Class 10 Maths Half Yearly Question Paper 2025 Answer Key (NCERT Based)
Instructions :
• All questions are compulsory.
• Questions (1-11) carry 1 mark each.
• Questions (12-14) carry 2 marks each.
• Questions (15-17) carry 3 marks each.
• Questions (18-19) carry 5 marks each.
• Question (20) case study, carry 4 marks.
1. 8, 9 और 15 का LCM ज्ञात कीजिए।
LCM of 8, 9 and 15 is :
(a) 30
(b) 60
(c) 90
(d) 360
Answer : (d) 360
2. k के किस मान के लिए, निम्न रैखिक समीकरणों के युग्म का कोई हल नहीं होगा?
What value of k does the pair of linear equations has no solution?
x – ky + 4 = 0, 2x – 6y – 5 = 0
(a) k = 3
(b) k ≠ 3
(c) k = –3
(d) None of these
Answer : (a) k = 3
a1/a2 = b1/b2 ≠ c1/c2
1/2 = (–k)/(–6)
k = 3
3. द्विघात बहुपद x2 – 5x + 6 के शुन्यक ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the zeros of quadratic polynomial x2 – 5x + 6.
(a) 2, 3
(b) –2, –3
(c) 4, 3
(d) –4, –3
Answer : (a) 2, 3
x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
x2 – 3x – 2x + 6 = 0
x(x – 3) – 2(x – 3) = 0
(x – 2)(x – 3) = 0
x = 2, 3
4. k का मान जिसके लिए द्विघात समीकरण 2x2 + kx + 2 = 0 के बराबर मूल है।
For what values of k, the quadratic equation 2x2 + kx + 2 = 0 has equal roots.
(a) ± 2
(b) ±4
(c) ± 3
(d) ± 5
Answer : (b) ±4
For equal roots, Discriminant = 0
Discriminant (D) = b2 − 4ac = 0
(k)2 – 4(2)(2) = 0
k2 − 16 = 0
k2 = 16
k = ±4
5. AP: 3, 8, 13, …………. का 20वां पद ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the 20th term of AP: 3, 8, 13, ………
(a) 58
(b) 68
(c) 78
(d) 98
Answer : (d) 98
a = 3, d = 8 – 3 = 5, n = 20
an = a + (n – 1)d
a20 = 3 + (20 – 1)(5) = 3 + (19)(5) = 3 + 95 = 98
6. निम्नलिखित में कौन सी संख्या किसी घटना की प्रायिकता नहीं हो सकती?
Which of the following cannot be the probability of an event?
(a) 2/3
(b) 0.5
(c) 2.5
(d) 0.4
Answer : (c) 2.5
0 ≤ Probability ≤ 1
7. वर्ग अंतराल 15-20 का वर्ग माप ज्ञात कीजिये।
Find the class size of the class interval 15-20?
Answer : Class size = 20 – 15 = 5
8. द्विघात बहुपद x2 – 3x + 2 के शुन्यको का गुणनफल ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the Product of zeros of the quadratic polynomial x2 – 3x + 2.
Answer : Product of zeros (αβ) = c/a = 2/1 = 2
9. सभी …………..त्रिभुज समरूप होते हैं। (समद्विबाहु / समबाहु)
All ………….. triangles are similar. (Isosceles / equilateral)
Answer : equilateral
10. बिन्दुओं (–2, 4) और (5, 7) के बीच की दूरी …………. है।
The distance between the points (–2, 4) and (5, 7) is …………..
Answer : Distance = √(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2
= √(5+2)2+(7–4)2
= √(7)2+(3)2
= √49+9
= √58
11. अभिकथन (A) : √3 एक अपरिमेय संख्या का एक उदाहरण है।
कारण (R) : सभी धनात्मक पुर्णांकों के वर्गमूल अपरिमेय संख्याएँ होती हैं।
(a) अभिकथन (A) और कारण (R) दोनों सही है और कारण (R), अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या करता है।
(b) अभिकथन (A) और कारण (R) दोनों सही है और कारण (R), अभिकथन (A) की सही व्याख्या नहीं करता है।
(c) अभिकथन (A) सही है लेकिन कारण (R) गलत है।
(d) अभिकथन (A) गलत है लेकिन कारण (R) सही है।
उत्तर – (c) अभिकथन (A) सही है लेकिन कारण (R) गलत है।
Assertion (A) : √3 is an example of irrational number.
Reason (R) : The square root of all positive integers are irrational numbers.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Answer : (c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
12. सिद्ध कीजिए कि √5 एक अपरिमेय संख्या है।
Prove that √5 is irrational.
