Haryana Board (HBSE) Class 8 Science Question Paper 2024 PDF Download. HBSE Class 8 Science Question Paper 2024. Haryana Board Class 8th Science Question Paper 2024. Class 8 Science Paper 2024 Haryana Board. HBSE Class 8th Science Question Paper 2024 with Answer. Haryana Board Class 8th Science Question Paper 2024 Solution. हरियाणा बोर्ड कक्षा 8 विज्ञान पेपर 2024.
HBSE Class 8 Science Question Paper 2024 Answer Key
Part A – MCQ (1 Mark)
1. अग्न्याशय इन में से किस के लिए जिम्मेदार है?
(a) वसा के चयापचय
(b) रक्त चाप
(c) रक्त शर्करा का स्तर
(d) विद्युत-अपघट्य संतुलन
उत्तर – (c) रक्त शर्करा का स्तर
Pancreas is responsible for maintaining :
(a) Fat metabolism
(b) Blood Pressure
(c) Blood Glucose level
(d) Electrolyte Balance
Answer – (c) Blood Glucose level
2. असंपर्क बल का उदाहरण है :
(a) बाल्टी उठाने के लिए हमारे द्वारा लगाया गया बल
(b) क्रिकेट की गेंद पर छक्का मारना
(c) चुंबक द्वारा लगाया गया बल
(d) एक स्थिर कार को धक्का देना
उत्तर – (c) चुंबक द्वारा लगाया गया बल
An example of a non-contact force is :
(a) Push a stationary car
(b) Force exerted by us to lift a bucket
(c) Force exerted by magnet
(d) Hit a cricket ball for a 6 Run
Answer – (c) Force exerted by magnet
3. बच्चो को रोलिंग, स्टेटिक और स्लाइडिंग घर्षण के कारण घर्षण बलों को बढ़ते क्रम में व्यवस्थित करने के लिए कहा गया था, यह व्यवस्था नीचे दी गई है सही व्यवस्था चुने।
Four children were asked to arrange friction forces due to Rolling, Static and Sliding frictions in an increasing order this arrangements are given below. Choose the correct arrangement :
(a) Rolling < Static < Sliding
(b) Static < Rolling < Sliding
(c) Rolling < Sliding < Static
(d) Sliding < Static < Rolling
Answer – (c) Rolling < Sliding < Static
4. निम्न में कहां पर बड़े भूकंप आने की संभावना कम होती है?
(a) राजस्थान
(b) उत्तर पूर्व भारत
(c) कच्छ का रण
(d) ओडिशा
उत्तर – (d) ओडिशा
Major earthquakes are less likely to occur in which of the following?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) North East India
(c) Rann of Kutch
(d) Orissa
Answer – (d) Orissa
5. निम्नलिखित में से कम प्रदूषण फैलाने वाला ईंधन कौन-सा है?
(a) पेट्रोल
(b) डीज़ल
(c) सीएनजी
(d) किरोसीन
उत्तर – (c) सीएनजी
Which one of the following is comparatively less polluting fuel?
(a) Petrol
(b) Diesel
(c) CNG
(d) Kerosene
Answer – (c) CNG
6. सूखे मौसम में बालों में कंघी करते समय बालों का कंघी की तरफ आकर्षित होने के लिए कौन-सा बल उत्तरदायी है?
(a) गुरुत्वाकर्षण का बल
(b) घर्षण बल
(c) विद्युत बल
(d) चुंबकीय बल
उत्तर – (c) विद्युत बल
During dry weather while combing hairs, sometimes we experience hairs flying apart. Which force is responsible for this?
(a) Force of gravity
(b) Force of friction
(c) Electrostatic force
(d) Magnetic force
Answer – (c) Electrostatic force
7. कैरम बोर्ड पर घर्षण को कम करने के लिए निम्नलिखित में से किसका उपयोग किया जाना चाहिए?
(a) एक स्नेहक तेल
(b) ग्रीस की परत
(c) एक शुष्क स्नेहक
(d) एक बॉल बेयरिंग
उत्तर – (c) एक शुष्क स्नेहक
Which of the following should be used to reduce friction on a carrom board?
(a) A lubricating oil
(b) A layer of Greece
(c) dry lubricant
(d) ball bearing
Answer – (c) dry lubricant
8. आपतन कोण परावर्तन कोण के बराबर होता है :
(a) हमेशा
(b) कभी-कभी
(c) विशेष परिस्थितियों में
(d) कभी नहीं
उत्तर – (a) हमेशा
Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection :
(a) Always
(b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions
(d) Never
Answer – (a) Always
9. क्षुद्रग्रह इनमें से किन कक्षाओं के बीच देखे जाते हैं?
(a) बुध और पृथ्वी
(b) मंगल और बृहस्पति
(c) पृथ्वी और मंगल
(d) बुध और शुक्र
उत्तर – (b) मंगल और बृहस्पति
Asteroids are seen between the orbits of which of the following?
