Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2024 Answer Key. BSEH (Board of School Education Haryana) Class 12 Biology Answer Key 2024. HBSE (Haryana Board of School Education) Class 12 Biology Solved Question Paper 2024. BSEH Class 12 Biology Paper 2024 Solution. Download PDF and check accurate answers carefully prepared through my personal understanding, subject knowledge, and dedication to help students based on the syllabus and exam pattern.
HBSE Class 12 Biology Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
SECTION – A (1 Mark)
1. LH acts on :
(A) Leydig cells
(B) Sertoli cells
(C) Both (A) & (B)
(D) Spermatogonia
Answer – (A) Leydig cells
2. Which hormone is secreted by Pituitary gland in human female?
(A) LH
(B) FSH
(C) Oxytocin
(D) All of these
Answer – (D) All of these
3. Which of the following is not pollinated by water?
(A) Vallisneria
(B) Hydrilla
(C) Zostera
(D) Water-lily
Answer – (D) Water-lily
4. Anticodon is present on :
(A) mRNA
(B) tRNA
(C) rRNA
(D) DNA
Answer – (B) tRNA
5. By how many hydrogen bonds guanine is bonded with cytosine?
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
Answer – (C) 3
6. Which of the following RNA polymerase transcribes rRNAs (28s, 18s & 5.8s)?
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) None of these
Answer – (A) I
7. A double stranded DNA has 15% cytosine. What will be the percentage of thiamine in it?
(A) 15%
(B) 25%
(C) 35%
(D) 45%
Answer – (C) 35%
8. Which of the following can fix atmospheric nitrogen?
(A) Anabaena
(B) Nostoc
(C) Oscillatoria
(D) All of these
Answer – (D) All of these
9. Which of the following is reservoir of Erythrocytes?
(A) Spleen
(B) Heart
(C) Lymph node
(D) All of these
Answer – (A) Spleen
10. Pollen grains of which plant cause allergy?
(A) Coriander
(B) Parthenium
(C) Triticum
(D) None of these
Answer – (B) Parthenium
11. The proteins encoded by which gene control corn borer?
(A) Cry I Ac
(B) Cry II Ab
(C) Both (A) & (B)
(D) Cry I Ab
Answer – (D) Cry I Ab
12. Which is a dipteran?
(A) Beetle
(B) Army worm
(C) Tobacco bud worm
(D) Mosquito
Answer – (D) Mosquito
13. Which is a part of in situ conservation?
(A) Wildlife Safari Park
(B) Zoological Park
(C) National Park
(D) None of these
Answer – (C) National Park
14. Interaction between sea anemone and clown fish is an example of :
(A) Commensalism
(B) Competition
(C) Parasitism
(D) Mutualism
Answer – (A) Commensalism
15. Assertion (A) : Net primary productivity is greater than gross primary productivity.
Reason (R) : A part of net primary productivity goes waste during respiration.
(A) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
Answer – (D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
16. Assertion (A) : Heroin is an opioid.
Reason (R) : Heroin is obtained from Poppy plant.
(A) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
Answer – (B) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
17. Assertion (A) : Biotechnology started with development of recombinant molecules.
Reason (R) : Biotechnology mostly involves in cutting & pasting of desired parts of DNA.
(A) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) are true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
Answer – (A) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
18. Assertion (A) : Interferons are a type of antibodies produced by bacteria infected cells of the body.
Reason (R) : Interferons stimulate inflammation at the site of injury.
(A) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) are true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
Answer – (D) Assertion (A) and Reason (R) both are false.
SECTION – B (2 Marks)
19. Name various male sex accessory ducts.
Answer – The male sex accessory ducts are the ducts that transport sperm from the testes to the urethra for ejaculation. These ducts include the rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis, vas deferens (or ductus deferens), the ejaculatory duct, and the urethra.
20. What is Aneuploidy? Write any two examples of it.
Answer – Aneuploidy is the condition in which a cell has an abnormal number of chromosomes, either more or fewer than the normal diploid number. e.g.
