Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. BSEH (Board of School Education Haryana) Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024. HBSE (Haryana Board of School Education) Class 12 Chemistry Solved Question Paper 2024. BSEH Class 12 Chemistry Paper 2024 Solution. Download PDF and check accurate answers carefully prepared through my personal understanding, subject knowledge, and dedication to help students based on the syllabus and exam pattern.
HBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (1 Mark)
1. The value of Henry’s constant KH :
(A) Increases with increase in temperature
(B) Decreases with increase in temperature
(C) Remains constant
(D) First increases, then decreases
Answer – (A) Increases with increase in temperature
2. Which of the following B-Group vitamin can be stored in our body?
(A) Vitamin B1
(B) Vitamin B2
(C) Vitamin B6
(D) Vitamin B12
Answer – (D) Vitamin B12
3. An electrochemical cell can behave like an electrolytic cell, when :
(A) Ecell = 0
(B) Ecell > Eext
(C) Eext > Ecell
(D) Ecell = Eext
Answer – (C) Eext > Ecell
4. The gas evolved when methyl amine reacts with nitrous acid is :
(A) NH3
(B) N2
(C) H2
(D) C2H6
Answer – (B) N2
5. Activation energy of a chemical reaction can be determined by :
(A) determining the rate constant at standard temperature
(B) determining the rate constant at two temperatures
(C) determining probability of collision
(D) using catalyst
Answer – (B) determining the rate constant at two temperatures
6. Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by :
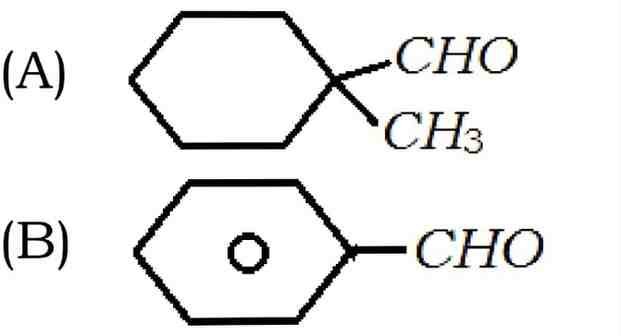
(C) HCHO
(D) CH3CHO
Answer – (D) CH3CHO
7. When alkaline KMnO4 is treated with Kl, iodide ion is oxidized to :
(A) I2
(B) IO–
(C) IO3–
(D) IO4–
Answer – (C) IO3–
8. Which of the following is most acidic?
(A) Benzyl alcohol
(B) Cyclohexanol
(C) Phenol
(D) m-Chlorophenol
Answer – (D) m-Chlorophenol
9. The CFSE for octahedral [CoCl6]4– is 18,000 cm–1. The CFSE for tetrahedral [CoCl4]2– will be :
(A) 18,000 cm–1
(В) 16,000 cm–1
(C) 8,000 cm–1
(D) 20,000 cm–1
Answer – (C) 8,000 cm–1
CFSE for tetrahedral: ∆t = 4/9 ∆o = 4/9 × 18000 = 8000 cm–1
10. Toluene reacts with a halogen in the presence of iron (III) chloride giving ortho and para halo compounds, the reaction is :
(A) Electrophilic elimination reaction
(B) Electrophilic substitution reaction
(C) Nucleophilic substitution reaction
(D) Nucleophilic addition reaction
Answer – (B) Electrophilic substitution reaction
11. In comparison to a 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in the freezing point of 0.01 M MgCl2 solution is :
(A) remains same
(B) about twice
(C) about three times
(D) about four times
Answer – (C) about three times
∆Tf ∝ i (van’t Hoff factor)
Glucose van’t Hoff factor (i) = 1
MgCl2 van’t Hoff factor (i) = 3
Same molarity, ∆Tf for MgCl2 = 3 × ∆Tf for glucose
12. Rate law for the reaction A + 2B → C is found to be Rate = K[A][B]. Concentration of reactant B is doubled keeping the concentration of A constant, the value of rate constant will be :
(A) the same
(B) doubled
(C) quadrupled
(D) halved
Answer – (A) the same
Rate constant is independent of concentrations, it depends only on temperature.
