This contradicts our assumption that they are co-primes. Therefore, p/q is not a rational number
Hence √3 is an irrational number.
27. द्विघात बहुपद 6x2 – 7x – 3 के शून्यक ज्ञात कीजिए और शून्यकों तथा गुणांकों के बीच के संबंध की सत्यता की जाँच कीजिए।
Find the zeroes of quadratic polynomial 6x2 – 7x – 3 and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients.
Answer : Compare 6x2 – 7x – 3 with ax2 + bx + c
Here a = 6, b = –7, c = –3
6x2 – 7x – 3 = 0
6x2 – 9x + 2x – 3 = 0
3x(2x – 3) + 1(2x – 3) = 0
(2x – 3)(3x + 1) = 0
x = 3/2, –1/3
so, α = 3/2 and β = –1/3
α + β = 3/2 – 1/3 = 7/6 = –b/a = –(–7)/6 = 7/6
αβ = 3/2 × 1/3 = –1/2 = c/a = –3/6 = –1/2
Thus, the basic relationships are verified.
28. दो संख्याओं का अंतर 26 है और एक संख्या दूसरी संख्या की तीन गुनी है। उन्हें ज्ञात कीजिए।
The difference between two numbers is 26 and one number is three times the other. Find them.
Answer : Let the two numbers be x and y.
ATQ,
x – y = 26 ……….(i)
x = 3y ……….(ii)
From eqn.(i) and (ii),
3y – y = 26
2y = 26
y = 13
Put y = 13 in eqn.(ii), we get
x = 3y = 3(13) = 39
Therefore x = 39 and y = 13
OR
रैखिक समीकरण युग्म को हल कीजिए :
Solve the pair of linear equations :
3x/2 – 5y/3 = – 2
x/3 + y/2 = 13/6
Answer : Multiply both eqn. by 6 both side,
9x – 10y = –12 ………(i)
2x + 3y = 13 ……….(ii)
Multiply eq.(i) by 2 and multiply eqn.(ii) by 9,
18x – 20y = –24 ……….(iii)
18x + 27y = 117 ………..(iv)
Subtract eqn.(iii) from eqn.(iv), we get
47y = 141
y = 3
Put y = 3 in eqn.(i), we get
9x – 10(3) = –12
9x = –12 + 30
9x = 18
x = 2
Therefore x = 2 and y = 3
29. सिद्ध कीजिए कि बाह्य बिन्दु से वृत्त पर खींची गई स्पर्श रेखाओं की लंबाइयाँ बराबर होती हैं।
Prove that the length of tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal.
Answer :
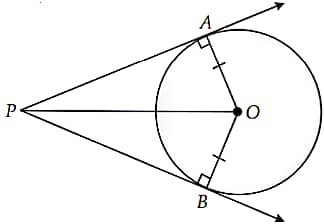
To prove: AP = BP
Construction: Join OP, OA and OB
Proof: In ∆OAP and ∆OBP
OA = OB (Radius of circle)
OP = OP (Common side)
∠OAP = ∠OBP = 90° (Radius ⟂ Tangent)
∆OAP ≅ ∆OBP (RHS congruence rule)
AP = BP (CPCT)
Hence proved.
30. ∆PQR में, जिसका कोण Q समकोण है, PR + QR = 25 सेमी और PQ = 5 सेमी है, तो cosP और tanP का मान ज्ञात कीजिए।
In ∆PQR, right angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the value of cosP tanP.
