HBSE Class 10 Science Pre-Board Question Paper 2026 Answer Key
SECTION – A (Physics)
1. ड्राइवर द्वारा पीछे की ओर देखने के लिए उपयोग किया जाने वाला दर्पण है : (1 Mark)
(A) अवतल
(B) उत्तल
(C) समतल
(D) उपरोक्त में से कोई नहीं
उत्तर – (B) उत्तल
The mirror used by a driver to view the rear side is :
(A) Concave
(B) Convex
(C) Plane
(D) None of the above
Answer – (B) Convex
2. किसी धातु चालक का प्रतिरोध निर्भर करता है : (1 Mark)
(A) चालक की लंबाई पर
(B) अनुप्रस्थ काट का क्षेत्रफल पर
(C) चालक की प्रकृति पर
(D) उपरोक्त सभी पर
उत्तर – (D) उपरोक्त सभी पर
The resistance of a metallic conductor depends on :
(A) Length of conductor
(B) Area of cross section
(C) Nature of material
(D) All of the above
Answer – (D) All of the above
3. विद्युत आवेश का SI मात्रक …………. है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – कूलाम
SI unit of electric charge is ………….
Answer – Coulomb
4. तारों का टिमटिमाना प्रकाश की कौन सी घटना पर आधारित है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – वायुमंडलीय अपवर्तन
Name the phenomenon of light responsible for twinkling of stars.
Answer – Atmospheric refraction
5. नीचे दिए गए प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं: अभिकथन (A) और कारण (R), नीचे दिए गए उपयुक्त विकल्प का चयन करके प्रश्न का उत्तर दें। (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : कांच के प्रिज्म से गुजरने पर सफेद प्रकाश सात रंगों में विभाजित हो जाता है।
कारण (R) : सफ़ेद प्रकाश को प्रिज्म से गुजारने पर प्रकाश का प्रकीर्णन होता है।
(A) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं और R, A की सही व्याख्या है।
(B) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं और R, A का सही व्याख्या नहीं है
(C) A सत्य है और R असत्य है।
(D) A असत्य है और R सत्य है।
उत्तर – (A) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं और R, A की सही व्याख्या है।
The question below consists of two statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer the question by selecting the appropriate option given below.
Assertion (A) : White light splits into seven colours when it passes through a glass prism.
Reason (R) : A glass prism scatters white light when it passes through a glass prism.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true and R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Answer – (A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
6. अंतरिक्ष यात्रियों को आकाश काला क्यों दिखाई देता है? (2 Marks)
उत्तर – अंतरिक्ष में वायुमंडल नहीं होता, इसलिए प्रकाश का प्रकीर्णन नहीं होता और आकाश काला दिखाई देता है।
Why sky appears black to astronauts?
Answer – Because there is no atmosphere in space, scattering of light does not occur, so the sky appears black.
7. एक 4 Ω प्रतिरोधक प्रति सेकंड 100 J ऊष्मा ऊर्जा उत्पन्न करता है। प्रतिरोधक के सिरों पर विभवांतर की ज्ञात करें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – दिया गया, R = 4 Ω, H = 100 J/s = 100 W
H = V2/R
V2 = H × R = 100 × 4 = 400
V = 20 V
Α 4 Ω resistor produces 100 J heat energy per second. Calculate the potential. difference across the resistor.
Answer – Given, R = 4 Ω, H = 100 J/s = 100 W
H = V2/R
V2 = H × R = 100 × 4 = 400
V = 20 V
8. विद्युत् विभवांतर मापने के लिए उपयोग किए जाने वाले यंत्र का नाम बताइए। इसे विद्युत परिपथ में कैसे जोड़ा जाता है? 1kWh को परिभाषित कीजिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – विद्युत विभवांतर मापने का यंत्र वोल्टमीटर है। इसे परिपथ में समांतर क्रम में जोड़ा जाता है। 1 kWh वह ऊर्जा है जो 1 kW शक्ति को 1 घंटे तक उपयोग करने पर व्यय होती है।
Name a device used to measure potential difference. How is it connected in an electric circuit? Define 1kWh.
Answer – The device is voltmeter. It is connected in parallel. 1 kWh is the energy consumed when a power of 1 kW is used for 1 hour.