(i) Down syndrome (Trisomy 21) – an extra copy of chromosome 21
(ii) Turner syndrome (Monosomy X) – only one X chromosome in females
21. Name first transgenic cow. What is the advantage of its milk over natural cow milk?
Answer – The first transgenic cow was named Rosie (developed in 1997). The milk produced by Rosie was enriched with human alpha-lactalbumin protein, making it nutritionally more balanced and especially beneficial for human babies compared to natural cow milk, which lacks this specific human protein.
22. What is the impact of loss of biodiversity in a region?
Answer – The impact of loss of biodiversity in a region includes ecological imbalance, economic loss, environmental degradation, loss of genetic resources and increased vulnerability.
23. What is detritus and decomposition?
Answer : Detritus – Dead organic matter, such as fallen leaves, dead plants, and animal remains, that serves as a source of nutrients for decomposers.
• Decomposition – The process by which detritus is broken down by decomposers (bacteria, fungi, and other organisms) into simpler inorganic substances, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
24. What are the reasons of rise in our population?
Answer – Population rises mainly because death rate has decreased due to better medical facilities, sanitation, and nutrition, while birth rate remains high due to early marriages, cultural preferences, lack of family planning, limited education, and poverty.
OR
Name various copper releasing IUDs. How do these help in contraception?
Answer – Copper releasing IUDs include Cu-T, Cu-7, Multiload Cu, Nova-T. They help in contraception by releasing copper ions that are toxic to sperm, reducing fertilization, and preventing implantation.
25. What is the genetic basis of proof that codon is a triplet and is read in contiguous manner?
Answer – The genetic proof that a codon is a triplet and read contiguously comes from Crick and Brenner’s frameshift experiments. They induced insertions or deletions of nucleotides in a gene of bacteriophage T4. Adding or removing one or two nucleotides disrupted the protein, but adding or removing three nucleotides restored function. This showed that three nucleotides form a codon and the code is read continuously without gaps.
OR
What is the dual function of AUG?
Answer – The AUG codon has a dual function in protein synthesis :
(i) Start codon – It signals the beginning of translation, marking where the ribosome should start assembling amino acids into a protein.
(ii) Codes for Methionine – It also specifies the amino acid methionine, which is the first amino acid incorporated into every newly synthesized protein in eukaryotes (and N-formylmethionine in prokaryotes).
SECTION – C (3 Marks)
