Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 10 Science SAT-1 Question Paper 2025 Answer Key. Get the Students Assessment Test (SAT) Class 10 Science question paper with complete solution, accurate answer key, and expert preparation tips. The Haryana Board of School Education (HBSE) conducts SAT as an important assessment for Class 10 students. Best resource for Haryana Board Class 10 SAT Science exam practice, quick revision, and scoring better marks.
HBSE Class 10 Science SAT-1 Question Paper 2025 Answer Key
Instructions :
• All questions are compulsory.
• Questions (1-8) carry 1 mark each.
• Questions (9-11) carry 2 marks each.
• Questions (12-13) carry 3 marks each.
• Questions (14-15) carry 5 marks each.
1. निम्न में से उषमाशोषी अभिक्रिया का चयन करें :
(A) शाक-सब्जियों का विघटित होकर काम्पोस्ट बनना
(B) कैल्शियम कार्बोनेट का बिना बुझा चूना और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड में वियोजित होना
(C) मोमबत्ती का जलना
(D) श्वसन अभिक्रिया
उत्तर – (B) कैल्शियम कार्बोनेट का बिना बुझा चूना और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड में वियोजित होना
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Select endothermic reaction from the following :
(A) Decomposition of vegetable matter into compost
(B) Decomposition of calcium carbonate to form quick lime and carbon dioxide
(C) Burning of a candle
(D) Process of respiration
Answer – (B) Decomposition of calcium carbonate to form quick lime and carbon dioxide
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
2. यदि लेंस के आवर्धन का मान धणात्मक है, तो छवि है :
(A) आभासी तथा सीधा
(B) वास्तविक तथा उलटा
(C) या तो A या B
(D) न तो A और न ही B
उत्तर – (A) आभासी तथा सीधा
If the magnification of a lens has positive value, the image is :
(A) Virtual and erect
(B) Real and inverted
(C) Either A or B
(D) Neither A nor B
Answer – (A) Virtual and erect
3. लार में कौन-सा एंजाइम होता है?
(A) पेप्सिन
(B) ट्रिप्सिन
(C) एमाइलेज
(D) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर – (C) एमाइलेज
Which enzyme is present in saliva?
(A) Pepsin
(B) Tripsin
(C) Amylase
(D) All of the above
Answer – (C) Amylase
4. कौन-सा ऊतक जड़ों से पौधों के विभिन्न भागों तक जल का परिवहन करता है?
उत्तर – जाइलम
Which tissue in plants is responsible for transportation of water from roots to different parts of plants?
Answer – Xylem
5. सफेदी के लिए किसी पदार्थ ‘X’ के विलयन का उपयोग किया जाता है। पदार्थ ‘X’ का सूत्र लिखिए।
उत्तर – Ca(OH)2 (Calcium hydroxide)
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing. Write the formula for substance ‘X’.
Answer – Ca(OH)2 (Calcium hydroxide)
6. उस लेंस की फोकस दूरी …………… होगी जिसकी क्षमता – 2.0 D है ।
उत्तर – यहां पर, क्षमता (P) = – 2 D
फोकस दूरी (f) = 1/P = 1/(–2) = – 0.5 m = – 50 cm
The focal length of a lens of power – 2.0 D is …………..
Answer – Here, Power (P) = – 2 D
Focal length (f) = 1/P = 1/(–2) = – 0.5 m = – 50 cm
7. भोजन के पाचन के लिए अमाशय …………. माध्यम प्रदान करता है।
उत्तर – अम्लीय माध्यम
Stomach provides ……………. medium for digestion of food.
Answer – Acidic medium
8. कथन (A) : अमल को हमेशा लगातार हिलाते हुए जल में मिलाया जाना चाहिए।
कारण (R) : अम्ल को जल में मिलाने से H+ आयनों की सांद्रता प्रति इकाई आयतन में कम हो जाती है।
(a) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं तथा R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण है।
(b) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं लेकिन R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण नहीं है।
(c) A सत्य है लेकिन R गलत है।
(d) A गलत है लेकिन R सही है।
उत्तर – (a) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं तथा R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण है।
Assertion (A) : The acid must always be added to water with constant stirring.