9. एक छड़ चुंबक के चारों ओर चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ खींचे और चुंबकीय बल रेखाओं के गुणों की सूचि बनाइए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – (i) चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ सदैव बंद वक्र होती हैं।
(ii) ये रेखाएँ उत्तर ध्रुव से निकलकर दक्षिण ध्रुव में प्रवेश करती हैं (बाह्य क्षेत्र में)।
(iii) दो चुंबकीय क्षेत्र रेखाएँ कभी एक-दूसरे को नहीं काटतीं।
(iv) जहाँ क्षेत्र रेखाएँ अधिक सघन होती हैं, वहाँ चुंबकीय क्षेत्र अधिक प्रबल होता है।
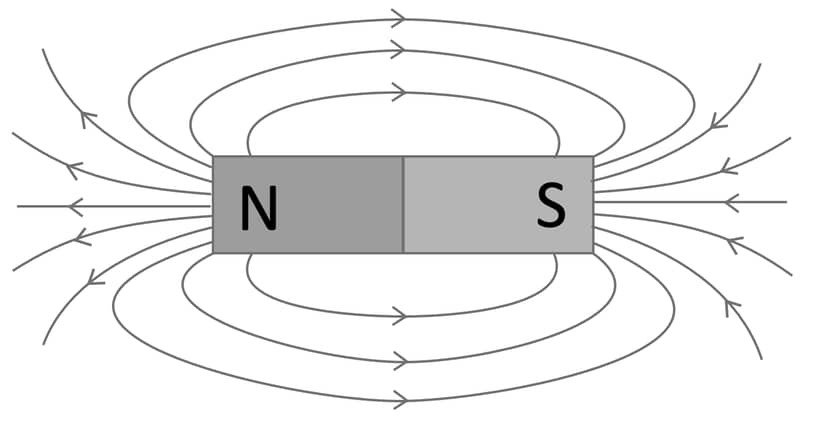
Draw magnetic field lines around a bar magnet and write the properties of magnetic lines of force.
Answer – (i) Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
(ii) They go from N to S outside the magnet.
(iii) No two field lines intersect each other.
(iv) Greater density of lines means stronger field.
10. (a) प्रकाश के अपवर्तन के नियम लिखिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – अपवर्तन के नियम: (i) आपतित किरण, अपवर्तित किरण और सतह का अभिलंब आपतन बिंदु पर एक ही तल में होते हैं। (ii) मीडिया के दिए गए जोड़े के लिए आपतन कोण की ज्या और अपवर्तन कोण की ज्या का अनुपात एक स्थिरांक है। इस नियम को स्नेल के अपवर्तन के नियम के रूप में भी जाना जाता है अर्थात sini/sinr = n
State the laws of refraction of light.
Answer – Laws of refraction: (i) The incident ray, refracted ray, and normal to the interface lie in the same plane at the point of incidence. (ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is a constant for a given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction i.e. sini/sinr = n
(b) लेंस की क्षमता से आप क्या समझते हैं? इसकी मात्रक को परिभाषित करें। 2 मीटर फोकस दूरी के उत्तल लेंस की क्षमता जात करें। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – लेंस की क्षमता वह राशि है जो यह दर्शाती है कि लेंस प्रकाश किरणों को कितनी अधिक अभिसारित या अपसारित करता है। लेंस की क्षमता फोकस दूरी के व्युत्क्रम के बराबर होती है। लेंस की क्षमता का सूत्र, P = 1/f
लेंस की क्षमता की मात्रक डायॉप्टर है, जिस लेंस की फोकस दूरी 1 मीटर हो, उसकी क्षमता 1 डायॉप्टर होती है।
फोकस दूरी, f = +2 m (उत्तल लेंस के लिए f धनात्मक होता है)
P = 1/f = 1/2 = +0.5 D
What do you mean by power of a lens? Define its unit. Calculate the power of a convex lens of focal length 2m.
Answer – The power of a lens indicates its ability to converge or diverge light rays. It is defined as the reciprocal of the focal length of the lens (in metres).
The unit of power of a lens is dioptre (D).
A lens having focal length of 1 metre has a power of 1 dioptre.
Focal length, f = +2m (for a convex lens, focal length is positive)
P = 1/f = 1/2 = +0.5 D
SECTION – B (Chemistry)
11. निम्नलिखित में से कौन ऑक्सीकरण को रोक सकता है?(1 Mark)
(A) नमी
(B) धूल
(C) एंटीऑक्सीडेंट
(D) उपर्युक्त सभी
उत्तर – (C) एंटीऑक्सीडेंट
Which of the following can prevent oxidation?