26. Draw a well labelled diagram of L.S. embryo of a grass.
Answer –
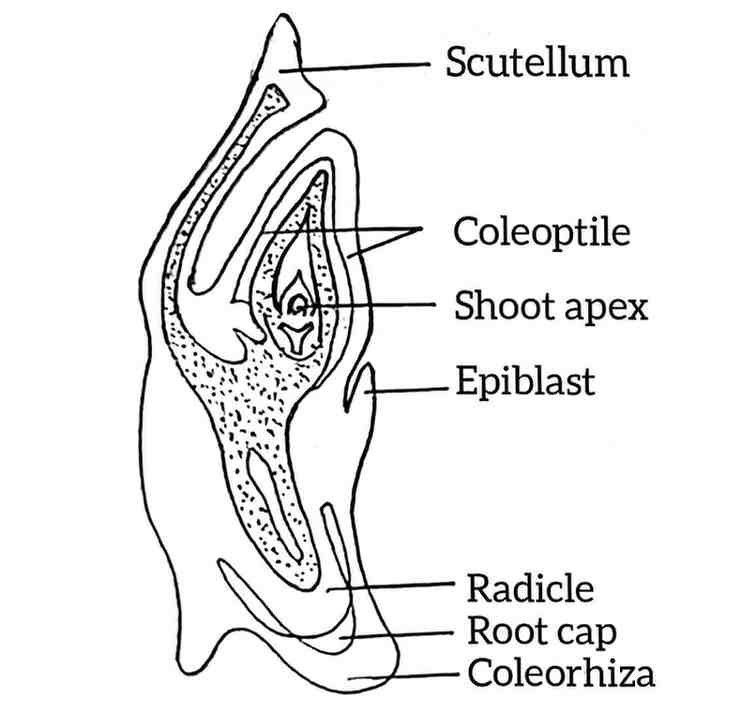
27. Write down the role of RNA polymerase I, II, III.
Answer – Here’s a clear breakdown of the roles of RNA polymerase I, II, and III in eukaryotes :
• RNA Polymerase I – It synthesizes 28S, 18S, and 5.8S rRNA in the nucleolus, which are essential for ribosome formation.
• RNA Polymerase II – It transcribes protein-coding genes into mRNA and also makes some snRNA and miRNA, playing the main role in gene expression.
• RNA Polymerase III – It produces tRNA, 5S rRNA, and other small RNAs that are important for translation and RNA processing.
28. What are the important defence mechanisms in plants against herbivory?
Answer – Plants protect themselves from herbivores by using morphological defenses like thorns, spines, hairs, and tough leaves that make feeding difficult, chemical defenses such as alkaloids, terpenoids, phenolics, and toxins that act as repellents or reduce digestibility, and ecological defenses where they attract natural enemies of herbivores or form protective associations with organisms like ants.
29. Write about various barriers of innate immunity.
Answer – The four main barriers of innate immunity are :
(i) Physical barriers – Skin, mucous membranes, cilia, etc., prevent entry of microbes.
(ii) Physiological barriers – Saliva, tears, hydrochloric acid in the stomach, and body temperature kill pathogens.
(iii) Cellular barriers – Phagocytic cells like neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer (NK) cells destroy microbes.
(iv) Cytokine barriers – Interferons and other cytokines protect against viral infections.
OR
What are the harmful effects of using tobacco?
Answer – Harmful Effects on the Body :
(i) Cancers – Tobacco is a carcinogen that can cause various cancers, including lung, mouth, neck, and pancreatic cancers.
(ii) Cardiovascular System – Tobacco use damages blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, high blood pressure, and other cardiovascular disorders.
(iii) Respiratory System – It damages the lungs, leading to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and increased coughing and mucus production.
30. How can DNA be cut at specific locations?
Answer – DNA can be cut at specific locations by using restriction endonucleases (also called molecular scissors). These enzymes recognize short, specific sequences of nucleotides in the DNA (called recognition sites) and cut the DNA at or near these sites. This property allows scientists to isolate, remove, or insert particular DNA fragments during genetic engineering.
OR
What are the three critical research areas of biotechnology?
Answer – The three critical research areas of biotechnology are :
(i) Providing best possible crop plants – Producing high-yield, pest-resistant, and stress-tolerant crops.
(ii) Designing better processes – Developing cleaner, eco-friendly technologies for chemical and industrial production.
(iii) Health care and disease management – Producing vaccines, medicines, and diagnostic tools for human welfare.