Reason (R) : Mixing of an acid with water decreases the concentration of H+ ions per unit volume.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is correct.
Answer – (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
9. अपवर्तन के नियम लिखें।
उत्तर – (i) आपतित किरण, अपवर्तित किरण और अभिलम्ब एक ही तल में होती हैं।
(ii) आपतन कोण का साइन और अपवर्तन कोण का साइन का अनुपात नियत होता है। (Snell’s Law)
Write down the laws of refraction.
Answer – (i) The incident ray, refracted ray and the normal lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to sine of angle of refraction is constant. (Snell’s Law)
10. हीरे का अपवर्तनांक 2.42 है। इस कथन से क्या अभिप्राय है?
उत्तर – हीरे का अपवर्तनांक 2.42 होने का अर्थ है कि निर्वात में प्रकाश की गति, हीरे में प्रकाश की गति से 2.42 गुना अधिक है।
The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer – The refractive index of diamond being 2.42 means the speed of light in vacuum is 2.42 times the speed of light in diamond.
11. वियोजन अभिक्रियाओं को संयोजन अभिक्रियाओं के विपरीत क्यों कहा जाता है? इन अभिक्रियाओं के लिए समीकरण लिखें।
उत्तर – वियोजन अभिक्रियाएँ संयोजन अभिक्रियाओं के विपरीत होती हैं क्योंकि संयोजन में दो या अधिक पदार्थ मिलकर एक उत्पाद बनाते हैं जबकि वियोजन में एक पदार्थ टूटकर दो या अधिक पदार्थ बनाता है।
संयोजन: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
वियोजन: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer – Decomposition reactions are opposite of combination reactions because in combination two or more substances combine to form one, while in decomposition one substance breaks into two or more.
Combination: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Decomposition: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
12. अवतल दर्पण द्वारा बनने वाले प्रतिबिम्ब का किरण आरेख खींचिए जब वस्तु को दर्पण के वक्रता केंद्र C पर रखा जाता है। प्रतिबिंब की स्थिति, आकार और प्रकृति का भी उल्लेख कीजिए।
उत्तर – जब वस्तु को अवतल दर्पण के वक्रता केंद्र C पर रखा जाता है :
• प्रतिबिंब C पर ही बनेगा
• आकार वस्तु के बराबर होगा
• प्रकृति वास्तविक और उलटा होगा
Draw a ray diagram and also state the position, the relative size and the nature of image formed by a concave mirror when the object is placed at center of curvature C.
Answer – When the object is placed at center of curvature C :
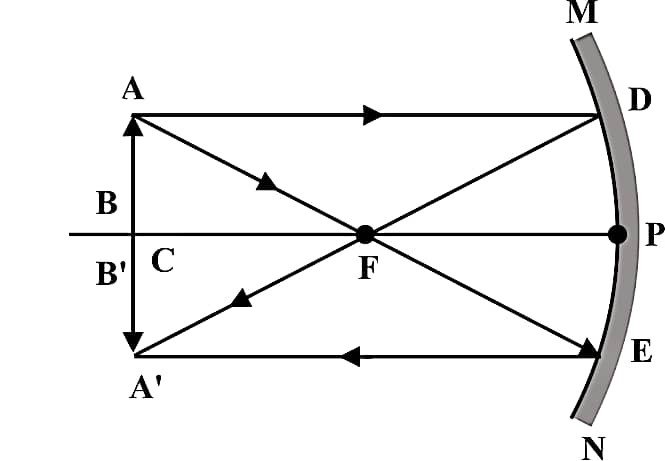
• Image forms at C
• same size
• real and inverted
13. वायवीय तथा अवायवीय श्वसन में अन्तर बताओ।
उत्तर –
| वायवीय श्वसन | अवायवीय श्वसन |
| 1. जब इस प्रकार का श्वसन होता है तो ऑक्सीजन मौजूद होती है। | 1. इस प्रकार की श्वसन प्रक्रिया में ऑक्सीजन अनुपस्थित होती है। |
| 2. श्वसन के इस रूप में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान होता है। | 2. श्वसन के इस रूप में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान नहीं होता है। |
| 3. यह साइटोप्लाज्म और माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया में पाया जा सकता है। | 3. यह केवल कोशिका द्रव्य में पाया जा सकता है। |
| 4. ग्लूकोज कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और पानी में टूट जाता है। | 4. ग्लूकोज एथिल अल्कोहल, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और ऊर्जा में टूट जाता है। |