(A) Moisture
(B) Dust
(C) Antioxidant
(D) All of these
Answer – (C) Antioxidant
12. सोडियम सल्फेट और बेरियम क्लोराइड के जलीय घोल को मिलाने पर किस प्रकार की रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया होती है? (1 Mark)
(A) अपघटन
(B) संयोजन
(C) अवक्षेपण
(D) विस्थापन
उत्तर – (C) अवक्षेपण
What type of chemical reaction occurs when aqueous solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed?
(A) Decomposition
(B) Combination
(C) Precipitation
(D) Displacement
Answer – (C) Precipitation
13. एथेनोइक अम्ल ………….. के साथ अभिक्रिया करके इथाइल एथेनोएट बनाता है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – एथेनॉल
Ethanoic acid reacts with …………. to form ethyl ethanoate.
Answer – Ethanol
14. ऐसी धातु का उदाहरण दीजिए जो ऊष्मा की सबसे अच्छी सुचालक है। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – चाँदी
Give an example of a metal which is the best conductor of heat.
Answer – Silver
15. नीचे दिए गए प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं: अभिकथन (A) और कारण (R), नीचे दिए गए उपयुक्त विकल्प का चयन करके प्रश्न का उत्तर दें। (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : शुष्क कॉपर सल्फेट क्रिस्टल नीले रंग के होते हैं।
कारण (R) : कॉपर सल्फेट क्रिस्टल में क्रिस्टलीकरण का पानी होता है।
(A) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं, और R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण है।
(B) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं, और R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण नहीं है।
(C) A सत्य है लेकिन R असत्य है।
(D) A असत्य है लेकिन R सत्य है।
उत्तर – (D) A असत्य है लेकिन R सत्य है।
The question below consists of two statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer the question by selecting the appropriate option given below.
Assertion (A) : Dry copper sulphate crystals are blue in colour.
Reason (R) : Copper sulphate crystals contain water of crystallization.
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false d) A is false but R is true.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Answer – (D) A is false and R is true.
16. ऊष्माक्षेपी और ऊष्माशोषी अभिक्रियाओं से क्या तात्पर्य है? उदाहरण दीजिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – जिन रासायनिक अभिक्रियाओं में ऊष्मा ऊर्जा निकलती है, उन्हें ऊष्माक्षेपी अभिक्रियाएँ कहते हैं। उदाहरण: ईंधन का दहन
• जिन रासायनिक अभिक्रियाओं में ऊष्मा ऊर्जा अवशोषित होती है, उन्हें ऊष्माशोषी अभिक्रियाएँ कहते हैं। उदाहरण: प्रकाश संश्लेषण
What do you mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer – Chemical reactions in which heat is released are called exothermic reactions. Example: Combustion of methane
• Chemical reactions in which heat is absorbed are called endothermic reactions. Example: Photosynthesis
17. एल्केन, एल्कीन और एल्काइन के लिए सामान्य सूत्र लिखें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – एल्केन: CnH2n+2
एल्कीन: CnH2n
एल्काइन: CnH2n–2
Write general formula for alkane, alkenes and alkynes.
Answer – Alkane: CnH2n+2
Alkene: CnH2n
Alkyne: CnH2n–2
18. बेकिंग सोडा के तीन उपयोग लिखिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – बेकिंग सोडा (सोडियम बाईकार्बोनेट, NaHCO3) के तीन उपयोग निम्नलिखित हैं :
(i) बेकिंग में केक, ब्रेड आदि को फुलाने के लिए किया जाता है।
(ii) यह अम्लता को दूर करने के लिए एंटासिड के रूप में उपयोग होता है।
(iii) इसका उपयोग अग्निशामक यंत्रों में किया जाता है।
Write three uses of baking soda.
Answer – Three uses of baking soda (Sodium bicarbonate, NaHCO3) are :
(i) It is used in baking to make cakes and bread soft and fluffy.
(ii) It is used as an antacid to relieve acidity.
(iii) It is used in fire extinguishers.
19. ब्लीचिंग पाउडर क्या है? इसका उत्पादन कैसे किया जाता है? इसके उत्पादन के लिए संतुलित रासायनिक समीकरण लिखिए। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – ब्लीचिंग पाउडर एक सफेद रंग का चूर्ण होता है, जिसका रासायनिक नाम कैल्शियम ऑक्सीक्लोराइड (CaOCl2) है। इसका उपयोग वस्त्रों की सफेदी, जल की शुद्धि तथा कीटाणुनाशक के रूप में किया जाता है।
ब्लीचिंग पाउडर का उत्पादन शुष्क बुझा हुआ चूना [Ca(OH)2] पर क्लोरीन गैस प्रवाहित करके किया जाता है।
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
What is bleaching powder? How is it produced? Write balanced chemical equation for its production.