(a) Mercury and Earth
(b) Mars and Jupiter
(c) Earth and Mars
(d) Mercury and Venus
Answer – (b) Mars and Jupiter
10. उच्च नमक सांद्रता वाले पानी को किस विधि द्वारा शुद्ध किया जा सकता है?
(a) छानना
(b) पराबैंगनी विकिरण
(c) क्वथन
(d) विपरीत परासरण
उत्तर – (d) विपरीत परासरण
Water containing high salt concentration can be purified by which of the following processes?
(a) Filtration
(b) UV Radiation
(c) Boiling
(d) Reverse Osmosis
Answer – (d) Reverse Osmosis
11. निम्न में से कौन संचारी रोग का सबसे सामान्य वाहक है?
(a) चींटी
(b) घरेलू मक्खी
(c) चूहा
(d) मकड़ी
उत्तर – (b) घरेलू मक्खी
Which one of the following is the most common career of communicable disease?
(a) Ant
(b) Housefly
(c) Rat
(d) Spider
Answer – (b) Housefly
12. राष्ट्रीय उद्यान, वन्य जीव अभ्यारण्य तथा बायोस्फियर रिजर्व बनाने का उद्देश्य क्या है?
(a) जंगली दुर्लभ प्रजातियों को सुविधाएं देने के लिए
(b) हमारे पर्यावरण और वन्य जीवन को संरक्षित करने के लिए
(c) केवल पिछड़ी और कमजोर प्रजातियों की रक्षा के लिए
(d) इनमें से कोई नहीं
उत्तर – (b) हमारे पर्यावरण और वन्य जीवन को संरक्षित करने के लिए
What is the purpose of making national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves?
(a) To give facilities to the wild rare species.
(b) To conserve and protect our environment and wildlife.
(c) To protect only rare and vulnerable species.
(d) None of the above
Answer – (b) To conserve and protect our environment and wildlife.
13. राजीव किसान हैं। उसने खेत की जुताई की है लेकिन उसे समतल करने की जरूरत है। मैदान को समतल करने के लिए वह निम्नलिखित में से किसका प्रयोग कर सकता है?
(a) पाटल
(b) हार्वेस्टर
(c) कल्टीवेटर
(d) सीड-ड्रील
उत्तर – (a) पाटल
Rajiv is a farmer. He has ploughed the field but needs to level it. Which one of the following can be used to level the field?.
(a) Leveler
(b) Harvester
(c) Cultivator Seed
(d) drill
Answer – (a) Leveler
14. PCRA का अर्थ है :
(a) पेट्रोलियम संरक्षण अनुसंधान संघ
(b) सार्वजनिक संरक्षण अनुसंधान संघ
(c) शेष संशोधन की आंशिक गणना
(d) सार्वजनिक संरक्षण अनुसंधान संघ
उत्तर – (a) पेट्रोलियम संरक्षण अनुसंधान संघ
PCRA stands for :
(a) Petroleum Conservation Research Association
(b) Partial Counting of Remaining Amendment
(c) Public Council of Research Association
(d) Public conservations research Association
Answer – (a) Petroleum Conservation Research Association
15. समतल दर्पण के दायें को बायें और इसके विपरीत दिखाने के गुण को क्या कहते हैं?
(a) परावर्तन
(b) अपवर्तन
(c) ऊर्ध्वाधर व्युत्क्रमण
(d) पार्श्व परिवर्तन
उत्तर – (d) पार्श्व परिवर्तन
The property of a plane mirror to make right appear as left and vice versa is called :
(a) Reflection
(b) Refraction
(c) Vertical inversion
(d) Lateral inversion
Answer – (d) Lateral inversion
Part B – Objective Question (1 Mark)
16. पेट्रोलियम से विभिन्न घटकों को अलग करने की प्रक्रिया को ……………. कहते हैं।
उत्तर – परिष्करण / शोधन
The process of separation of different constituents from patrol is called …………….
Answer – Refining
17. नायलॉन रेशे के निर्माण के लिए ……………… का उपयोग किया जाता है।
उत्तर – कैप्रोलैक्टम
……………… is used in the manufacture of nylon fibre.
Answer – Caprolactam
18. एक आदर्श ईंधन सस्ता, आसानी से उपलब्ध, आसानी से ज्वलनशील और परिवहन में आसान होता है। (सही / गलत)
उत्तर – सही
An ideal fuel is cheap, readily available, readily combustible and easy to transport. (True / False)
Answer – True
19. क्लोरीनीकरण पानी में कीटाणुओं को मारने के लिए आमतौर पर इस्तेमाल की जाने वाली रासायनिक विधि है। (सही / गलत)
उत्तर – सही
Chlorination is a commonly used chemical method for killing germs in water. (True / False)
Answer – True
20. धातु के चालक के माध्यम से विद्युत आवेश को आवेशित वस्तु से दूसरी वस्तु में स्थानांतरित किया जा सकता है। (सही / गलत)
उत्तर – सही
Electric charge can be transferred from a charged object to another object through a metal conductor. (True / False)
Answer – True
21. उस पुस्तक का नाम बताइए जिसमें पौधों और जानवरों की सभी लुप्तप्राय प्रजातियों का रिकॉर्ड है।
उत्तर – रेड डेटा बुक
Name the book which contains record of all the endangered species of plants and animals.