Answer :
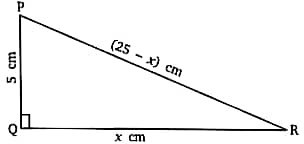
PQ = 5 cm
PR + QR = 25 cm
Let QR = x cm
PR = 25 cm – QR = (25 – x) cm
Using Pythagoras theorem, H2 = P2 + B2
PR2 = PQ2 + QR2
(25 – x)2 = 52 + x2
625 – 50x + x2 = 25 + x2
50x = 600
x = 600/50 = 12
QR = x = 12 cm
PR = 25 – 12 = 13 cm
cosP = Base/Hypotenuse = QP/RP = 5/13
tanP = Perpendicular/Base = QR/PQ = 12/5
OR
सिद्ध कीजिए : (cosecθ – cotθ)2 = (1–cosθ)/(1+cosθ)
Prove that : (cosecθ – cotθ)2 = (1–cosθ)/(1+cosθ)
Answer : RHS = (1–cosθ)/(1+cosθ)
Rationalisation of denominator,
= (1–cosθ)/(1+cosθ) × (1–cosθ)/(1+cosθ)
= (1–cosθ)2 / (12–cos2θ)
= [1+cos2θ–2cosθ] / sin2θ
= 1/sin2θ + cos2θ/sin2θ – 2cosθ/sin2θ
= cosec2θ + cot2θ – 2cotθcosecθ
= (cosecθ – cotθ)2 = LHS
31. एक पासे को एक बार फेंका जाता है। निम्नलिखित को प्राप्त करने की प्रायिकता ज्ञात कीजिए :
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting :
(i) एक अभाज्य संख्या
a prime number
Answer : Prime numbers = 3 (2,3,5)
Total numbers = 6 (1,2,3,4,5,6)
P(E) = 3/6 = 1/2
(ii) 2 और 6 के बीच स्थित कोई संख्या
a number lying between 2 and 6
Answer : Numbers = 3 (3,4,5)
Total numbers = 6 (1,2,3,4,5,6)
P(E) = 3/6 = 1/2
(iii) एक विषम संख्या
an odd number
Answer : Odd numbers = 3 (1,3,5)
Total numbers = 6 (1,2,3,4,5,6)
P(E) = 3/6 = 1/2
SECTION – D (5 Marks)
32. एक मोटर बोट, जिसकी स्थिर जल में चाल 18 किमी/घण्टा है, 24 किमी धारा के प्रतिकूल जाने में, वही दूरी धारा के अनुकूल जाने की अपेक्षा 1 घण्टा अधिक लेती है। धारा की चाल ज्ञात कीजिए।
A motor boat whose speed is 8 km/h in still water takes 1 hour more to go 24 km upstream than to return downstream to the same spot. Find the speed of the stream.
Answer : Speed of boat in still water = 18 km/h
Let speed of the stream = x
Speed of boat upstream = Speed of boat in still water – speed of stream = 18 – x
Speed of boat downstream = Speed of boat in still water + speed of stream = 18 + x
Time = Distance/Speed
Time taken for upstream = Time taken for downstream + 1
24/(18+x) = 24/(18–x) + 1
x2 + 48x – 324 = 0
x2 + 54x – 6x – 324 = 0
x(x + 54) – 6(x + 54) = 0
(x + 54)(x – 6) = 0
x = 6 (x ≠ –54 speed not negative)
Thus, the speed of the stream is 6 km/h.
OR
3 वर्ष पूर्व सीमा की आयु (वर्षों में) का व्युत्क्रम और अब से 5 वर्ष पश्चात् आयु के व्युत्क्रम का योग 1/3 है। उसकी वर्तमान आयु ज्ञात कीजिए।
The sum of the reciprocals of Seema’s ages (in years) 3 years ago and 5 years from now is 1/3. Find her present age.
Answer : Let the present age of Seema = x years
3 years ago, Seema’s age = x – 3 years
5 years from now, his age will be = x + 5
According to question,
1/(x–3) + 1/(x+5) = 1/3
6x + 6 = x2 + 2x – 15
x2 – 4x – 21 = 0
x2 – 7x + 3x – 21 = 0
x(x – 7) + 3(x – 7) = 0
(x – 7)(x + 3) = 0
x = 7 (x ≠ –3 age can’t negative)
Therefore, Seema’s present age is 7 years.