Answer – Bleaching powder is a white powder whose chemical name is calcium oxychloride (CaOCl2). It is used for bleaching cotton and linen, disinfecting drinking water and as a germicide.
It is produced by passing chlorine gas over dry slaked lime [Ca(OH)2].
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
20. (a) उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड क्या हैं? उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड के दो उदाहरण दीजिए। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – उभयधर्मी ऑक्साइड वे ऑक्साइड होते हैं जो अम्ल और क्षार दोनों के साथ अभिक्रिया करके लवण और जल बनाते हैं, अर्थात् ये अम्लीय और क्षारीय दोनों प्रकार के गुण प्रदर्शित करते हैं। उदाहरण: Al2O3, ZnO
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer – Amphoteric oxides are those oxides which react with both acids and bases to form salt and water. Thus, they show both acidic and basic properties. Example: Al2O3, ZnO
(b) साबुन की सफाई क्रिया की क्रियाविधि समझाएँ। (3 Marks)
उत्तर – साबुन की सफाई प्रक्रिया में साबुन के अणु एक लंबी हाइड्रोकार्बन श्रृंखला (कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल भाग) और एक आयनिक सिरा (COO– Na+) रखते हैं, जिससे उनमें एक जलरागी तथा एक जलविरागी सिरा होता है। पानी में घुलने पर ये अणु मिलकर मिसेल नामक गोलाकार संरचना बनाते हैं, जिसमें जलरागी सिरे बाहर पानी की ओर रहते हैं, जबकि जलविरागी पूँछें अंदर की ओर मुड़कर तेल या गंदगी में फँस जाती हैं। इस प्रकार गंदगी मिसेल के भीतर बंद होकर पानी में निलंबित हो जाती है और धुलाई के समय पानी के साथ बह जाती है, जिससे कपड़े साफ हो जाते हैं।
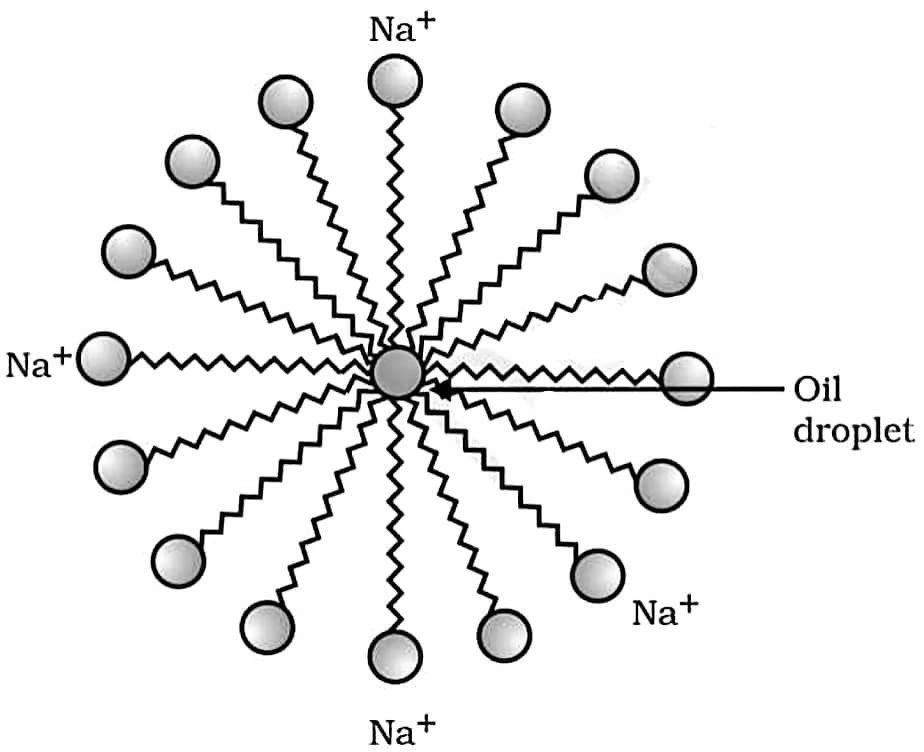
Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer – In the cleaning action of soap, soap molecules consist of a long hydrocarbon chain (carboxylic acid part) and an ionic end (COO⁻ Na⁺), due to which each molecule has one hydrophilic and one hydrophobic end. When soap dissolves in water, the molecules form micelles, with hydrophilic ends facing water and hydrophobic tails embedded in oil or dirt. Thus, the dirt gets trapped inside the micelles, remains suspended in water, and is washed away during rinsing, leaving the clothes clean.