| 5. स्तनधारियों जैसे सभी उच्च जीवों में इस प्रकार की श्वसन क्रिया होती है। | 5. निचले जीव जैसे बैक्टीरिया और यीस्ट इस प्रकार का उपयोग करते हैं। अन्य जीवों में यह भारी गतिविधियों के दौरान होता है। |
Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Answer –
| Aerobic Respiration | Anaerobic Respiration |
| 1. Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. | 1. Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. |
| 2. Gases are exchanged in this form of respiration. | 2. Gases are not exchanged in this form of respiration. |
| 3. It can be found in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. | 3. It can be found only in the cytoplasm. |
| 4. Glucose breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. | 4. Glucose breaks down into ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy. |
| 5. All higher organisms such as mammals have this type of respiration. | 5. Lower organisms such as bacteria and yeast use this type. In other organisms, it occurs during heavy activities. |
14. (a) पीतल एवं तांबे के बर्तनों में दही और खट्टे पदार्थ क्यों नहीं रखने चाहिए?
उत्तर – दही और खट्टे पदार्थों में लैक्टिक अम्ल और अन्य कार्बनिक अम्ल होते हैं। जब इन्हें तांबे या पीतल के बर्तनों में रखा जाता है, तो ये अम्ल धातु के साथ अभिक्रिया करते हैं। इस अभिक्रिया से तांबे के लवण या जस्ता लवण बनते हैं, जो हरे या नीले रंग की परत के रूप में दिखाई देते हैं। ये लवण विषैले (जहरीले) होते हैं। अगर ऐसा भोजन खाया जाए, तो इससे फ़ूड पॉइज़निंग, उल्टी, पेट की समस्याएँ और अन्य स्वास्थ्य समस्याएँ हो सकती हैं।
इसलिए, दही और खट्टे पदार्थों को कभी भी पीतल और तांबे के बर्तनों में नहीं रखना चाहिए।
Why should curd and sour substances not be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer – Curd and sour substances contain lactic acid and other organic acids. When these are kept in copper or brass vessels, the acids react with the metal. This reaction forms copper salts or zinc salts, which appear as a greenish or bluish layer. These salts are toxic (poisonous) in nature. If such food is eaten, it may cause food poisoning, vomiting, stomach problems, and other health issues.
Therefore, curd and sour substances should never be kept in brass and copper vessels.
(b) धोने का सोडा के दो महत्वपूर्ण उपयोग बताइए।
उत्तर – वाशिंग सोडा (Na2CO3·10H2O) के दो महत्वपूर्ण उपयोग हैं :
• इसका उपयोग पानी की स्थायी कठोरता को दूर करने के लिए किया जाता है।
• इसका उपयोग कपड़े धोने और सफाई एजेंट के रूप में किया जाता है।
Give two important uses of washing soda.
Answer – Two important uses of washing soda (Na2CO3·10H2O) are :
• It is used to remove the permanent hardness of water.
• It is used in washing clothes and as a cleaning agent.
(c) भोजन के पाचन में पितरस की क्या भूमिका है?
उत्तर – यकृत द्वारा निर्मित और पित्ताशय में संग्रहित पित्त, बड़ी वसा की गोलियाँ को छोटी बूंदों में बदलकर वसा के पाचन में मदद करता है। इससे एंजाइमों के कार्य करने के लिए सतह क्षेत्र बढ़ जाता है, जिससे वसा का पाचन और अवशोषण आसान हो जाता है।
What is the role of bile in digestion of food?