33. सिद्ध कीजिए “यदि किसी त्रिभुज की एक भुजा के समांतर अन्य दो भुजाओं को भिन्न-भिन्न बिन्दुओं पर प्रतिच्छेद करने के लिए एक रेखा खींची जाए, तो ये अन्य दो भुजाएँ एक ही अनुपात में विभाजित हो जाती है”।
Prove that “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then other two sides are divided in the same ratio”.
Answer :
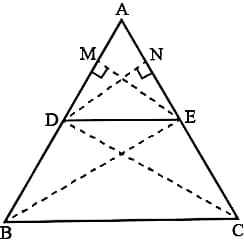
To Prove: AD/DB = AE/EC
Construction: Draw EM ⊥ AB and DN ⊥ AC. Join BE and CD.
Proof: In ∆ADE and ∆BDE,
ar(∆ADE) / ar(∆BDE) = (½×AD×EM) / (½×DB×EM) = AD/DB ……….(i)
In ∆ADE and ∆CDE,
ar(∆ADE) / ar(∆CDE) = (½×AE×DN) / (½×EC×DN) = AE/EC ……….(ii)
Since, DE || BC [Given]
∴ ar(∆BDE) = ar(CDE) ……….(iii)
[∆’s having same base and between the same parallel lines then they are equal in area]
From eqn.(i), (ii) and (iii), we get
AD/DB = AE/EC
Hence Proved.
34. कोई तंबू एक बेलन के आकार का है जिस पर एक शंकु अध्यारोपित है। यदि बेलनाकार भाग की ऊँचाई और व्यास क्रमशः 2.1 मी और 4 मी हैं तथा शंकु की तिर्यक ऊँचाई 2.8 मी है, तो इस तंबू को बनाने में प्रयुक्त कैनवास का क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए। साथ ही ₹ 500 प्रति मी2 की दर से इसमें प्रयुक्त कैनवास की लागत ज्ञात कीजिए। (ध्यान दीजिए कि तंबू के आधार को कैनवास से नहीं ढका जाता है।)