13. Which of the following oxidation state is common for all lanthanoids?
(A) +2
(B) +3
(C) +4
(D) +5
Answer – (B) +3
14. The reagent which does not react with both acetone and benzaldehyde :
(A) NaHSO3
(B) Phenyl hydrazine
(C) Fehling solution
(D) Tollen’s reagent
Answer – (C) Fehling solution
15. Assertion [A] : When NaCl is added to water, a depression in freezing point is observed.
Reason [R] : The lowering of vapour pressure of a solution causes depression in the freezing point.
(A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
(B) Both [A] and [R] are true, but [R] is not the correct explanation of [A].
(C) [A] is true, but [R] is false.
(D) [A] is false, but [R] is true.
Answer – (A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
16. Assertion [A] : Complexes of MX6 and MX5L type [X and L are unidentate] do not show geometrical isomerism.
Reason [R] : Geometrical isomerism is not shown by the complexes of coordination number 6.
(A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
(B) Both [A] and [R] are true, but [R] is not the correct explanation of [A].
(C) [A] is true, but [R] is false.
(D) [A] is false, but [R] is true.
Answer – (C) [A] is true, but [R] is false.
17. Assertion [A] : The boiling point of alkyl halides decreases in the order RI > RBr > RCl > RF for same alkyl group.
Reason [R] : The boiling point of alkyl halide having chloride, bromide and iodides are higher than that of the hydrocarbon of comparable molecular mass.
(A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
(B) Both [A] and [R] are true, but [R] is not the correct explanation of [A].
(C) [A] is true, but [R] is false.
(D) [A] is false, but [R] is true.
Answer – (B) Both [A] and [R] are true, but [R] is not the correct explanation of [A].
18. Assertion [A] : Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason [R] : It contains sp2 hybridized carbon atom.
(A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
(B) Both [A] and [R] are true, but [R] is not the correct explanation of [A].
(C) [A] is true, but [R] is false.
(D) [A] is false, but [R] is true.
Answer – (A) Both [A] and [R] are true and [R] is the correct explanation of [A].
SECTION – B (2 Marks)
19. What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Answer – Denaturation unfolds a protein’s three-dimensional structure by disrupting secondary and tertiary bonds (like hydrogen and ionic bonds), but the primary structure (amino acid sequence) remains unchanged. This loss of specific shape causes the protein to lose its unique biological function.
20. Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial amount is 60 minutes. If the decomposition is a first order reaction, then calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Answer – For a first-order reaction :
t1/2 = 0.693 / k
k = 0.693 / t1/2 = 0.693 / 60 = 0.01155 min–1 = 1.16 × 10–2 min–1
Rate constant (k) = 1.16 × 10–2 min–1
OR
For the reaction R → P the concentration of a reactant changes from 0.03 M to 0.02 M in 25 minutes. Calculate the average rate of reaction using units of time in minutes.
Answer – Initial concentration, [R]i = 0.03 M
Final concentration, [R]f = 0.02 M
Time, ∆t = 25 min
Average rate = ∆[R] / ∆t = ([R]i – [R]f) / 25 = (0.03 – 0.02) / 25 = 0.0004 M/min = 4 × 10–4 M/min
Average rate = 4 × 10–4 M/min
21. Write the IUPAC name of the following coordination compounds :
(i) [Co(NH3)5CO3]Cl
Answer – Pentaamminecarbonatocobalt(III) chloride
(ii) K3[Fe(C2O4)3
Answer – Potassium tris(oxalato)ferrate(III)
22. What happens, when :
(a) Methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether?
Answer – When methyl bromide (CH3Br) reacts with sodium metal in dry ether, it undergoes the Wurtz reaction and form ethane (C2H6), with sodium bromide as a by-product.
2CH3Br + 2Na + dry ether → CH3CH3 + 2NaBr
(b) Ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH?
Answer – When ethyl chloride (CH3CH2Cl) is treated with aqueous potassium hydroxide (KOH), it undergoes a nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2) to form ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and potassium chloride (KCl).