SECTION – D (4 Marks)
31. See the above diagram of Miller’s experiment and answer the following questions :
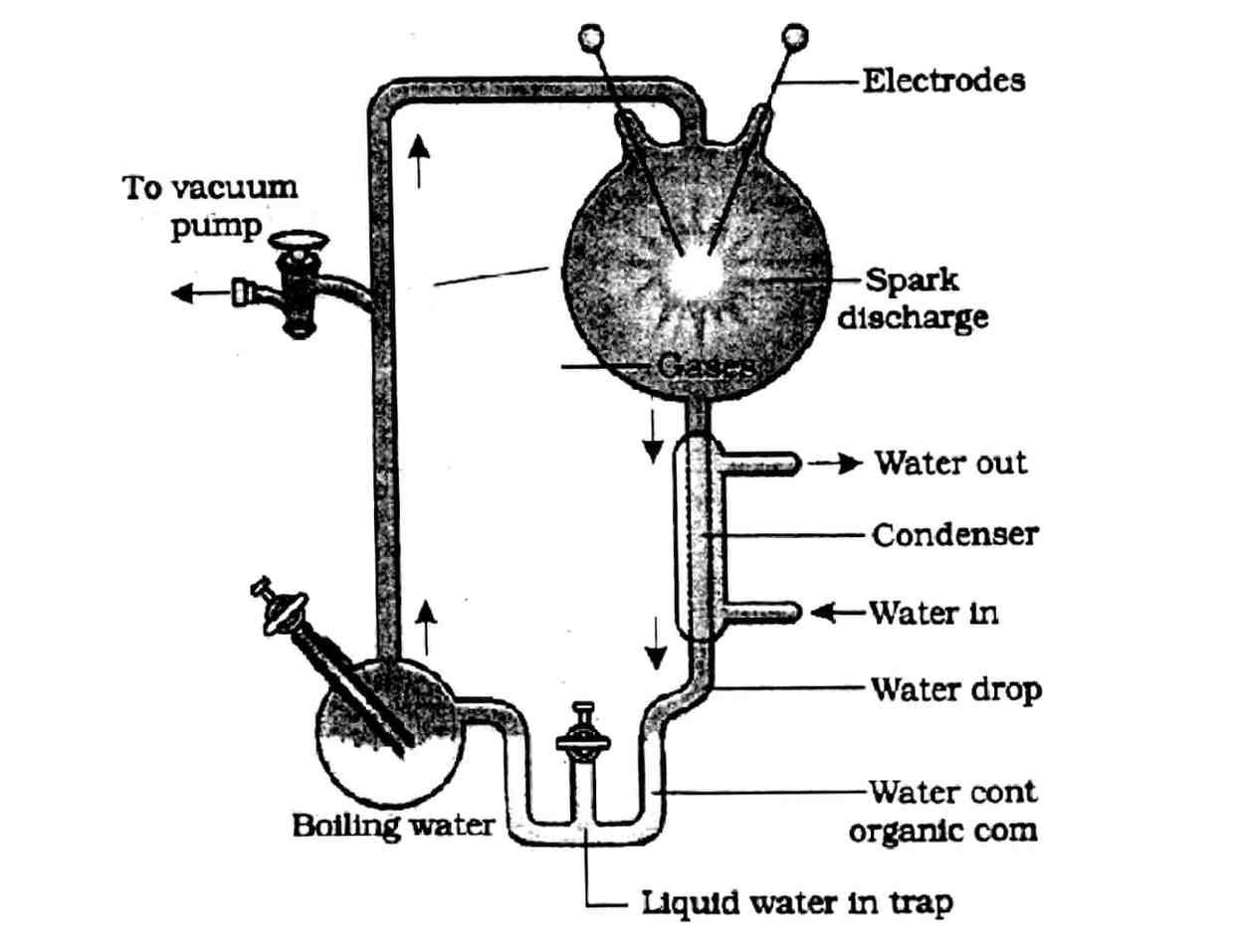
(i) State the hypothesis which Miller tried to prove in the laboratory with the help of setup of experiment given above.
Answer – Miller tried to prove that life originated from simple inorganic molecules present in the primitive atmosphere, which, under the influence of physical conditions like heat and lightning, could give rise to organic compounds essential for life.
OR
Which gases were used in this experiment?
Answer – The gases used in this experiment were methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), hydrogen (H2), and water vapour (H2O).
(ii) In which year Miller performed this experiment?
Answer – In 1953
(iii) Name the organic compounds observed by him in liquid after running the experiment.
Answer – The organic compounds observed in the liquid after running the experiment were amino acids such as glycine, alanine, and aspartic acid.