A tent is in the shape of a cylinder surmounted by a conical top. If the height and diameter of cylindrical part are 2.1 m and 4 m respectively and the slant height of the top is 2.8 m. Find the area of the canvas used for making the tent. Also find the cost of the canvas of the tent at the rate of ₹ 500 per m2. (Note that the base of the tent will not be covered with canvas.)
Answer :
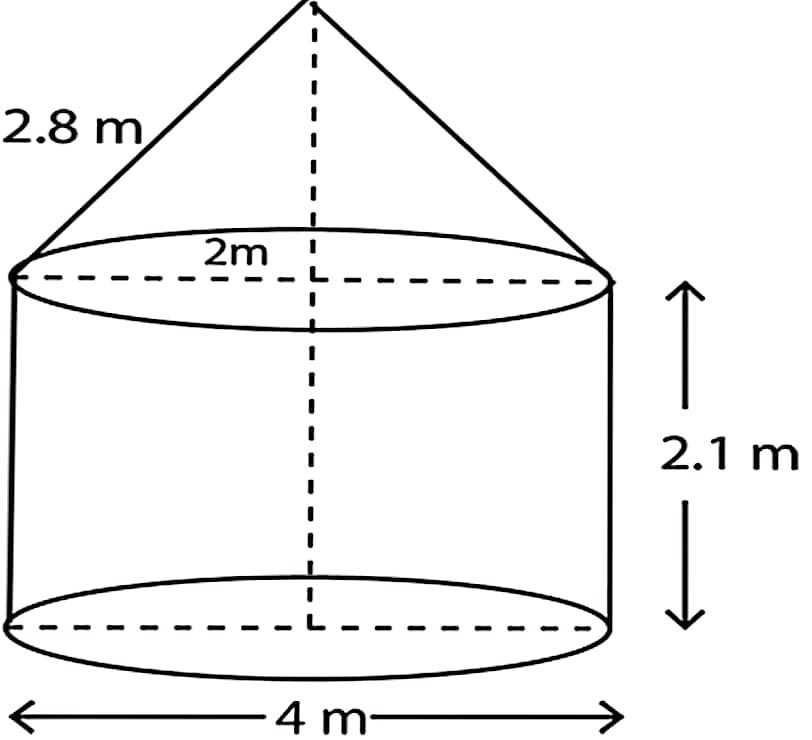
Radius of cylindrical part = 2 m
Height of cylindrical part = 2.1 m
Slant height of conical part = 2.8 m
Radius of the conical part = 2 m
Area of canvas used = CSA of cylindrical part + CSA of conical part = 2πrh + πrl = (2 × 22/7 × 2 × 2.1) + (22/7 × 2 × 2.8) = 26.4 + 17.6 = 44 m²
Cost of 1 m2 = ₹ 500
Cost of 44 m2 canvas = 500 × 44 = ₹ 22000
OR
भुजा 7 सेमी वाले एक घनाकार ब्लॉक के ऊपर एक अर्धगोला रखा हुआ है। अर्धगोले का अधिकतम व्यास क्या हो सकता है? इस प्रकार बने ठोस का पृष्ठीय क्षेत्रफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
A cubical block of side 7 cm is surmounted by a hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the surface area of the solid.
Answer :
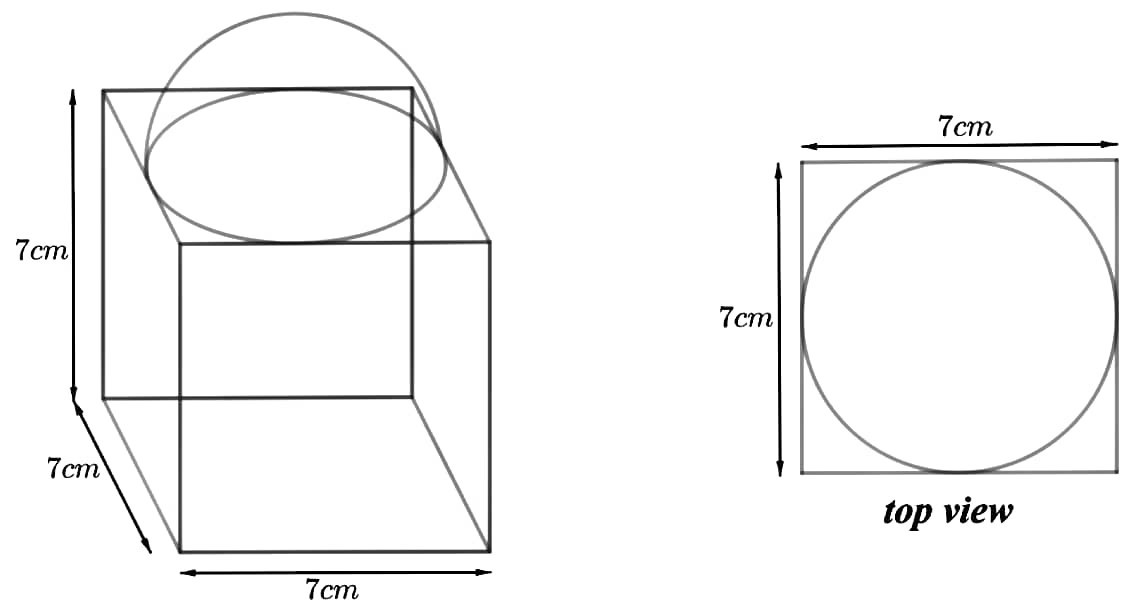
From the figure, it can be observed that the greatest diameter possible for such a hemisphere is equal to the cube’s edge, i.e., 7cm.