CH3CH2Cl + KOH (aq) → CH3CH2OH + KCl
23. Estimate the products obtained from the following reactions :
(a) C6H5OC2H5 + HBr →
Answer : C6H5OH + C2H5Br
(b) (CH3)3C–OC2H5 + HI →
Answer : (CH3)3CI + C2H5OH
OR
Explain how does OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activate it towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Answer – The –OH group attached to benzene activates the ring due to its +R effect, as the lone pair of oxygen is delocalized into the aromatic ring. This increases the electron density of the ring, especially at the ortho and para positions, making it more reactive towards electrophilic substitution. Hence, –OH is an ortho-para directing group.
24. Give the structure of A and B in the following reaction :
C6H5NO2 + Fe/HCl → A + NaNO2 + HCl + 273 K → B
Answer : A = Aniline (C6H5NH2)
B = Benzenediazonium chloride (C6H5N2+Cl–)
25. Which alkyl halide from the following pair would you expect to react more rapidly by SN2 mechanism?
(i) CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3 or (CH3)2CBr
Answer – CH3CH2CH(Br)CH3
(ii) CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2Br or CH3CH2CH(CH3)CH2Br
Answer – CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2Br
SECTION – C (3 Marks)
26. For the first order reaction show that the time required for 99% completion of first order reaction is twice the time required for the completion of 90%.
Answer – For a first-order reaction, the time required for the completion of a certain percentage of reaction can be given by the formula:
t = 2.303/k log[100 / 100–% completion]
Time for 99% completion,
t99 = 2.303/k log[100/100–99] = 2.303/k log[100/1] = 2.303/k log(100) = 2.303/k (2) = 4.606/k
Time for 90% completion,
t90 = 2.303/k log[100/100–90] = 2.303/k log[100/10] = 2.303/k log(10) = 2.303/k (1) = 2.303/k
Relating t99 and t90 : t99 = 2 × t90
Hence, the time required for 99% completion of a first-order reaction is twice the time required for completion of 90%.
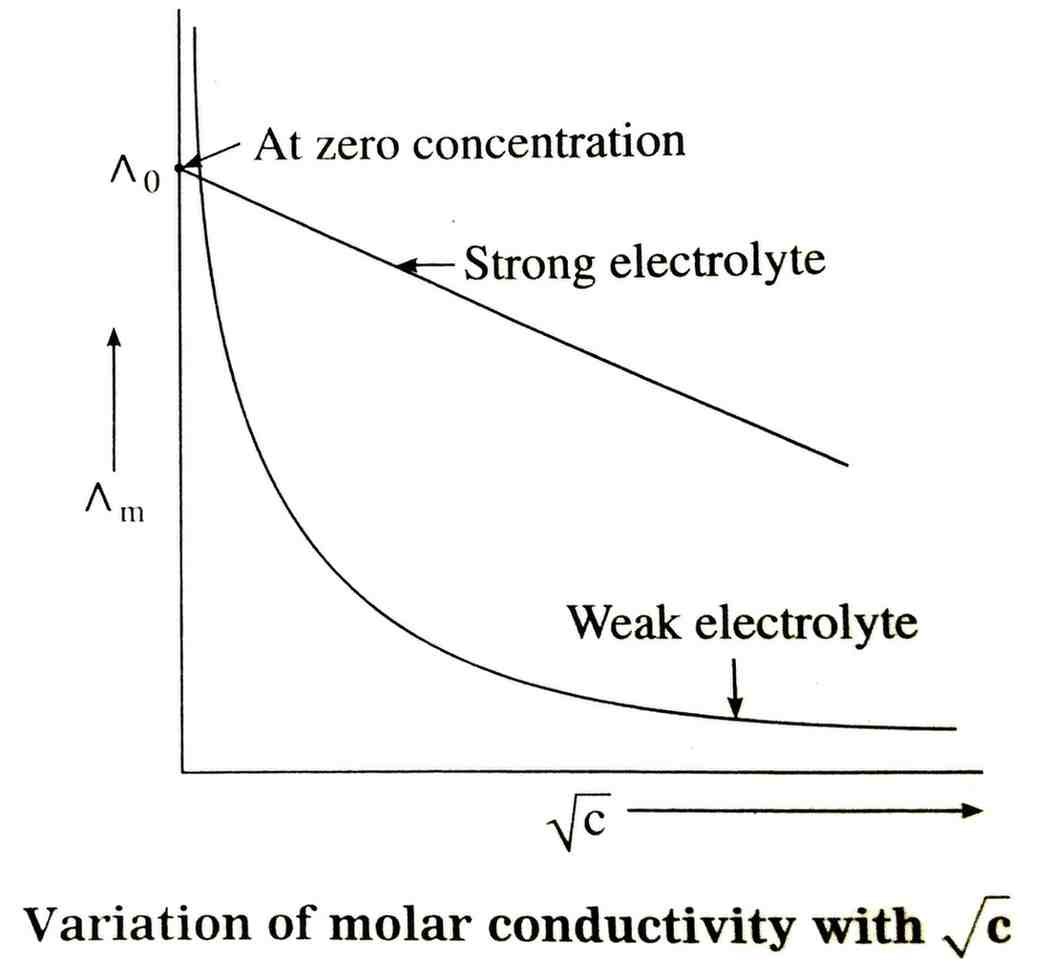
27. Explain the variation of molar conductivity of a strong electrolyte and weak electrolyte with concentration through a graph.
Answer – Strong Electrolyte (e.g. NaCl, HCl, KNO3) :