Answer : Let us assume that √5 is a rational number.
Now √5 = p/q where p and q are co-prime integers and q ≠ 0
p = √5q
Squaring both sides, we get
p2 = 5q2 ……..(i)
5 divides p2, then 5 also divides p
Put p = 5m in eqn.(i),
(5m)2 = 5q2
25m2 = 5q2
5m2 = q2
5 divides q2 then 5 also divides q
Here p, q have a common factor is 5. This contradicts our assumption that they are co-primes. Therefore, p/q is not a rational number
Hence √5 is an irrational number.
13. निम्नलिखित रैखिक समीकरणों के युग्म को हल कीजिए :
Solve the following pair of linear equations :
7x + 2y = 20, 2x – 4y = – 8
Answer : Given equations,
7x + 2y = 20 ……….(i)
2x – 4y = – 8 ……….(ii)
Multiply eqn.(i) by 2, we get
14x + 4y = 40 ……….(iii)
Add eqn.(ii) and (iii), we get
(2x – 4y) + (14x + 4y) = – 8 + 40
16x = 32
x = 32/16 = 2
Put x = 2 in eqn.(i), we get
7(2) + 2y = 20
2y = 20 – 14
2y = 6
y = 6/2 = 3
so, x = 2 and y = 3
14. यदि एक A.P. का तीसरा पद 12 और दसवां पद 26 है तो उसका 20 वां पद ज्ञात करें।
If in a A.P., 3rd term is 12 and 10th term is 26 then find 20th term.
Answer : a3 = 12, a10 = 26
a + 2d = 12 ………(i)
a + 9d = 26 ………(ii)
Subtract eqn.(i) from (ii), we get
(a + 9d) – (a + 2d) = 26 – 12
7d = 14
d = 14/7 = 2
Put d = 2 in eqn.(i), we get
a + 2(2) = 12
a = 12 – 4 = 8
a20 = a + 19d = 8 + 19(2) = 8 + 38 = 46
15. दो क्रमागत धनात्मक पूर्णांक ज्ञात कीजिये जिनके वर्गों का योग 365 हो।
Find two consecutive positive integers, sum of whose squares is 365.
Answer : Let the two consecutive integers be x and x + 1
ATQ,
x2 + (x + 1)2 = 365
x2 + x2 + 2x + 1 = 365
2x2 + 2x + 1 = 365
2x2 + 2x − 364 = 0
Divide eqn. by 2, we get
x2 + x − 182 = 0
x2 + 14x – 13x – 182 = 0
x(x + 14) – 13(x + 14) = 0
(x + 14)(x – 13) = 0
x = 13 (reject x = – 14)
x + 1 = 13 + 1 = 14
so, the numbers are 13 and 14.
16. वह अनुपात जात कीजिए जिसमे बिन्दुओ A (1, –5) और B (–4, 5) को मिलाने वाला रेखाखण्ड x अक्ष से विभाजित होता है।
Find the ratio in which line segment joining A (1, –5) and B (–4, 5) is divided by the x-axis.
Answer : Let ratio = m1 : m2 = k : 1
Line segment divided by x-axis, then y = 0
x1 = 1, x2 = –4, y1 = –5, y2 = 5
y = (m1y2 + m2y1) ÷ (m1 + m2)
0 = [k(5) + 1(–5)] ÷ (k + 1)
(5k – 5) ÷ (k + 1) = 0
5k – 5 = 0
5k = 5
k = 5/5 = 1
17. 52 पत्तों की अच्छी प्रकार से फैटी गई एक गड्डी में से एक पत्ता निकाला जाता है।
निम्नलिखित को प्राप्त करने की प्रायिकता ज्ञात कीजिए :
One card is drawn from a well shuffled pack of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting :
(i) हुकुम का पत्ता (a spade)
Answer : Total spades = 13
P(E) = 13/52 = 1/4
(ii) लाल रंग का तस्वीर वाला पत्ता (a red face card)
Answer : Red face cards = 6
P(E) = 6/52 = 3/26
(iii) पान का गुलाम (the jack of heart)
Answer : Jack of heart = 1
P(E) = 1/52
18. सिद्ध कीजिए “यदि किसी त्रिभुज की एक भुजा के समांतर अन्य दो भुजाओं को भिन्न-भिन्न बिन्दुओं पर प्रतिच्छेद करने के लिए एक रेखा खींची जाए, तो ये अन्य दो भुजाएँ एक ही अनुपात में विभाजित हो जाती है”।
Prove that “If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, then the other two sides are divided in the same ratio”.