Radius (r) of hemispherical part = 7/2 = 3.5 cm
Total surface area of solid = Surface area of cubical part + CSA of hemispherical part – Area of base of hemispherical part = 6(Edge)2 + 2πr2 – πr2 = 6(Edge)2 + πr2 = 6(Edge)2 + πr2 = 6(7)2 + 22/7 × (3.5)2 = 294 + 38.5 = 332.5 cm2
Total surface area of solid = 332.5 cm2
35. दिया हुआ बंटन विश्व के कुछ श्रेष्ठतम बल्लेबाजों द्वारा एकदिवसीय अंतर्राष्ट्रीय क्रिकेट मैचों में बनाए रनों को दर्शाता है :
इन आँकड़ों का बहुलक ज्ञात कीजिए।
The given distribution shows the number of runs scored by some top Batsmen of the world in one day international cricket matches :
Find the mode of the data.
Answer : Modal class = 4000-5000
h = 1000
l = 4000
f1 = 18
fo = 4
f2 = 9
Mode = l + [(f1 – fo)/(2f1 – fo – f2)] × h
= 4000 + [(18 – 4)/(2×18 – 4 – 9)] × 1000
= 4000 + [14/(36–13)] × 1000
= 4000 + (14/23) × 1000
= 4000 + 608.695
= 4608.695
= 4608.7
Hence the mode is 4608.7
SECTION – E (CASE STUDY : 4 Marks)
36. अन्वी के द्वारा 810 सेबों को टोकरियों में इस प्रकार रखा गया है कि पहली टोकरी में 5 सेब, दूसरी में 12 सेब व तीसरी में 19 सेब इत्यादि।
उपरोक्त लिखित सूचना के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए :
Anvi has 810 apples and she arranged them in baskets in such a way that 5 apples are in first basket, 12 in second basket, 19 apples in third basket and so on.
Based on the above information, answer the following questions :
(i) टोकरियों में रखे सेबों की संख्या क्या एक AP है?
Is the number of apples in baskets in AP?
Answer : 5, 12, 19, ….
Common difference (d) = 12 – 5 = 19 – 12 = 7
Yes, the number of apples in baskets in AP.
(ii) 9वीं टोकरी में रखे सेबों की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the number of apples kept in the 9th basket.
Answer : a = 5, d = 7
an = a + (n – 1)d
a9 = 5 + (9 – 1) × 7 = 5 + 56 = 61
(iii) पहली 13 टोकरियों में कुल सेबों की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the total number of apples in the first 13 baskets.
Answer : Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
S13 = 13/2 [2(5) + (13 – 1) × 7]
= 13/2 [10 + 84] = 13/2 × 94 = 611
OR
कितनी टोकरियों में 95 सेब रखे गए हैं?
In how many baskets 95 apples can be kept?
Answer : Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
95 = n/2 [2(5) + (n – 1) × 7]
95 × 2 = n [10 + 7n – 7]
190 = n(7n + 3)
190 = 7n2 + 3n
7n2 + 3n – 190 = 0
n = 5 (after solving)
Therefore, 95 apples can be kept in 5 baskets.
37. एक कक्षा में 4 दोस्त राम, राजन, प्रवीण और रमन चित्र में दिखाए अनुसार बिन्दु A, B, C और D पर बैठे हैं। यह मानते हुए कि O मूल बिन्दु है। आकृति का अवलोकन करें और आकृति के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए :
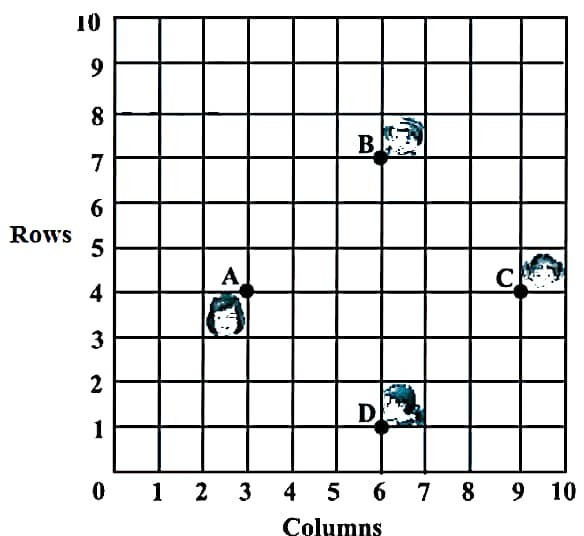
In a classroom 4 friends Ram, Rajan, Praveen and Raman are sitting on the points A, B, C and D as shown in the fig. Assuming O be the origin. Observe the figure and answer the following questions based on the figure :
(i) राजन की स्थिति ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the position of Rajan.