Strong electrolytes are completely dissociated into ions at all concentrations. As concentration increases (i.e. dilution decreases), the number of ions does not change (they were already 100% dissociated). But at higher concentration, ions are close together → strong interionic attractions → lower mobility of ions. When diluted, ions move freely (interionic attraction decreases) → molar conductivity increases.
Graph: For strong electrolytes, the graph of Λm (molar conductivity) vs √c is almost a straight line decreasing with √c.
At √c → 0 (infinite dilution), extrapolation gives Λmo (limiting molar conductivity).
• Weak Electrolyte (e.g. CH3COOH, NH4OH):
Weak electrolytes are partially dissociated at normal concentration. On dilution, degree of dissociation (α) increases significantly.
More ions are produced, so molar conductivity increases sharply.
Graph: For weak electrolytes, the curve of Λm vs √c is highly curved, not a straight line.
Instead, we use Ostwald’s dilution law or Kohlrausch’s law (by combining data of strong electrolytes having common ions).
28. Convert :
(i) Propene into Propan-2-ol
Answer – When propene (CH3–CH=CH2) is treated with dilute H2SO4 (hydration), water adds across the double bond according to Markovnikov’s rule (–OH goes to the more substituted carbon).
CH3–CH=CH2 + H2O/H2SO4 → CH3–CHOH–CH3
(ii) Benzyl Chloride into Benzyl Alcohol
Answer – Benzyl chloride (C6H5–CH2Cl) undergoes nucleophilic substitution with aqueous alkali to form benzyl alcohol.
C6H5CH2Cl + NaOH (aq) → C6H5CH2OH + NaCl
(iii) Ethyl Magnesium Chloride into Propan-1-ol
Answer – React ethyl magnesium chloride with formaldehyde (HCHO) in dry ether to form the alkoxide intermediate.
CH3CH2MgCl + HCHO + dry ether → CH3CH2CH2OMgCl
Hydrolyze the intermediate with water or dilute acid (e.g., H3O+) to yield the alcohol.
CH3CH2CH2OMgCl + H2O → CH3CH2CH2OH + Mg(OH)CI
29. Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of Valence Bond Theory :
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4–
Answer – In [Fe(CN)6]4–, iron is in the +2 oxidation state with a 3d6 electronic configuration. The cyanide (CN–) ligand is a strong field ligand, which causes the pairing of the six 3d electrons in the inner orbitals, resulting in d2sp3 hybridization. This leads to the formation of a diamagnetic complex with an octahedral geometry.
