Class 12 Physics Half Yearly Question Paper 2025 Answer Key (NCERT Based)
Instructions :
• All questions are compulsory.
• Questions (1-9) carry 1 mark each.
• Questions (10-12) carry 2 marks each.
• Questions (13-14) carry 3 marks each.
• Question (15) case study, carry 4 marks.
• Questions (16-17) carry 5 marks each.
1. The opposition offered by the electrolyte of the cell to the flow of current through itself is known as :
(a) External resistance
(b) Internal resistance
(c) Non-resistance
(d) None of these options
Answer – (b) Internal resistance
2. The quantization of charge indicates that :
(a) There exists a minimum permissible charge on a particle
(b) Charge cannot be destroyed
(c) Charge exists on particles
(d) None of the above
Answer – (a) There exists a minimum permissible charge on a particle
3. An electromagnetic wave can be produced by :
(a) A stationary charge
(b) Charge moving with a constant velocity
(c) Charge in accelerated motion
(d) None of the above
Answer – (c) Charge in accelerated motion
4. For which of the following the power factor of the circuit comes out to be 1 ?
(a) Pure resistive circuit
(b) Pure inductive circuit
(c) Pure capacitive circuit
(d) All the above
Answer – (a) Pure resistive circuit
5. Write Ampere’s circuital Law’s mathematical form ……………
Answer : ∮ B.dl = μoI
6. What is the resistance of the ideal Ammeter?
Answer – Zero
7. Henry is the SI unit of ………..
Answer – inductance
8. White relation between Electric field and electric potential.
Answer : E = – dV/dx
9. Assertion (A) : If an electron is not deflected when moving through a certain region of space, then the only possibility is that no magnetic field is present in that region.
Reason (R) : Force on electron is directly proportional to the strength of the magnetic field.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
Answer – (d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
10. State Gauss’s Law.
Answer – Gauss’s Law states that the total electric flux passing through any closed surface is equal to 1/∈o times the net charge enclosed by that surface.
Mathematically written: ∮ E.dA = Q/∈o
11. Explain Lenz’s Law for electromagnetic induction.
Answer – Lenz’s Law states that the direction of the induced current in a circuit is always such that it opposes the change in magnetic flux that produces it. Thus, the induced current creates a magnetic effect and force opposing the cause of induction, ensuring conservation of energy.
12. The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 Volt. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4 ohm, what is the maximum current drawn from the battery?
Answer – Maximum current is obtained when the external resistance of the circuit is zero (i.e., the battery is short-circuited).
Using Ohm’s law,
Imax = E/r = 12/0.4 = 30 A
13. The force of attraction between a positively charged particle and a negatively charged particle is F, when distance between them is made one-fourth, what will be the value of this force?
Answer : Initial Force (F) = kq1q2/r2
New force (F’) = kq1q2/(¼)2 = 16kq1q2/r2 = 16F
F’ = 16F
So, when the distance between the two charges is one-fourth, the force is increased 16 times.
14. Explain Paramagnetism and Ferromagnetism.
Answer – Paramagnetism is a weak magnetic property where materials are weakly attracted to an external magnetic field but lose their magnetism once the field is removed.
• Ferromagnetism is a strong magnetic property where materials are strongly attracted to a magnet and retain their magnetism even after the external field is removed, forming permanent magnets.
15. CASE STUDY : AC generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. The AC Generator’s input supply is mechanical energy supplied by steam turbines, gas turbines and combustion engines. The output is alternating electrical power in the form of alternating voltage and current. AC generators work on the principle of Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction, which states that electromotive force EMF or voltage is generated in a current-carrying conductor that cuts a uniform magnetic field. This can either be achieved by rotating a conducting coil in a static magnetic field or rotating the magnetic field containing the stationary conductor. The preferred arrangement is to keep the coil stationary because it is easier to draw induced alternating current from a stationary armature coil than from a rotating coil. The generated EMF depends on the number of armature coil turns, magnetic field strength, and the speed of the rotating field.
Questions :
(a) On what factors does the generated emf of an AC generator depend?
Answer – The induced emf in an AC generator depends on the number of turns in the armature coil, the strength of the magnetic field, and the speed at which the magnetic field or coil rotates.
(b) Which law explains the working principle of an AC generator?
Answer – Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
(c) What is the source of energy generation in this device?
Answer – Mechanical energy
(d) Can the current produced by an ac generator be measured with a moving coil galvanometer?
Answer – No
16. Discuss the variation in resistivity with temperature for (i) Conductor, (ii) Semiconductor. Write SI unit of electric power.
Answer – (i) In a conductor, resistivity increases with rise in temperature. This happens because as temperature increases, the vibration of atoms in the metal lattice increases, making it harder for electrons to flow. Thus, metals show a positive temperature coefficient of resistivity.