Answer : B(6, 7)
(ii) प्रवीण की स्थिति ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the position of Praveen.
Answer : C(9, 4)
(iii) AC के मध्यबिन्दु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the coordinates of the mid point of AC.
Answer : (6, 4)
OR
प्रवीण की मूल बिन्दु से दूरी ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the distance of Praveen from origin.
Answer : Here C(9, 4) and O(0, 0)
x1 = 9, x2 = 0, y1 = 4, y2 = 0
Using Distance Formula,
CO = √(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2
= √(0–9)2+(0–4)2
= √(–9)2+(–4)2
= √16+81
= √97 units
38. एक लड़का लाइट हाउस के शीर्ष पर खड़ा है। उसने देखा कि नाव P और नाव Q विपरीत दिशाओं से लाइट हाउस की ओर आ रही हैं। उसने पाया कि नाव P का अवनमन कोण 45° है और नाव Q का अवनमन कोण 30° है। वह यह भी जानता है कि लाइट हाउस की ऊँचाई 100 मीटर है।
उपरोक्त जानकारी के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए :
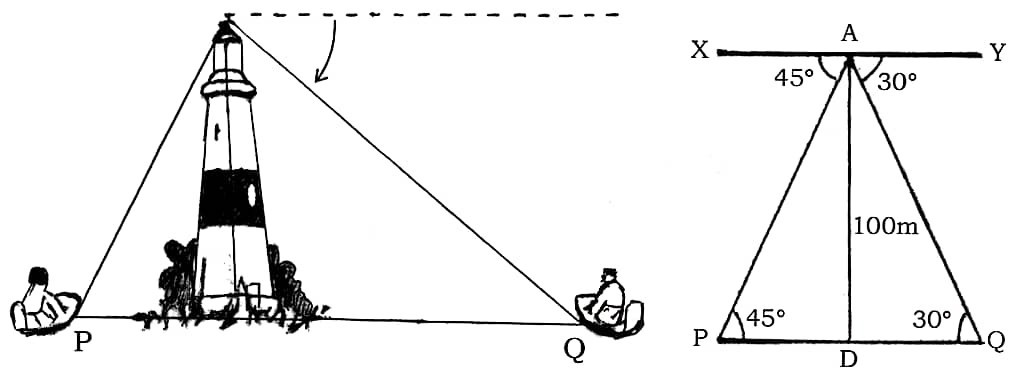
A boy standing on the top of a light house. He saw that two boats P and Q were approaching towards light house from opposite sides of it. He observed that angle of depression of boat P is 45° and that of boat Q is 30°. He also knows the height of light house is 100 m.
Using above information answer the following questions :
(i) ∠APQ का माप क्या होगा?
What will be the measure of ∠APQ?
Answer : ∠APQ = 45°
(ii) PD की लंबाई ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the length of PD.
Answer : tanP = Perpendicular/Base
tan45° = AD/PD = 100/PD
1 = 100/PD
PD = 100 m
(iii) QD की लंबाई ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the length of QD.
Answer : tanQ = Perpendicular/Base
tan30° = AD/QD = 100/QD
1/√3 = 100/QD
QD = 100√3 m
(iv) AP की लंबाई ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the length of AP.
Answer : sinP = Perpendicular/Hypotenuse
sin45° = AD/AP = 100/AP
1/√2 = 100/AP
AP = 100√2 m