(ii) [CoF6]3–
Answer – In the coordination entity [CoF6]3–, cobalt is in the +3 oxidation state, and F– is a weak field ligand, which does not cause pairing of 3d electrons. The central Co3+ ion undergoes sp3d2 hybridization, forming six empty hybrid orbitals. These orbitals are occupied by lone pairs from the six F– ligands, resulting in an octahedral geometry. The complex is high-spin and paramagnetic, with four unpaired electrons.
OR
What is crystal field splitting energy? How does the magnitude of ∆o, decide the actual configuration of d orbital in a coordination entity having d4 configuration.
Answer – Crystal field splitting energy (Δo) is the energy difference between t2g and eg d-orbitals in a transition metal ion caused by approaching ligands. Orbitals pointing at ligands (eg) have higher energy than those between ligands (t2g).
For a d4 octahedral complex, if Δo is less than the pairing energy (P), electrons occupy eg orbitals unpaired (high-spin, t2g3 eg1); if Δo is greater than P, electrons pair in t₂g orbitals (low-spin, t2g4 eg0). Thus, Δo determines the d-orbital arrangement, spin state, and magnetic properties.
30. (i) Write the IUPAC name of the amide that gives propanamine by Hoffmann’s bromamide reaction.
Answer – Butanamide (CH3CH2CH2CONH2)
(ii) Arrange the following in the increasing order of basic strength :
C6H5NH2, NH3, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH
Answer : C6H5NH2 (aniline) < NH3 (ammonia) < C2H5NH2 (ethylamine) < (C2H5)2NH (diethylamine)
(iii) Give one chemical test to distinguish between aniline and benzylamine.
Answer – Nitrous Acid Test and Hinsberg Test
OR
(i) pKb of aniline is more than that of methylamine, why?
Answer – The pKb of aniline is higher (meaning it’s a weaker base) than methylamine because the lone pair of electrons on aniline’s nitrogen atom is delocalized into the benzene ring through resonance, making it less available to accept a proton.
(ii) Convert Benzyl chloride into 2-phenylethanamine.
Answer – Formation of cyanide:
C6H5CH2Cl + KCN → C6H5CH2CN + KCl
Reduction of nitrile:
C6H5CH2CN + LiAlH4/H2O → C6H5CH2CH2NH2
(iii) Why do primary amines have higher boiling point than tertiary amines?
Answer – Primary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines because they can form stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonds due to the presence of N–H bonds, which are absent in tertiary amines.
SECTION – D (4 Marks : CASE STUDY)
31. The spontaneous flow of the solvent through a semipermeable membrane from a pure solvent to a solution or from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution is called osmosis. The phenomenon of osmosis can be demonstrated by taking two eggs of the same size. In an egg the membrane below the shell and around the egg material is semipermeable. The outer hard shell can be removed by putting the egg in dilute hydrochloric acid. After removing the hard shell, one egg is placed in distilled water and the other in a saturated salt solution. After some time, the egg placed in distilled water swells up while the egg placed in salt solution shrinks. The external pressure applied to stop the osmosis is termed as osmotic pressure. Reverse osmosis takes place when the applied external pressure becomes larger than the osmotic pressure.
Questions :
(i) What happens when RBCs are placed in 0.9% NaCl solution?
Answer – RBCs remain unchanged because 0.9% NaCl is an isotonic solution.
(ii) Which one of the following has higher osmotic pressure : 1M KCI or 1 M Urea ?
Answer – 1M KCl, because it dissociates into two ions (K+ and Cl–), giving greater particle concentration.
(iii) What is Reverse Osmosis? Name one SPM which can be used in this reverse osmosis.
Answer – Reverse osmosis is the process in which pure solvent is forced out of a solution through a semipermeable membrane by applying external pressure greater than the osmotic pressure. Example of SPM: Cellulose acetate membrane.
OR
How the molecular mass of substance can be determined by the method based on measurement of osmotic pressure?
Answer – The molecular mass of a substance can be determined by measuring its osmotic pressure using van’t Hoff’s equation (π = CRT). Since C = w / MV, the equation becomes π = MV Rearranging gives M = wRT / πV, where w is the mass of solute, V is the volume of solution, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature.