SECTION – C (Biology)
21. मस्तिष्क का कौन-सा भाग मुख्य सोचने वाला भाग है? (1 Mark)
(A) अग्रमस्तिष्क
(B) मध्यमस्तिष्क
(C) पश्चमस्तिष्क
(D) अनुमस्तिष्क
उत्तर – (A) अग्रमस्तिष्क
Which part of brain is main thinking part?
(A) Fore-brain
(B) Mid-brain
(C) Hind-brain
(D) Cerebellum
Answer – (A) Fore-brain
22. मानव महिलाओं में कौन सा गुणसूत्र पाया जाता है? (1 mark)
(A) X
(B) Y
(C) ये दोनों
(D) इनमें से कोई नहीं
उत्तर – (A) X
Which chromosome is found in human females?
(A) X
(B) Y
(C) Both of these
(D) None of these
Answer – (A) X
23. ओजोन अणु ऑक्सीजन के …………. परमाणुओं से बनते हैं। (1 Mark)
उत्तर – तीन
Ozone molecules are formed from …………. atoms of oxygen.
Answer – Three
24. गुरुत्वानुवर्तन क्या है? (1 Mark)
उत्तर – गुरुत्वानुवर्तन वह प्रक्रिया है जिसमें पौधों के भाग गुरुत्वाकर्षण बल के प्रति प्रतिक्रिया में वृद्धि करते हैं।
What is geotropism?
Answer – Geotropism is the growth movement of plant parts in response to gravity.
25. नीचे दिए गए प्रश्न में दो कथन हैं: अभिकथन (A) और कारण (R), नीचे दिए गए उपयुक्त विकल्प का चयन करके प्रश्न का उत्तर दें। (1 Mark)
अभिकथन (A) : सभी पपीते के पौधे फल नहीं देते हैं।
कारण (R) : पपीते के पौधों में केवल एकलिंगी फूल होते हैं।
(A) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं, और R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण है।
(B) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं, और R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण नहीं है।
(C) A सत्य है लेकिन R असत्य है।
(D) A असत्य है लेकिन R सत्य है।
उत्तर – (A) A और R दोनों सत्य हैं, और R, A का सही स्पष्टीकरण है।
The question below consists of two statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer the question by selecting the appropriate option given below.
Assertion (A) : All papaya plants do not bear fruits.
Reason (R) : Papaya plants have only unisexual flowers.
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
(C) A is true and R is false.
(D) A is false and R is true.
Answer – (A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
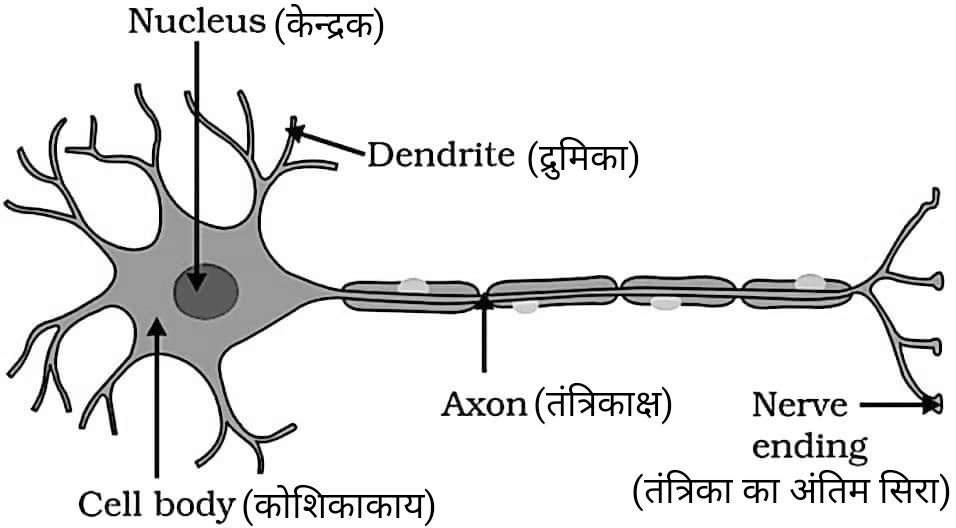
26. तंत्रिका कोशिका की संरचना बनाएँ। (2 Marks)
Draw the labelled structure of a neuron.