Answer – Red Data Book
22. नीले हरे शैवाल सीधे हवा से ……………. को स्थिर करते हैं और मिट्टी की उर्वरता बढ़ाते हैं।
उत्तर – नाइट्रोजन
Blue green algae fix ………….. directly from air and enhance fertility of the soil.
Answer – Nitrogen
23. ध्वनि ठोसों की तुलना में द्रवों में अधिक तेजी से यात्रा करती है। (सही / गलत)
उत्तर – गलत
Sound travels faster in liquids than in solids. (True / False)
Answer – False
24. फलीदार पौधों की गांठों की जड़ों में पाए जाने वाले जीवाणु को …………….. कहा जाता है।
उत्तर – राइजोबियम
Bacterias found in the roots of nodules of leguminous plants are known as …………….
Answer – Rhizobium
25. …………….. अंतरिक्ष में मौजूद खगोलीय पिंडों को देखने के लिए इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला उपकरण है।
उत्तर – टेलीस्कोप
…………….. is a device used to see celestial bodies present in space.
Answer – Telescope
Part C – Very Short Question (2 Marks)
26. बीजों को सीड-ड्रील के माध्यम से बोना, प्रसारण विधि द्वारा बोने से बेहतर क्यों है?
उत्तर – सीड ड्रिल का प्रयोग बेहतर होता है क्योंकि सीड ड्रिल के प्रयोग से बीज उचित स्थान एवं उचित गहराई पर बोए जाते हैं। इससे समय और श्रम की भी बचत होती है।
Why sowing seeds with seed drill is better than broadcasting?
Answer – The use of seed drill is better because by using seed drill, seeds are down at proper places and proper depth. It also saves time and labour.
27. जब किसी विद्युत उपकरण में आग लग जाती है तो पानी का उपयोग न करने की सलाह क्यों दी जाती है?
उत्तर – पानी बिजली का सुचालक है, इसलिए यह आसानी से विद्युत प्रवाह का संचालन कर सकता है और बिजली के झटके या शॉर्ट-सर्किट का खतरा पैदा कर सकता है। इसलिए, बिजली के उपकरणों से लगी आग पर काबू पाने के लिए पानी का उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता।
Why is it not advised to use water if electrical equipment catches fire?
Answer – Water is a conductor of electricity, so it can easily conduct electric current and cause danger of electric shocks or short-circuits. Therefore, water cannot be used to control the fire involving electrical equipment.
28. भोजन को भंडारित करने वाले लोहे के बर्तनों पर टीन की परत क्यों चढ़ाई जाती है?
उत्तर – टिन लोहे की तुलना में कम प्रतिक्रियाशील है। टिन की कोटिंग भोजन को लोहे के संपर्क में आने से रोकती है और इस प्रकार उसे खराब होने से बचाती है।
Why is tin electroplated on iron to make canes used for storing food?
Answer – Tin is less reactive than iron. Tin coating prevents food from coming in contact with iron and thus prevents it from getting spoiled.
29. तारे टिमटिमाते हैं लेकिन ग्रह नहीं। ऐसा क्यों?
उत्तर – तारे प्रकाश के वायुमंडलीय अपवर्तन के कारण टिमटिमाते हैं। चूँकि तारे बहुत दूर हैं, वे लगभग प्रकाश के एक बिंदु स्रोत के रूप में व्यवहार करते हैं, जबकि ग्रहों को बड़ी संख्या में प्रकाश के बिंदु स्रोत का संग्रह माना जाता है।
Stars twinkle but planets do not. Why?
Answer – Stars twinkle due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. As the stars are very far away, they behave as almost a point source of light, while planets are considered as a collection of a large number of point source of light.
30. ज्वाला के सबसे भीतरी क्षेत्र का रंग काला क्यों होता है?
उत्तर – बिना जले मोम के वाष्प की उपस्थिति के कारण लौ का सबसे भीतरी क्षेत्र काले रंग का होता है।
Why is the innermost zone of a flame black in colour?
Answer – The innermost zone of a flame is black in colour due to presence of unburnt wax vapours.
31. घर्षण की विधि से बॉल पॉइंट पेन रीफिल को कैसे चार्ज किया जा सकता है?