32. Schematic representation of the steps in PCR is shown below.
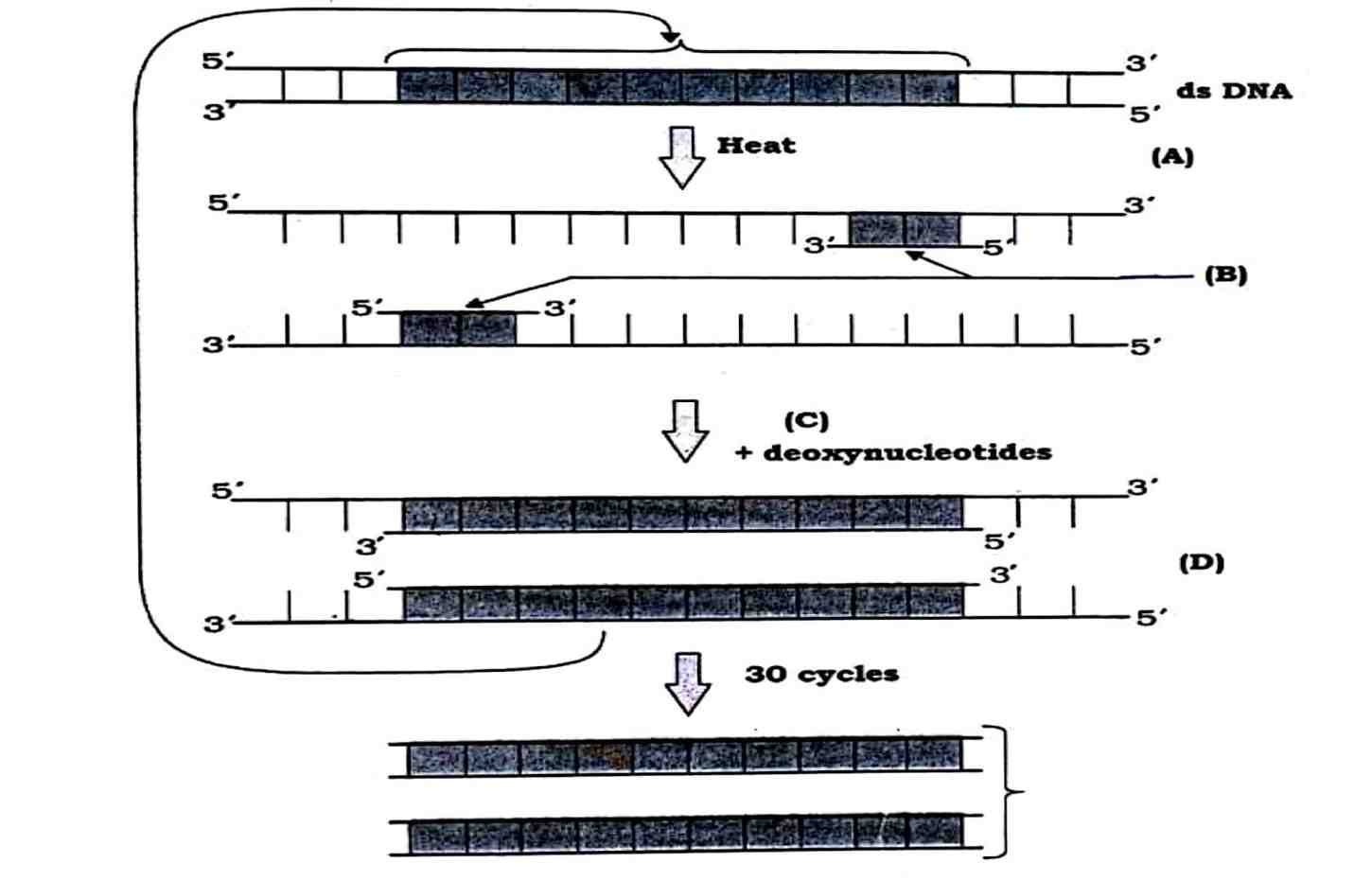
Answer its related following questions :
(i) Name the step of A and D.
Answer – Step A is Denaturation, Step D is Extension (elongation).
(ii) What is the functions of PCR?
Answer – The function of PCR is to amplify (produce multiple copies of) a specific segment of DNA.
(iii) Identify B and what is its chemical nature?