Answer –
27. आप अपशिष्ट निपटान की समस्या को कम करने में कैसे मदद कर सकते हैं? कोई दो तरीके बताएँ। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – हम अपशिष्ट निपटान की समस्या को कम करने में इस प्रकार सहायता कर सकते हैं :
(i) जैव अपघट्य और अजैव अपघट्य कचरे का पृथक्करण करके।
(ii) वस्तुओं का पुनः उपयोग करके कचरे की मात्रा कम करके।
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer – We can help in reducing the problem of waste disposal by :
(i) Segregating waste into biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste.
(ii) Reusing materials to reduce the amount of waste generated.
28. यौवन के समय लड़कों में क्या परिवर्तन दिखाई देते हैं? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – यौवन के समय लड़कों में निम्नलिखित परिवर्तन दिखाई देते हैं :
(i) कद में वृद्धि होती है तथा मांसपेशियों का विकास होता है, जिससे कंधे चौड़े हो जाते हैं।
(ii) स्वरयंत्र (लैरिंक्स) के विकास के कारण आवाज भारी हो जाती है।
(iii) चेहरे (दाढ़ी-मूंछ), छाती, बगल और जननांगों के पास बाल उगते हैं तथा जनन अंगों का विकास होता है।
What are the changes seen in boys at the time of puberty?
Answer – At the time of puberty, the following changes are seen in boys :
(i) Increase in height and development of muscles; shoulders become broader.
(ii) Voice becomes deep due to the development of the voice box (larynx).
(iii) Growth of hair on face (beard and moustache), chest, armpits and pubic region, and development of reproductive organs.
29. मंडल के प्रयोगों से कैसे पता चलता है कि लक्षण प्रभावी या अप्रभावी हो सकते हैं? (3 Marks)
उत्तर – मंडल के मटर के पौधों पर किए गए प्रयोगों से यह सिद्ध हुआ कि लक्षण प्रभावी और अप्रभावी हो सकते हैं। जब शुद्ध लंबे तथा शुद्ध बौने मटर के पौधों का संकरण किया गया, तो F1 पीढ़ी में सभी पौधे लंबे प्राप्त हुए। इससे यह स्पष्ट हुआ कि लंबापन प्रभावी लक्षण है।
जब F1 पीढ़ी के पौधों का आपस में संकरण किया गया, तो F2 पीढ़ी में लंबे और बौने पौधे 3 : 1 के अनुपात में प्राप्त हुए। इससे यह सिद्ध हुआ कि बौनापन एक अप्रभावी लक्षण है, जो F1 पीढ़ी में दबा रहता है लेकिन F2 पीढ़ी में पुनः प्रकट हो जाता है।
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer – Mendel’s experiments on pea plants proved that traits can be dominant or recessive. When pure tall and pure dwarf pea plants were crossed, all the plants obtained in the F1 generation were tall. This showed that tallness is a dominant trait.
When the plants of the F1 generation were self-pollinated, the F2 generation produced tall and dwarf plants in the ratio of 3 : 1. This proved that dwarfness is a recessive trait, which remains hidden in the F1 generation but reappears in the F2 generation.
30. (a) गर्भनिरोधक क्या है? गर्भनिरोधक के विभिन्न तरीकों की व्याख्या करें। (2 Marks)
उत्तर – गर्भनिरोधक वे विधियाँ हैं जिनका उपयोग गर्भधारण को रोकने के लिए किया जाता है। इनमें यांत्रिक विधियाँ जैसे कंडोम और कॉपर-T शामिल हैं, जो शुक्राणुओं को अंडाणु तक पहुँचने से रोकती हैं। हार्मोनल विधियाँ जैसे गर्भनिरोधक गोलियाँ अंडोत्सर्जन को रोकती हैं, जबकि शल्य विधियाँ जैसे वासेक्टॉमी और ट्यूबेक्टॉमी स्थायी गर्भनिरोधक उपाय हैं।
What is contraception? Explain different methods of contraception.
Answer – Contraception refers to methods used to prevent pregnancy. Mechanical methods such as condoms and Copper-T prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Hormonal methods like contraceptive pills prevent ovulation, while surgical methods such as vasectomy and tubectomy are permanent methods of contraception.
(b) मानव पाचन तंत्र का एक नामांकित आरेख बनाएँ। (3 Marks)
Draw a labelled diagram of human digestive system.
Answer –