उत्तर – बॉलपॉइंट पेन रीफिल को ऊनी कपड़े से रगड़कर चार्ज किया जा सकता है। यह ऋणात्मक रूप से आवेशित हो जाता है। जब हम इसे कागज के टुकड़ों के पास लाते हैं तो कागज इसकी ओर आकर्षित हो जाता है। कागज विद्युत रूप से तटस्थ है।
How can a ballpoint pen refill be charged by the method of friction?
Answer – A ballpoint pen refill can be charged by rubbing it against the wool cloth. It becomes negatively charged. When we bring it close to bits of paper, the paper gets attracted to it. Paper is electrically neutral.
32. स्मॉग क्या है?
उत्तर – स्मॉग एक प्रकार का वायु प्रदूषण है जो तब होता है जब हवा में धुएँ और कोहरे का मिश्रण होता है। यह मुख्य रूप से धुआं, सल्फर डाइऑक्साइड, नाइट्रोजन ऑक्साइड और अन्य कण जैसे प्रदूषकों से बना है, जो मानव स्वास्थ्य और पर्यावरण के लिए हानिकारक हो सकता है।
What is smog?
Answer – Smog is a type of air pollution that occurs when there is a mixture of smoke and fog in the air. It is mainly composed of pollutants such as smoke, sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and other particulate matter, which can be harmful to human health and the environment.
33. पृथ्वी पर दिन और रात किस कारण से बनते हैं?
उत्तर – पृथ्वी पर दिन और रात पृथ्वी के अपनी धुरी पर घूमने के कारण होते हैं। पृथ्वी पश्चिम से पूर्व की ओर घूमती है, लगभग हर 24 घंटे में एक पूर्ण चक्कर पूरा करती है। घूर्णन के दौरान, पृथ्वी की सतह जो सूर्य के सामने होती है, वहां दिन का समय होता है। दूसरा भाग, जो सूर्य से विमुख है, वहां रात्रि का समय होता है।
What causes day and night on earth?
Answer – Day and night on Earth are caused by the rotation of the Earth on its axis. The Earth rotates from west to east, completing one full rotation approximately every 24 hours. During rotation, the surface of the earth that faces the sun, has daytime. The other part, which is facing away from the sun, has night time.
Part D – Short Question (3 Marks)
34. खाद्य परिरक्षक क्या हैं? कुछ सामान्य खाद्य परिरक्षकों की व्याख्या कीजिए।
उत्तर – वे रासायनिक पदार्थ जो खाद्य पदार्थों को खराब होने से बचाने और उनके पोषक मूल्य को लंबे समय तक बनाए रखने के लिए उनमें मिलाए जाते हैं, खाद्य परिरक्षक कहलाते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, नमक, चीनी, तेल, सिरका और सोडियम बेंजोएट आदि।
What are the food preservatives? Explain some common food preservatives.
Answer – The chemical substances which are added to the food materials to prevent their spoilage and to retain their nutritive value for long periods are called food preservatives. For example, salt, sugar, oil, vinegar and sodium benzoate etc.
35. हमें कोयला और पेट्रोलियम जैसे संसाधनों का सीमित मात्रा में उपयोग क्यों करना चाहिए?
उत्तर – कोयला और पेट्रोलियम जीवाश्म ईंधन हैं जिन्हें बनने में लाखों वर्ष लगते हैं। वे प्राकृतिक संसाधन हैं और आपूर्ति में सीमित हैं। ये संपूर्ण अनवीकरणीय संसाधन हैं। साथ ही, यह जीवाश्म ईंधन जलने पर कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड पैदा करता है जो हमारे पर्यावरण के लिए बहुत हानिकारक है, जिससे वायु प्रदूषण के साथ-साथ ग्लोबल वार्मिंग भी होती है। अतः हमें कोयला एवं पेट्रोलियम का प्रयोग सीमित मात्रा में करना चाहिए।
Why should we use resources like coal and petroleum in limit?
Answer – Coal and petroleum are fossil fuels that require millions of years to be formed. They are natural resources and are limited in supply. These are exhaustible nonrenewable resources. Also, this fossil fuel produces carbon dioxide on burning which is very harmful to our environment causing air pollution as well as global warming. Hence, we should use coal and petroleum in limited amounts.