Answer – B is primer; its chemical nature is a short single-stranded DNA sequence.
OR
What is C? Name its source organism.
Answer – C is Taq DNA polymerase; its source organism is Thermus aquaticus.
SECTION – E (5 Marks)
33. Describe the changes that take place from the formation of zygote to implantation in human.
Answer – From the formation of the zygote to implantation, this flow (zygote → cleavage → morula → blastocyst → implantation).
After fertilization, the diploid zygote is formed in the fallopian tube. It undergoes repeated mitotic divisions called cleavage, producing a solid ball of cells known as the morula. As cleavage continues, the morula transforms into a hollow structure called the blastocyst. The blastocyst consists of an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast, which later forms part of the placenta, and an inner cell mass that develops into the embryo. Around 6–7 days after fertilization, the blastocyst reaches the uterus and attaches itself to the endometrium of the uterine wall. This process of attachment and embedding of the blastocyst into the uterine lining is called implantation, which marks the beginning of pregnancy.
OR
Describe the structure of pollen grain in detail.
Answer –
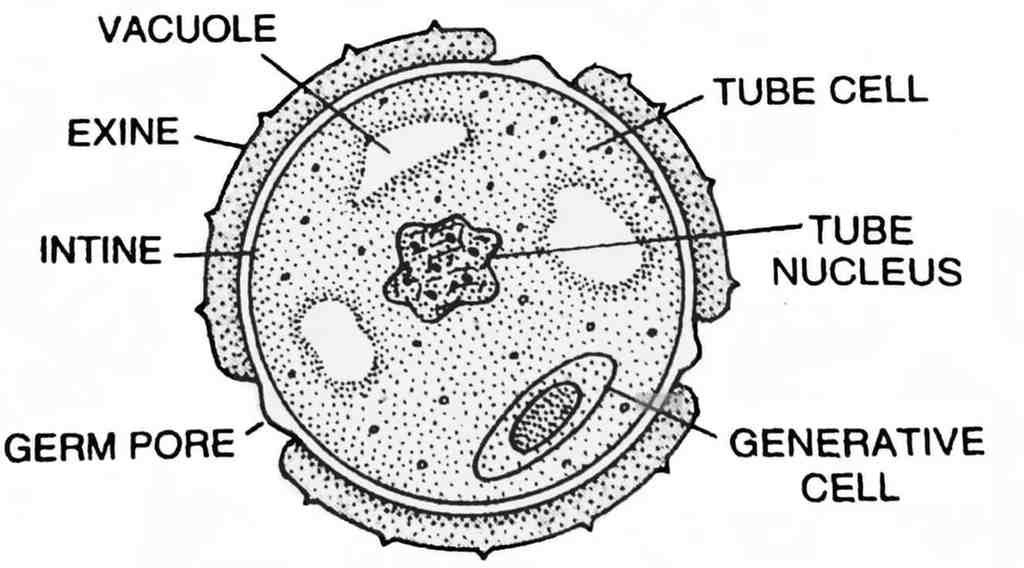
Pollen grain is the male gametophyte of flowering plants. It is generally spherical in shape and very small, about 25–50 µm in diameter. It is surrounded by a two-layered wall. The outer layer (exine) is made of sporopollenin, a highly resistant substance that protects the pollen. Exine has germ pores through which the pollen tube emerges. The inner layer (intine) is thin, made of cellulose and pectin, and helps in the formation of the pollen tube. Inside the pollen grain, there are usually two cells. The vegetative cell is large with abundant cytoplasm and a nucleus, and it forms the pollen tube. The generative cell is small and divides to form two male gametes. Pollen grains may be shed in a 2-celled stage (most plants) or a 3-celled stage (some cereals). Their viability differs among species – short-lived in rice and wheat, but longer in legumes and some other plants.