32. Monosaccharides are simple carbohydrates that can’t be broken further into smaller units on hydrolysis. For example Glucose, Fructose Ribose etc. Oligo-saccharides are the carbohydrates which on hydrolysis give two to ten units of monosaccharides eg. Sucrose, Maltose, Lactose etc. Polysaccharides produce large number of monosaccharides units on hydrolysis eg. starch cellulose.
Questions :
(i) Name the linkage that holds the two units in the disaccharide.
Answer – Glycosidic Linkage
(ii) Which disaccharide is found only in animals, not in plants?
Answer – Lactose
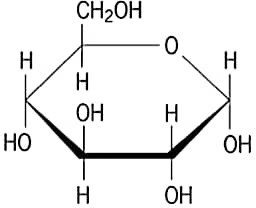
(iii) Draw Haworth projection of α-D Glucose.
Answer –
OR
What is Glycogen? How it is different from Starch?
Answer – Glycogen is a highly branched storage polysaccharide in animals, while starch is a plant storage polysaccharide with both linear and branched parts.
SECTION – E (5 Marks)
33. (i) Write the Nernst equation and calculate the emf of the following cell at 298 K :
Mg (s) | Mg2+ (0.001M) || Cu2+ (0.0001M) | Cu (s)
EoMg2+ | Mg = – 2.37 V
EoCu2+ | Cu = 0.34 V
Answer – Standard cell potential
Eocell = Eocathode – Eoanode = 0.34 – (–2.37) = 2.71 V
Reaction quotient (Q) = [Mg2+] / [Cu2+] = 0.001 / 0.0001 = 10
Ecell = Eocell – 0.0591/n logQ = 2.71 – 0.0591/2 log10 = 2.71 – 0.02955 × 1 = 2.68045
Emf = 2.68045 V
(ii) Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution?
Answer – The conductivity of a solution decreases with dilution because conductivity depends on the number of ions per unit volume. Dilution increases the volume, reducing ion concentration in that volume, which lowers the number of charge carriers and thus decreases conductivity.
OR
(i) Calculate the standard cell potential of galvanic cell in which the following reaction takes place. Also calculate the value of ∆rGo of the reaction :
2Cr(s) + 3Cd2+(aq) → 2Cr3+ (aq) + 3Cd(s)
EoCr3+ | Cr = – 0.74 V
EoCd2+ | Cd = – 0.40 V
Answer – Standard cell potential
Eocell = Eocathode – Eoanode = – 0.40 – (–0.74) = 0.34 V
Total electrons transferred (n) = LCM of 3 (from Cr) and 2 (from Cd)
n = 6
Faraday constant F = 96485 C/mol
∆rGo = – nFEocell = – 6 × 96485 × 0.34 = – 196000 J/mol = – 196 kJ/mol
(ii) Define Kohlrausch’s law by taking suitable example.
Answer – Kohlrausch’s Law states that the limiting molar conductivity (Λm) of an electrolyte at infinite dilution is the sum of the individual contributions of its ions. e.g.
Λmo(NaCl) = λo(Na+) + λo(Cl–)
34. (i) Why transition elements have the high enthalpy of atomization?
Answer – Transition elements have high enthalpy of atomization because their unpaired d-electrons form strong metallic bonds, requiring more energy to break.
(ii) Why highest oxidation state is exhibited in oxoanions of a metal?
Answer – The highest oxidation state is exhibited in oxoanions because oxygen is highly electronegative and stabilizes the high positive charge on the metal atom.
(iii) Indicate the steps in the preparation of K2Cr2O7 from the chromite ore.
Answer –
4FeCr2O4 + 8Na2CO3 + 7O2 → 8Na2CrO4 + 2Fe2O3 + 8CO2
2Na2CrO4 + H2SO4 → Na2Cr2O7 + Na2SO4 + H2O
Na2Cr2O7 + 2KCl → K2Cr2O7 + 2NaCl
OR
(i) How does acidified permanganate solution react with oxalic acid? Write ionic equation for this reaction.
Answer – Acidified permanganate solution oxidizes oxalic acid to carbon dioxide and is itself reduced to manganese(II) ions in a redox reaction.