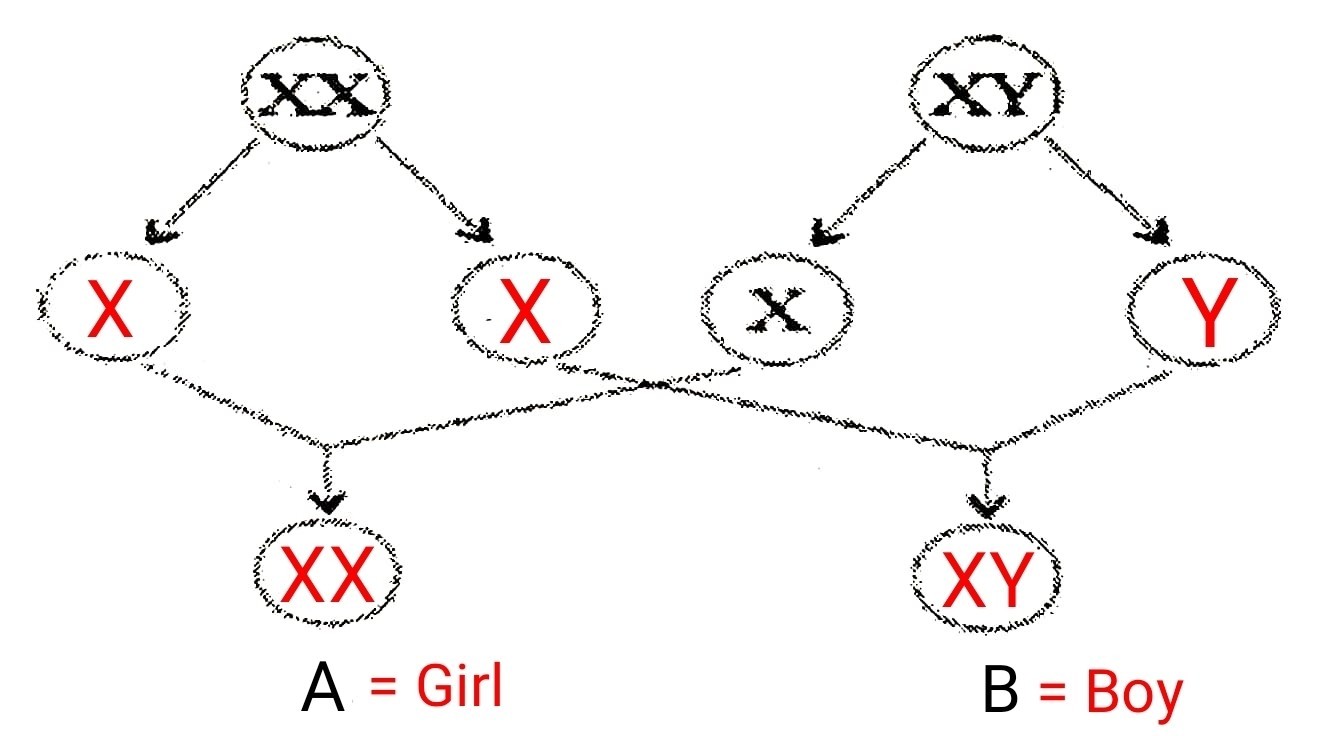
36. दी गई आकृति में रिक्त वृतों को भरिए और बच्चे A और B का लिंग पहचानिए और समझाइए।
Fill the blank circles in the given figure and identify the sex of child A and B and explain it.
Answer –
37. मानव के उस अंग का नाम बताइए जो ध्वनि उत्पन्न करता है और यह कैसे कार्य करता है?
उत्तर – मनुष्य में स्वरयंत्र या वॉक यंत्र ध्वनि उत्पन्न करता है। यह एक खोखली, ट्यूबलर संरचना है जो श्वासनली (ट्रेकिआ) के शीर्ष से जुड़ी होती है। स्वरयंत्र में दो स्वर रज्जु होते हैं जो वायु के प्रवाह के लिए एक संकीर्ण छिद्र से अलग होते हैं। जैसे ही फेफड़ों से हवा भट्ठा से होकर गुजरती है, ये स्वर रज्जु ध्वनि उत्पन्न करने के लिए कंपन करते हैं।
Name the organ in humans that produces sound and how does it work?
Answer – Larynx or voice box in humans is produces sound. It is a hollow, tubular structure connected to the top of the windpipe (trachea). Larynx is provided with two vocal cords which are separated by a narrow slit for the passage of air. As air from lungs passes through the slit, these vocal cords vibrate to produce sound.
38. निम्नलिखित सर्किट को ध्यान से देखें। बल्ब किस परिपथ में प्रकाशित होगा। दिये गये परिपथ के दिये गये रिक्त स्थान में हाँ या नहीं लिखें और इसका कारण स्पष्ट करें।
Observe the following circuit carefully. In which circuit will the bulb glows. Write yes or no in the blank space provided along each side of the circuit given and explain the reason for it.