Answer – Bile, produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder, helps in the digestion of fats by emulsifying large fat globules into small droplets. This increases the surface area for enzymes to act, making fat digestion and absorption easier.
OR
(a) CaOCl2 यौगिक का प्रचलित नाम क्या है? CaOCl2 यौगिक के दो उपयोग भी लिखिए।
उत्तर – CaOCl2 का सामान्य नाम ब्लीचिंग पाउडर है।
ब्लीचिंग पाउडर के उपयोग इस प्रकार हैं :
• इसका उपयोग पीने के पानी को कीटाणुओं से मुक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है।
• इसका उपयोग कपड़ा और कागज़ उद्योगों में विरंजन कारक के रूप में किया जाता है।
What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2? Also write two uses of CaOCl2.
Answer – The common name of CaOCl2 is Bleaching Powder.
Uses of bleaching powder are :
• It is used for disinfecting drinking water to kill germs.
• It is used as a bleaching agent in the textile and paper industries.
(b) आसवित जल विद्युत का चालक क्यों नहीं होता, जबकि वर्षा का जल होता है?
उत्तर – आसवित (आसुत) जल शुद्ध जल होता है और इसमें कोई भी घुला हुआ लवण या खनिज नहीं होता। चूँकि इसमें कोई मुक्त आयन नहीं होते, इसलिए यह विद्युत का संचालन नहीं कर सकता।
दूसरी ओर, वर्षा का जल वायुमंडल से कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (CO2) को घोलता है और कुछ घुले हुए लवण और खनिज भी अपने साथ ले जाता है। ये विलयन में आयन प्रदान करते हैं, जो विद्युत के चालन में सहायक होते हैं।
इसलिए, आसवित जल विद्युत का कुचालक होता है, जबकि वर्षा का जल सुचालक होता है।
Why does distilled water not conduct electricity, whereas rain water does?
Answer – Distilled water is pure water and does not contain any dissolved salts or minerals. Since it has no free ions, it cannot conduct electricity.
Rain water, on the other hand, dissolves carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and also carries some dissolved salts and minerals. These provide ions in the solution, which help in the conduction of electricity.
Therefore, distilled water is a poor conductor of electricity, while rain water is a good conductor.
(c) तेल एवं वसा युक्त खाद्य पदार्थों को नाइट्रोजन के साथ प्रभावित क्यों किया जाता है?
उत्तर – तेल और वसा युक्त खाद्य पदार्थों को ऑक्सीकरण के कारण खराब होने से बचाने के लिए नाइट्रोजन से प्रभावित किया जाता है क्योंकि उनमें बासीपन आ सकता है और उनका स्वाद और गंध खराब हो सकता है।
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer – Oil and fat-containing food items are flushed with nitrogen because it prevent spoilage due to oxidation, which can lead to rancidity and an unpleasant taste and smell.
15. मानव हृदय कितने कक्षीय होता है? हृदय का नामांकित चित्र बनाकर रक्त के दोहरे परिसंचरण की व्याख्या करें।
उत्तर – मानव हृदय में चार कक्ष होते हैं: दो आलिंद (दायाँ और बायाँ) तथा दो निलय (दायाँ और बायाँ)।
हृदय की द्विगुणी परिसंचरण प्रणाली में दो अलग-अलग मार्ग शामिल होते हैं : फुफ्फुसीय परिसंचरण – हृदय से फेफड़ों तक और वापस, प्रणालीगत परिसंचरण – हृदय से शरीर के अन्य भागों तक और वापस।
द्विगुणी परिसंचरण की व्याख्या :
(1) फुफ्फुसीय परिसंचरण (Pulmonary Circulation) –
• शरीर से अशुद्ध (डीऑक्सीजन युक्त) रक्त दाएँ आलिंद में प्रवेश करता है।
• इसके बाद यह दाएँ निलय में चला जाता है।
• दायाँ निलय इस रक्त को फुफ्फुसीय धमनी के माध्यम से फेफड़ों तक पंप करता है।
• फेफड़ों में रक्त शुद्ध (ऑक्सीजन युक्त) हो जाता है।
• शुद्ध रक्त फुफ्फुसीय शिराओं के द्वारा बाएँ आलिंद में लौट आता है।
(2) प्रणालीगत परिसंचरण / सामान्य परिसंचरण (Systemic Circulation) –
• बाएँ आलिंद से शुद्ध रक्त बाएँ निलय में पहुँचता है।
• बायाँ निलय इस शुद्ध रक्त को शरीर के सभी भागों में महाधमनी (Aorta) के द्वारा पंप करता है।
• रक्त धमनियों, धमनिकाओं और केशिकाओं से होकर शरीर की कोशिकाओं तक ऑक्सीजन और पोषक तत्व पहुँचाता है।
• अशुद्ध रक्त वापस शिरिकाओं (Venules) और शिराओं (Veins) के माध्यम से हृदय के दाएँ आलिंद में लौट आता है।
How many Chambers are there in human heart? Draw a well labeled diagram of human heart and explain the process of double circulation.