34. Describe transcription unit.
Answer –
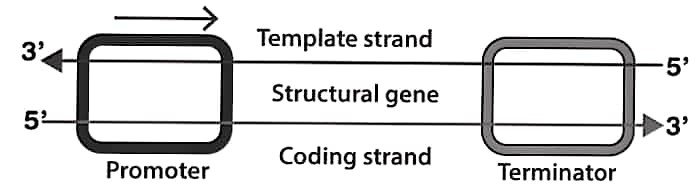
(i) A transcription unit is a segment of DNA transcribed into RNA by RNA polymerase.
(ii) It consists of three regions :
• Promoter : Located towards the 5′ end; provides binding site for RNA polymerase and initiates transcription.
• Structural gene : The DNA sequence that is transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA, or rRNA depending on the gene).
• Terminator : A sequence at the 3′ end where transcription stops and RNA is released.
(iii) In a transcription unit, only one strand of DNA (called the template strand) is transcribed, while the other strand (the coding strand) has the same sequence as RNA (except thymine is replaced by uracil).
(iv) The promoter defines the template strand and direction of transcription.
(v) The RNA formed is complementary to the template strand and plays a role in protein synthesis or other cellular functions.
OR
Describe various chromosomal disorders found in human beings.
Answer – Chromosomal disorders are caused by numerical or structural abnormalities in chromosomes. Some important disorders are :
(i) Down’s syndrome (Trisomy 21) – Caused by an extra copy of chromosome 21. Affected individuals show short stature, flat face, broad forehead, mental retardation, and weak muscles.
(ii) Klinefelter’s syndrome (47, XXY) – Caused by an extra X chromosome in males. Such males are sterile, tall, have underdeveloped testes, enlarged breasts (gynecomastia), and lack secondary sexual characters.
(iii) Turner’s syndrome (45, XO) – Caused by absence of one X chromosome in females. Such females are sterile, short-statured, have underdeveloped ovaries, lack secondary sexual characters, and a webbed neck.
(iv) Cri-du-chat syndrome – Caused by deletion in the short arm of chromosome 5. Infants have a characteristic cat-like cry, mental retardation, and defective development.
(v) Edward’s syndrome (Trisomy 18) – Caused by an extra chromosome 18. It leads to severe developmental delays, small head, clenched fists, and heart/kidney defects.
35. Describe the role of microbes in household products.
Answer – The role of microbes in household products are :
(i) Curd – Lactic acid bacteria (Lactobacillus) convert milk into curd and increase its nutritional quality (e.g., vitamin B12).
(ii) Dosa/Idli batter – Bacteria ferment the rice–urad dal batter, making it soft and fluffy.
(iii) Bread – Yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) produces CO2 during fermentation, helping the dough rise.
(iv) Alcoholic Beverages – Fermentation of sap from palm trees by yeast produces this traditional alcoholic drink.
(v) Cheese and pickles – Different microbes are used in their preparation, giving characteristic taste, aroma, and texture.
(vi) Cleaning Agents – Some cleaning products and bio-enzymatic cleaners contain microbes that break down stains and organic matter.
OR
Describe the role of microbes in the production of Industrial chemicals and enzymes.
Answer – The role of microbes in the production of Industrial chemicals and enzymes are :
(i) Citric Acid Production – Aspergillus niger (fungus) produces citric acid, widely used as a preservative and flavoring agent in food and beverages.
(ii) Vinegar Production – Acetobacter aceti (bacterium) produces acetic acid (vinegar), used in food preservation and pickles.
(iii) Butyric Acid Production – Clostridium butylicum produces butyric acid, used in chemical and plastic industries.
(iv) Lactic Acid Production: Lactobacillus species produce lactic acid, applied in food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries.
(v) Enzyme Production – Aspergillus niger produces pectinase (fruit juice clarification) and lipase (detergent industry). Streptococcus produces streptokinase, a clot-buster medicine used for dissolving blood clots in heart attack patients.
(vi) Antibiotics – Fungi, particularly Penicillium, were the source of the first antibiotic, penicillin, and continue to be used for producing antibiotics to combat bacterial infections.