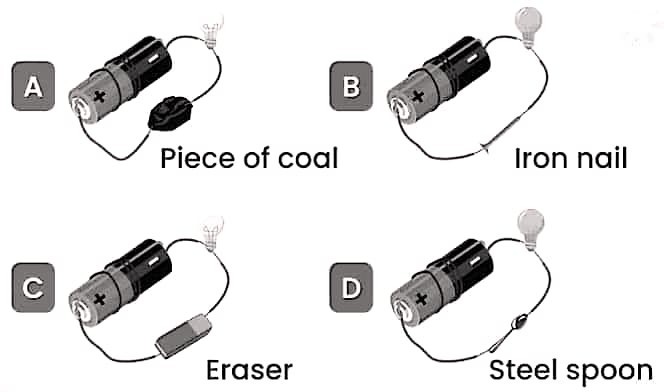
Answer –
(A) No (coal is bad conductor)
(B) Yes (iron nail is god conductor)
(C) No (eraser is bad conductor)
(D) Yes (steel spoon us god conductor)
39. दिए गए चित्र को नामांकित करें और इनके बीच तीन अंतर बताएँ।
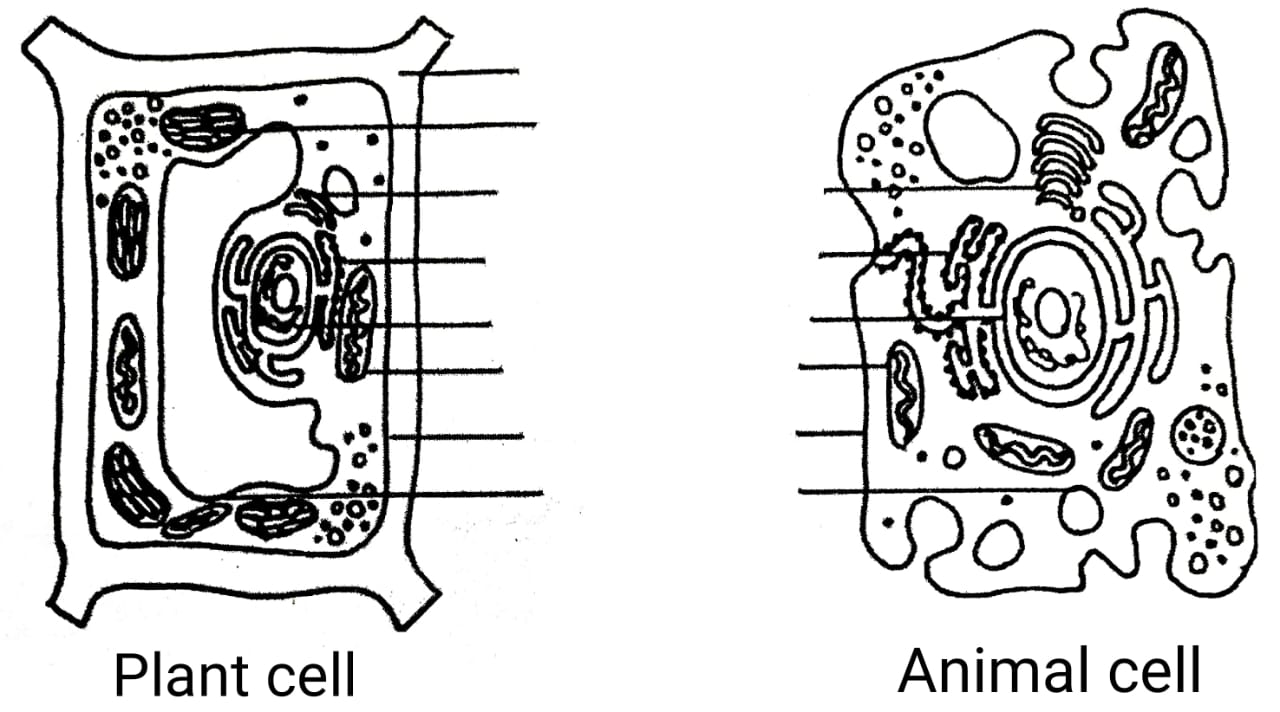
उत्तर –
| पादप कोशिका | जंतु कोशिका |
| 1. पादप कोशिका एक कठोर कोशिका भित्ति से घिरी होती है। | 1. जंतु कोशिका में कोशिका भित्ति नहीं होती है। |
| 2. ये आकार में नियमित या आयताकार होती है। | 2. ये आकार में अनियमित या गोल होती है। |
| 3. ये आकार में बड़ी होती हैं। | 3. ये आकार में छोटी होती हैं। |
Identify the given picture and write three comparisons between them.
Answer –
| Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
| 1. A plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall. | 1. An animal cell does not have a cell wall. |
| 2. These are regular or rectangular in shape. | 2. These are irregular or round in shape. |
| 3. These are larger in size. | 3. These are smaller in size. |
40. क्या वनों की कटाई ग्लोबल वार्मिंग से जुड़ी हुई है? व्याख्या करें।
उत्तर – हाँ, वनों की कटाई ग्लोबल वार्मिंग से जुड़ी है। जब पेड़ काटे जाते हैं तो वातावरण में कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड की मात्रा बढ़ जाती है। इससे पृथ्वी की सतह के तापमान में वृद्धि होती है जिसका अर्थ है ग्लोबल वार्मिंग। पृथ्वी के तापमान में वृद्धि से जल चक्र गड़बड़ा जाता है और इससे वर्षा में कमी आ सकती है।
Is deforestation associated with global warming? Explain.