Answer :
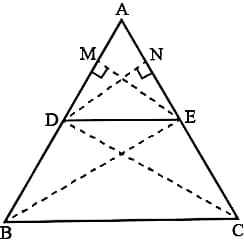
To Prove: AD/DB = AE/EC
Construction: Draw EM ⊥ AB and DN ⊥ AC. Join BE and CD.
Proof: In ∆ADE and ∆BDE,
ar(∆ADE) / ar(∆BDE) = (½×AD×EM) / (½×DB×EM) = AD/DB ……….(i)
In ∆ADE and ∆CDE,
ar(∆ADE) / ar(∆CDE) = (½×AE×DN) / (½×EC×DN) = AE/EC ……….(ii)
Since, DE || BC [Given]
∴ ar(∆BDE) = ar(CDE) ……….(iii)
[∆’s having same base and between the same parallel lines then they are equal in area]
From eqn.(i), (ii) and (iii), we get
AD/DB = AE/EC
Hence Proved.
19. दिया हुआ बंटन विश्व के कुछ श्रेष्ठतम बल्लेबाजों द्वारा एकदिवसीय अंतर्राष्ट्रीय क्रिकेट मैचों में बनाए रनों को दर्शाता है :
The given distribution shows the number of runs scored by some top Batsmen of the world in one day international cricket matches :
| Runs Scored | No. of Batsman |
| 3000-4000 | 4 |
| 4000-5000 | 18 |
| 5000-6000 | 9 |
| 6000-7000 | 7 |
| 7000-8000 | 6 |
| 8000-9000 | 3 |
| 9000-10000 | 1 |
| 10000-11000 | 1 |
इन आँकड़ों का बहुलक ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the mode of the data.
Answer : Modal class = 4000-5000
h = 1000
l = 4000
f1 = 18
fo = 4
f2 = 9
Mode = l + [(f1 – fo)/(2f1 – fo – f2)] × h
= 4000 + [(18 – 4)/(2×18 – 4 – 9)] × 1000
= 4000 + [14/(36–13)] × 1000
= 4000 + (14/23) × 1000
= 4000 + 608.695
= 4608.695
= 4608.7
Hence the mode is 4608.7
20. एक कक्षा में 4 दोस्त राम, राजन, प्रवीण और रमन चित्र में दिखाए अनुसार बिन्दु A, B, C और D पर बैठे हैं। यह मानते हुए कि O मूल बिन्दु है।
In a classroom 4 friends Ram, Rajan, Praveen and Raman are sitting on the points A, B, C and D as shown in the fig. Assuming O be the origin.
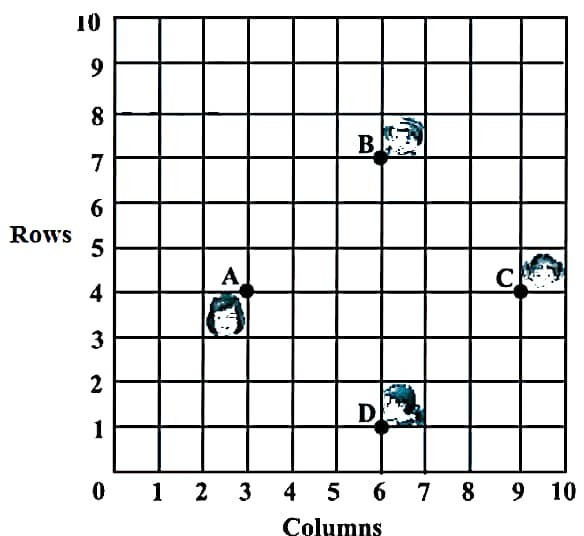
आकृति का अवलोकन करें और आकृति के आधार पर निम्नलिखित प्रश्नों के उत्तर दीजिए :
Observe the figure and answer the following questions based on the figure :
(i) राजन की स्थिति ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the position of Rajan.
Answer : B(6, 7)
(ii) प्रवीण की स्थिति ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the position of Praveen.
Answer : C(9, 4)
(iii) प्रवीण की मूल बिन्दु से दूरी ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the distance of Praveen from origin.
Answer : Here C(9, 4) and O(0, 0)
x1 = 9, x2 = 0, y1 = 4, y2 = 0
Using Distance Formula,
CO = √(x2–x1)2+(y2–y1)2
= √(0–9)2+(0–4)2
= √(–9)2+(–4)2
= √81+16
= √97 units
(iv) AC के मध्यबिन्दु के निर्देशांक ज्ञात कीजिए।
Find the coordinates of the mid point of AC.
Answer : (6, 4)