(ii) In a semiconductor, resistivity decreases when temperature increases. With rising temperature, more electrons gain sufficient energy to jump to the conduction band, increasing conductivity and reducing resistivity. Therefore, semiconductors show a negative temperature coefficient of resistivity.
• The SI unit of electric power is watt (W).
17. Explain the principle of a moving coil galvanometer and also draw diagram. How it can be converted into a voltmeter?
Answer – A moving coil galvanometer works on the principle that when a current flows through a coil placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque and the coil deflects. The deflection of the pointer is proportional to the current flowing through the coil, thus measuring small currents.
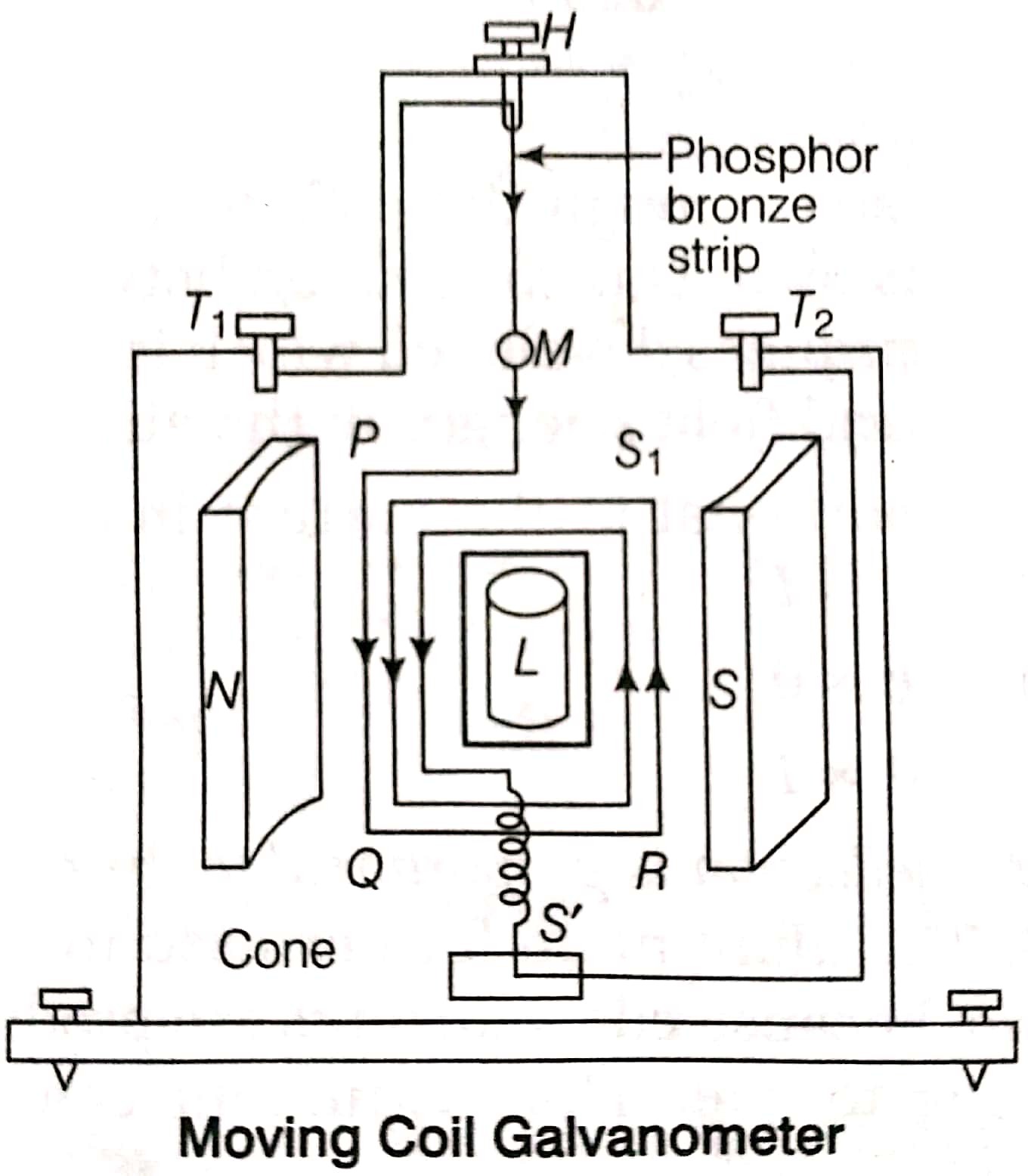
• A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance (called a multiplier) in series with its coil. This increases the total resistance so only a small current flows for a given potential difference, and the instrument can then measure voltage directly.