Answer – Yes, deforestation associated with global warming. When trees are cut down, then increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. This leads to increase in the temperature of the earth’s surface which means global warming. The increase in the temperature of the earth disturbs the water cycle and this can lead to decrease in the rainfall.
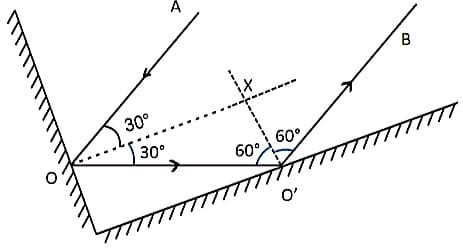
41. दो दर्पण समकोण पर मिलते हैं। प्रकाश की एक किरण एक दर्पण पर 30 डिग्री के कोण पर आपतित होती है जैसा कि चित्र में दिखाया गया है। दूसरे दर्पण से परावर्तित किरण खीचिए।
Two mirrors meet at right angles. A Ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30 degree as shown in the figure. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
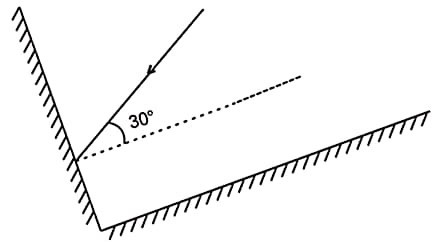
Answer –
Part E – Long Question (5 Marks)
42. धातुओं और अधातुओं को उनके भौतिक गुणों के आधार पर अंतर स्पष्ट कीजिए।
उत्तर –
| धातु | अधातु |
| 1. धातुएँ ऊष्मा और विद्युत की सुचालक होती हैं। | 1. अधातुएँ सामान्यतः ऊष्मा और विद्युत की कुचालक होती हैं (ग्रेफाइट को छोड़कर)। |
| 2. ये चमकदार एवं चमकीली होती हैं। | 2. ये चमकदार नही होती एवं चमकीली भी नहीं होती हैं। |
| 3. धातुएँ सामान्यतः आघातवर्ध्य एवं तन्य होती हैं। | 3. अधातुएँ आम तौर पर भंगुर होती हैं और छोटे टुकड़ों में टूट सकती हैं। |
| 4. धातुएँ बहुत कठोर होती हैं (सोडियम को छोड़कर)। | 4. अधातुएँ नरम होती हैं (हीरे को छोड़कर)। |
| 5. उदाहरण: तांबा, चांदी, सोना आदि। | 5. उदाहरण: कार्बन, ऑक्सीजन, सल्फर आदि। |
Differentiate between metals and nonmetals on the basis of their physical properties.
Answer –
| Metals | Non metals |
| 1. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. | 1. Non metals are generally bad conductors of heat and electricity (except graphite). |
| 2. These are shiny and lustrous. | 2. These are not shiny and non lustrous. |
| 3. Metals are generally malleable and ductile. | 3. Non metals are generally brittle and can break down into smaller pieces. |
| 4. Metals are very hard (except sodium). | 4. Non metals are soft (except diamonds). |
| 5. Example: Copper, silver, gold etc. | 5. Example: Carbon, oxygen, sulphur etc. |
43. “स्वस्थ पर्यावरण के लिए प्लास्टिक का उपयोग कम से कम करें” इस सलाह पर टिप्पणी कीजिए।
उत्तर – प्लास्टिक एक गैर-बायोडिग्रेडेबल पदार्थ है और इस तरह यह भूमि प्रदूषण का कारण बनता है। साथ ही ऐसी सामग्रियों को कूड़े के रूप में जलाने से गंभीर वायु प्रदूषण होता है।
• प्लास्टिक का अनुचित निपटान कई समस्याओं का कारण बनता है :
(i) खुले स्थानों में प्लास्टिक का कूड़ा फैलाने से अस्वच्छता की स्थिति पैदा होती है।
(ii) प्लास्टिक का क्षरण नहीं होता है, इसलिए यह कई वर्षों तक मिट्टी में बना रहता है।
(iii) यदि प्लास्टिक जल निकासी और सीवरेज प्रणाली में प्रवेश करता है तो यह पाइपों को अवरुद्ध कर देता है।
• इसके उपभोग को सीमित करने के कुछ तरीके हैं :
(i) प्लास्टिक के स्थान पर पेपर बैग का उपयोग करने की अत्यधिक अनुशंसा की जाती है।
(ii) यदि प्लास्टिक की खपत को कम करना संभव हो तो पुन: उपयोग करें।
(iii) प्लास्टिक के पर्यावरणीय प्रभाव और उनके उपयोग को कम करने के महत्व के बारे में दूसरों को शिक्षित करें।
“Minimise use of plastics for a healthy environment,” Comment on this advice.
Answer – Plastic is a non-biodegradable material and as such it causes land pollution. At the same time burning such materials in the form of garbage causes serious air pollution.