Answer – The human heart has four chambers: two atria (right and left) and two ventricles (right and left). The heart’s double circulatory system involves two separate pathways: the pulmonary circulation (heart to lungs and back) and the systemic circulation (heart to body and back).
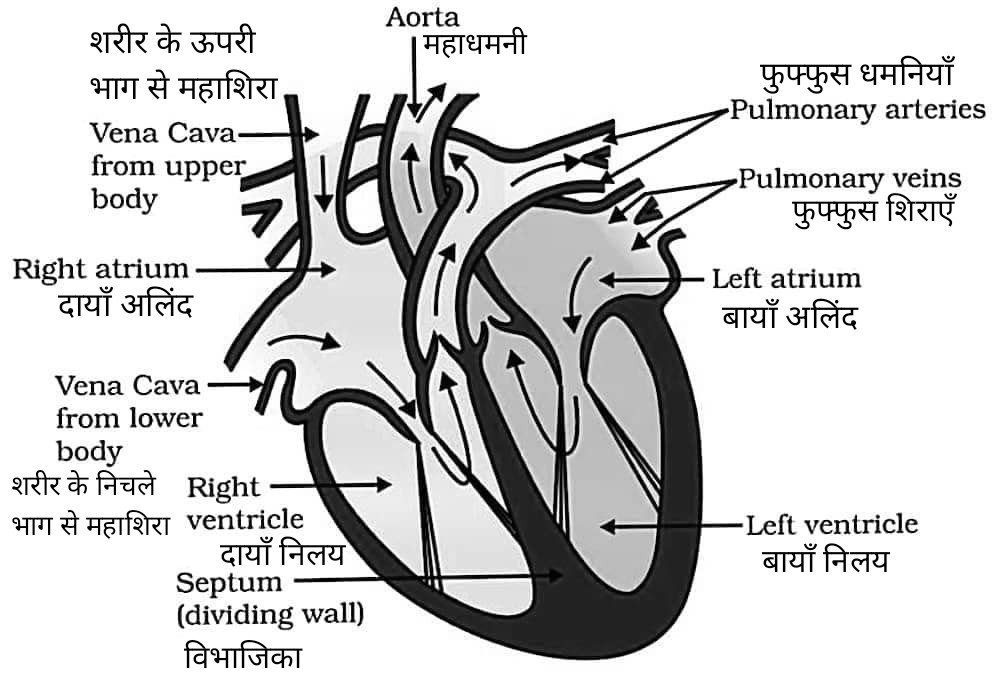
Explanation of Double Circulation :
(1) Pulmonary Circulation –
• Deoxygenated blood from the body enters the right atrium.
• It then passes into the right ventricle.
• The right ventricle pumps the blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery.
• In the lungs, the blood gets oxygenated.
Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium via the pulmonary veins.
(2) Systemic Circulation –
• Oxygenated blood from the left atrium enters the left ventricle.
• The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body through the aorta, the largest artery.
• Blood travels through arteries, arterioles, and capillaries, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues.
• Deoxygenated blood then returns to the heart through venules and veins.