2MnO4– + 16H+ + 5C2O42– → 2Mn2+ + 8H2O + 10CO2
(ii) Why Eo(M2+ | M) value of copper is the positive value (0.34 V) ?
Answer – The standard electrode potential of copper is positive (+0.34 V) because Cu2+ ions have a strong tendency to gain electrons and get reduced to stable Cu metal, while oxidation of Cu to Cu2+ is less favorable due to high atomization and ionization energy not fully compensated by the hydration energy of Cu2+.
(iii) Compare Lanthanoids and Actinoids with special reference to electronic configuration, oxidation state and atomic and ionic size.
Answer –
| Lanthanoids | Actinoids |
| 1. Filling of the 4f orbital occurs; general configuration is [Xe]4f1–145d0–16s2 | 1. Filling of the 5f orbital occurs; general configuration is [Rn]5f1–146d0–27s2 |
| 2. Typically show a +3 oxidation state, with some elements showing +2 and +4 rarely due to the large energy gap between 4f and 5d subshells. | 2. Show a wider range of oxidation states (from +3 up to +7 for some elements) due to smaller energy differences between 5f and 6d subshells. |
| 3. This shows a gradual decrease in atomic and ionic sizes with increasing atomic number. | 3. This shows a gradual decrease in atomic and ionic sizes with increasing atomic number. |
35. An organic compound with molecular formula C9H10O forms 2,4-DNP. Derivative reduces Tollen’s reagent and undergoes Cannizaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1,2-benzene dicarboxylic acid. Identify the organic compound. Write its IUPAC name. Write all chemical equations involved in reaction.
Answer – Molecular formula: C9H10O
Reactions indicate:
Forms 2,4-DNP → has aldehyde group
Reduces Tollen’s → aldehyde
Cannizzaro reaction → no α-H
Oxidation → phthalic acid (1,2-benzene dicarboxylic acid)
Chemical Reactions :
2,4-DNP Test:
C6H4(CH3)CHO + C6H6N2O2→ C6H4(CH3)CH=N-C6H3(NO2)2 + H2O
Tollen’s Test:
CH(CH3)CHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ + 3OH– → CH(CH3)COO– + 2Ag + 4NH3 + 2H2O
Cannizzaro Reaction:
2C6H4(CH3)CHO + NaOH → C6H4(CH3)CH2OH + C6H4(CH3)COONa
Vigorous Oxidation:
C6H4(CH3)CHO + [O] → C6H4(CO2H)2
OR
(i) Write the structure of product of the following reaction :
CH3–C ≡ CH + Hg2+ + H2SO4 →
Answer : CH3–CO–CH3 (acetone)
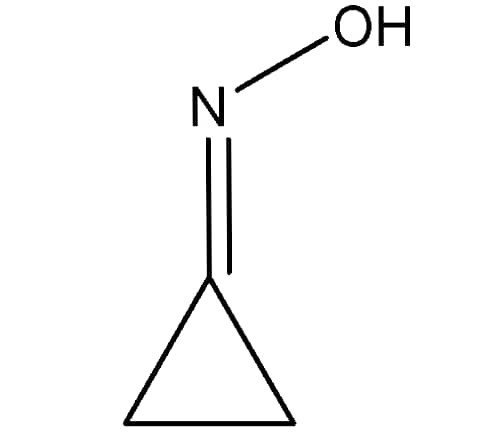
(ii) Draw the structure of : Cyclo-propanone Oxime.
Answer –
(iii) There are two NH2 groups in Semicarbazide, but only one is involved in semicarbazone formation, why?
Answer – The –NH2 group directly attached to the carbonyl group is less nucleophilic because its lone pair is delocalized by resonance with the C=O group, so it cannot react.
(iv) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of reactivity towards HCN :
Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Ditertbutyl Ketone
Answer – Ditertbutyl Ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
(v) Write a short note on ‘Aldol Condensation’.
Answer – It is a reaction in which an aldehyde or ketone with α-hydrogen reacts in the presence of a base or acid to form a β-hydroxy aldehyde or β-hydroxy ketone (aldol), which on heating gives an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound.