• Improper disposal of plastics causes several problems :
(i) The littering of plastics in open spaces creates unhygienic conditions.
(ii) Plastics do not undergo degradation, thus, stay in the soil for many years.
(iii) Plastic blocks the pipes if it enters the drainage and sewerage system.
• Some ways to limit its consumption are :
(i) Paper bags are highly recommended to use instead of plastics.
(ii) Reuse if it is possible to reduce the consumption of plastic.
(iii) Educate others about the environmental impact of plastics and the importance of reducing their use.
44. निम्न वक्तव्यों की व्याख्या करेंः 1. प्रजनन, 2. निषेचन, 3. कायान्तरण, 4. भ्रूण, 5. द्विखंडन।
उत्तर –
1. प्रजनन – प्रजनन वह जैविक प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा नए व्यक्तिगत जीव (संतान) अपने माता-पिता से उत्पन्न होते हैं। यह पीढ़ी-दर-पीढ़ी प्रजातियों की निरंतरता सुनिश्चित करता है। प्रजनन के दो मुख्य प्रकार हैं: लैंगिक प्रजनन, अलैंगिक प्रजनन।
2. निषेचन – निषेचन वह प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा नर युग्मक (शुक्राणु) और मादा युग्मक (अंडाणु) मिलकर युग्मनज बनाते हैं। यह प्रक्रिया गुणसूत्रों की द्विगुणित संख्या को पुनर्स्थापित करती है और एक नए जीव के विकास की शुरुआत करती है।
3. कायान्तरण – कायान्तरण वह जैविक प्रक्रिया है जिसके द्वारा एक जीव अपने विकास के प्रारंभिक चरण से लेकर वयस्क अवस्था तक रूप और संरचना में महत्वपूर्ण परिवर्तन से गुजरता है। यह प्रक्रिया कई कीड़ों (जैसे तितलियाँ और भृंग), उभयचर (जैसे मेंढक) और अन्य जानवरों में आम है। कायापलट पूर्ण हो सकता है (अंडा, लार्वा, प्यूपा और वयस्क जैसे अलग-अलग चरणों के साथ) या अधूरा (अंडा, अप्सरा और वयस्क जैसे चरणों के साथ)।
4. भ्रूण – भ्रूण चरण के बाद और जन्म से पहले एक स्तनधारी भ्रूण का विकासात्मक चरण है। मनुष्यों में, यह अवस्था निषेचन के आठवें सप्ताह के अंत में शुरू होती है और जन्म तक जारी रहती है। इस अवधि के दौरान, विभिन्न अंगों और प्रणालियों के गठन और परिपक्वता के साथ, भ्रूण महत्वपूर्ण वृद्धि और विकास से गुजरता है।
5. द्विखंडन – द्विखंडन अलैंगिक प्रजनन और कोशिका विभाजन का एक रूप है जो आमतौर पर बैक्टीरिया जैसे प्रोकैरियोटिक जीवों में पाया जाता है। द्विआधारी विखंडन में, एक कोशिका दो समान संतति कोशिकाओं में विभाजित हो जाती है। इस प्रक्रिया में जीव के डीएनए की प्रतिकृति शामिल होती है, जिसके बाद साइटोप्लाज्म और कोशिका झिल्ली का विभाजन होता है, जिसके परिणामस्वरूप दो आनुवंशिक रूप से समान कोशिकाएं बनती हैं। यह विधि अनुकूल परिस्थितियों में तेजी से जनसंख्या वृद्धि की अनुमति देती है।
Define following terms : 1. Reproduction, 2. Fertilization, 3. Metamorphosis, 4. Foetus, 5. Binary fission
Answer –
1. Reproduction – Reproduction is the biological process by which new individual organisms (offspring) are produced from their parents. It ensures the continuity of species from generation to generation. There are two main types of reproduction: sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction.
2. Fertilization – Fertilization is the process by which male gametes (sperm) and female gametes (egg cells) combine to form a zygote. This process restores the diploid number of chromosomes and initiates the development of a new organism.
3. Metamorphosis – Metamorphosis is the biological process by which an organism undergoes a significant change in form and structure from its early stages of development to its adult stage. This process is common in many insects (like butterflies and beetles), amphibians (like frogs), and other animals. Metamorphosis can be complete (with distinct stages such as egg, larva, pupa, and adult) or incomplete (with stages like egg, nymph, and adult).
4. Foetus (Fetus) – A foetus is the developmental stage of a mammalian embryo following the embryonic stage and before birth. In humans, this stage begins at the end of the eighth week after fertilization and continues until birth. During this period, the foetus undergoes significant growth and development, with the formation and maturation of various organs and systems.
5. Binary Fission – Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction and cell division commonly found in prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria. In binary fission, a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The process involves the replication of the organism’s DNA, followed by the division of the cytoplasm and cell membrane, resulting in two genetically identical cells. This method allows for rapid population growth under favorable conditions.
